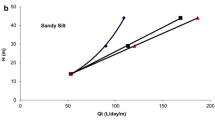
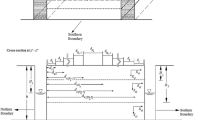
In this work the hydraulic efficiency of a parallel draining trenches system is evaluated by performing a series of pseudo-3D consolidation analyses using the finite element method. A parametric study has been conducted to investigate the influence of relevant aspects of the problem such as the slope inclination and trench length, which are not considered in currently available 2D solutions. Starting from a case study as a reference, an ideal slope has been considered, in silty, saturated soil. The evolution in space and time of the pore-water pressure and hydraulic head has been evaluated and, consequently, the evolution of the average hydraulic efficiency of the drainage system has been assessed, starting from the construction phase to the final steady-state conditions. The temporal evolution of the hydraulic efficiency has been assessed as a function of the trench inclination, depth, length and interspacing. Results have showed that the trench inclination and depth have a limited effect on the average value of the hydraulic efficiency, whereas the trench interspacing and length (the latter accountable only with a 3D model) have a remarkable effect on it.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Di Maio, A. Evangelista, and G. Viggiani, “Analisi dell’efficienza di sistemi di dreni tubolari,” RIG, 4, 187-199 (1988).
A. Desideri, S. Miliziano, and S. Rampello, “Drenaggi a gravità per la stabilizzazione dei pendii,” Hevelius (1997).
F. Ponziani, N. Berni, M. Stelluti, R. Zauri, C. Pandolfo, L. Brocca, T. Moramarco, D. Salciarini, and C. Tamagnini, "Landwarn: An operative early warning system for landslides forecasting based on rainfall thresholds and soil moisture," Landslide Science and Practice: Early Warning, Instrumentation and Monitoring, 2, 627-624 (2013).
D. Salciarini, E. Volpe, S. Kelley, L. Brocca, S. Camici, G. Fanelli, and C. Tamagnini, “Modeling the effects induced by the expected climatic trends on landslide activity at large scale,” Procedia Eng., 158, 541-545 (2016).
D. Salciarini, C. Tamagnini, F. Ronchi, E. Volpe, and G. Fanelli, “An approach for large-scale soil characterization for the application of non-structural landslide risk mitigation,” RIG, 51(3), 7-21 (2017).
D. Salciarini, E. Volpe, and E. Cattoni, “Probabilistic vs. deterministic approach in landslide triggering prediction at large-scale,” Lect. Notes Civ. Eng., 40, 62-70 (2020).
E. Volpe, L. Ciabatta, D. Salciarini, S. Camici, E. Cattoni, and L. Brocca, “The impact of probability density functions assessment on model performance for slope stability analysis,” Geosciences, 11(8), art. No. 322 (2021).
D. Salciarini, C. Tamagnini, and P. Conversini, "Numerical approaches for rockfall analysis: A comparison," Proc. 18th World IMACS Congress and MODSIM 2009 - International Congress on Modelling and Simulation: Interfacing Modelling and Simulation with Mathematical and Computational Sciences, 2706-2712 (2009).
A. Capone, A. Dello Russo, M. Pirone, S. Sica, and G. Urciuoli, “Modellazione delle pressioni neutre in un pendio stabilizzato con aste drenanti,” Proc. XXV CNG-AGI-Roma, ISBN 978-88-97517-05-04 (2014).
G. Urciuoli and M. Pirone, “Subsurface drainage for slope stabilization,” Landslide Sci. Pract., 6 (2013).
A. Desideri and S. Rampello, “Stabilizzazione dei pendii mediante sistemi di drenaggio,” Proc. of Conferenze di Geotecnica di Torino, 1-48 (2009).
D. Salciarini, E. Volpe, L. Di Pietro, and E. Cattoni, “A case-study of sustainable countermeasures against shallow landslides in central Italy,” Geosciences, 10(4), art. No. 130 (2020).
D. Salciarini, R. Morbidelli, E. Cattoni, and E. Volpe, “Physical and numerical modelling of the response of slopes under different rainfalls, inclinations and vegetation conditions,” Riv. Ital. Geotec., 3, (2022).
B. Stanic, “Influence of drainage trenches on slope stability,” J. Geotech. Eng, 110(11), 1624-1636 (1984).
F. Cotecchia, P. Lollino, and R. Petti, “Efficacy of drainage trenches to stabilise deep slow landslides in clay slopes,” Geotech. Lett., 6, 1-6 (2016).
J. N. Hutchinson, “Assessment of the effectiveness of corrective measures in relation to geological conditions and types of slope movement,” Symposium on Landslides and Other Mass Movement, Prague. Bull. Int. Assoc. Eng. Geol, 16, 131-155 (1977).
F. Cotecchia, R. Petti, D. Milella, and P. Lollino, “Design of medium depth drainage trench systems for the mitigation of deep Llandsliding”, Geosciences, 10, 174 (2020).
G. Vaciago, “The SafeLand compendium of landslide risk mitigation measures,” Landslide Science and Practice, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2013).
H. Rahardjo, K. J. Hritzuk, E. C. Leong, and R. B. Rezaur, “Effectiveness of horizontal drains for slope stability,” Eng. Geol., 69(3), 295-308 (2003).
B. G. D’Acunto and G. Urciuoli, “Groundwater regime in a slope stabilized by drain trenches,” Math. Comput. Model., 43, 754-765 (2006).
C. Di Maio, P. Santagata, and C. Viggiani, “Analisi del processo di consolidazione indotto da un sistema di trincee drenanti,” Proc. of the XVI Convegno Nazionale di Geotecnica, Bologna, Italy, 283-289 (1986).
E. Conte and A. Troncone “A performance-based method for the design of drainage trenches used to stabilize slopes,” Eng. Geol., 239, 158-166 (2018).
G. Urciuoli, L. Comegna, M. Pirone, and L. Picarelli, “The beneficial role of stratigraphy on slope stabilization by drainage trenches,” Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss., 1-11 (2019).
V. Tagarelli and F. Cotecchia, “Coupled hydro-mechanical analysis of the effects of medium depth drainage trenches mitigating deep landslide activity,” Eng. Geol., 297, 106510 (2022).
F. Aloi, M. Pirone, and G. Urciuoli, “Modellazione numerica 3D di pozzi drenanti per la stabilizzazione dei pendii,” Proc. Iarg, Chieti (2014).
R. Meriggi and A. Ziraldo, “Effects of trench drains on slope stability during heavy rainfalls,” Landslides: Evaluation and Stabilization, 2, 1677 (2004).
R. W. Lewis and B. A. Schrefler, The Finite Element Method in the Static and Dynamic Deformation and Consolidation of Porous Media, Wiley, Chichester (1988).
K. Terzaghi, Theoretical Soil Mechanics, Wiley & Sons, New York (1943).
A. Burghignoli and A. Desideri, “Analisi dei moti di filtrazione indotti dall’esecuzione di scavi e trincee,” Proc. XV Conv. Nazionale di Geotecnica, Spoleto, Patron Editore, Bologna, Italy, 51-56 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Osnovaniya, Fundamenty i Mekhanika Gruntov, No. 3, May-June, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Volpe, E., Cattoni, E. & Salciarini, D. 3D Finite Element Modelling of Hydraulic Efficiency of Drainage Trenches. Soil Mech Found Eng 60, 198–208 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-023-09882-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-023-09882-3