Abstract
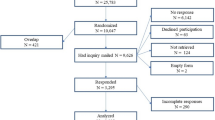
This study aims to understand the perception of academic communities—both stationed in Nepal and abroad— on various aspects of research environment in Nepal and the challenges in carrying out research here. It further seeks to explore the relationship between different levels of research satisfaction, publications, funding and work experience. Here, we present the results of online questionnaire survey of 472 researchers from 47 countries who published research articles and collaborated with Nepal based researchers. A significantly high proportion of researchers stationed in Nepal reported an unfavourable research environment compared to their foreign counterparts. There were, however, no significant differences between the proportion of respondents stationed in Nepal and abroad who had favourable and neutral views on the research environment in Nepal. Researchers who were satisfied and very satisfied with their own performance had a favourable view on Nepal’s research environment. Lack of funding was the most agreed challenge among all researchers whereas “no government policies” received the most support from researchers based in foreign countries, and “no research culture”, “research facilities” obtained more responses from Nepal based researchers. With the exception of very dissatisfied ones, the number of publications, years in research experience and total funding (median) increased gradually from ‘not satisfied” to ‘very satisfied’ in both Nepal and foreign country-based researchers. Nepal based researchers published significantly fewer journal articles as lead authors compared to their foreign counterparts. They received a high proportion of funding from international grants and often self-funded their research projects. It is crucial to address funding challenges and foster a supportive research culture to enhance the research environment in Nepal.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya, K. P., Phuyal, S., Chand, R., & Kaphle, K. (2021). Current scenario of and future perspective for scientific research in Nepal. Heliyon, 7(1), e05751.
Adair, J. G. (1995). The research environment in developing countries: Contributions to the national development of the discipline. International Journal of Psychology, 30(6), 643–662.
Ahlmann-Eltze, C. (2017). ggsignif: Significance Brackets for ‘ggplot2.’ R package version 0.4. 0.
Ahmed, K. (2020). Academic integrity: Challenges and strategies for Asia and the Middle East. Accountability in Research, 27(5), 256–270.
Albrecht, D., & Ziderman, A. (1992). Funding mechanisms for higher education: financing for stability, efficiency, and responsiveness. World Bank.
Bajracharya, D., Bhuju, D., & Pokhrel, J. R. (2006). Science, research, and technology in Nepal (Research Report). Kathmandu Nepal: UNESCO, Kathmandu Office.
Basak, S. K., & Govender, D. W. (2015). Theoretical framework of the factors affecting university academics job satisfaction. International Business & Economics Research Journal (IBER), 14(2), 317–326. https://doi.org/10.19030/iber.v14i2.9167
Bentley, P. J., & Kyvik, S. (2013). Individual differences in faculty research time allocations across 13 countries. Research in Higher Education, 54(3), 329–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11162-012-9273-4
Bista, K., Sharma, S., Raby, R. L., Sharma, S., & Raby, R. L. (2019). Higher education in Nepal: Policies and perspectives. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781351139205
Bland, C. J., & Ruffin, M. T. (1992). Characteristics of a productive research environment: Literature review. Academic Medicine: Journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges, 67(6), 385–397.
Bloch, C., & Sørensen, M. P. (2015). The size of research funding: Trends and implications. Science and Public Policy, 42(1), 30–43.
Bojko, M. M., Knapińska, A., & Tomczyńska, A. (2021). Academic entrepreneurship and the research productivity in Poland. Industry and Innovation, 28(4), 486–506.
Bostock, M., Rodden, K., & Russell, K. (2019). sunburstR: ‘Htmlwidget’ for ’Kerry Rodden’ ‘d3.js’ Sequence and ‘d2b’ Sunburst (R package version 0.6.5), 2017, https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=sunburstR.
Boulton, G., Campbell, P., Collins, B., Elias, P., Hall, W., Laurie, G., et al. (2012). Science as an open enterprise. The Royal Society.
Bryer, J., Speerschneider, K., & Bryer, M. J. (2016). Package ‘likert’. Likert: Analysis and Visualization Likert Items (1.3. 5)[Computer software]. Retrieved December 31, 2016, from https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=likert.
Coccia, M. (2008). Science, funding and economic growth: Analysis and science policy implications. World Review of Science, Technology and Sustainable Development, 5(1), 1–27.
Crossley, M., & Vulliamy, G. (2013). Qualitative educational research in developing countries: Current perspectives. Routledge.
Dhillon, S. K., Ibrahim, R., & Selamat, A. (2015). Factors associated with scholarly publication productivity among academic staff: Case of a Malaysian public university. Technology in Society, 42, 160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2015.04.004
Docquier, F., Lohest, O., & Marfouk, A. (2007). Brain drain in developing countries. The World Bank Economic Review, 21(2), 193–218. https://doi.org/10.1093/wber/lhm008
Dodani, S., & LaPorte, R. E. (2005). Brain drain from developing countries: How can brain drain be converted into wisdom gain? Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 98(11), 487–491.
Evans, L. (2011). What research administrators need to know about researcher development: Towards a new conceptual model. Journal of Research Administration, 42(1), 15–37.
Fleming, L., Greene, H., Li, G., Marx, M., & Yao, D. (2019). Government-funded research increasingly fuels innovation. Science, 364(6446), 1139–1141.
Gautam, P. (2017). An overview of the Web of Science record of scientific publications (2004–2013) from Nepal: Focus on disciplinary diversity and international collaboration. Scientometrics, 113(3), 1245–1267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2538-0
Ghabban, F., Selamat, A., Ibrahim, R., Krejcar, O., Maresova, P., & Herrera-Viedma, E. (2019). The influence of personal and organizational factors on researchers’ attitudes towards sustainable research productivity in Saudi Universities. sustainability, 11(17), 4804. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174804
Goldfarb, B. (2008). The effect of government contracting on academic research: Does the source of funding affect scientific output? Research Policy, 37(1), 41–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2007.07.011
Grosjean, P., Ibanez, F., & Etienne, M. (2018). Pastecs: Package for analysis of space-time ecological series. R Package Version, 1, 21.
Grossman, G. D. (2014). Improving the reviewing process in Ecology and Evolutionary Biology. Animal Biodiversity and Conservation, 37(1), 101–105.
Gupta, B. M., & Bala, A. (2012). S&T publications output of Nepal: A quantitative analysis, 2001–10. Scientometrics, 93(3), 1029–1046. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-012-0778-6
Guskov, A. E., Kosyakov, D. V., & Selivanova, I. V. (2018). Boosting research productivity in top Russian universities: The circumstances of breakthrough. Scientometrics, 117(2), 1053–1080.
Guthman, J. (1997). Representing crisis: The theory of himalayan environmental degradation and the project of development in post-Rana Nepal. Development and Change, 28(1), 45–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-7660.00034
Hachhethu, K. (2002). Social sciences research in Nepal. Economic and Political Weekly, 37(35), 3631–3643.
Hanssen, T.-E.S., Jørgensen, F., & Larsen, B. (2018). The relation between the quality of research, researchers’ experience, and their academic environment. Scientometrics, 114(3), 933–950.
Harari, Y. N. (2014). Sapiens: A brief history of humankind. Random House.
Hasan, I., & Tucci, C. L. (2010). The innovation–economic growth nexus: Global evidence. Research Policy, 39(10), 1264–1276.
Horta, H., Cattaneo, M., & Meoli, M. (2018). PhD funding as a determinant of PhD and career research performance. Studies in Higher Education, 43(3), 542–570. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2016.1185406
Hotez, P. J. (2017). The poverty-related neglected diseases: Why basic research matters. PLoS Biology, 15(11), e2004186.
ICAI. (2021). The Fundamental Values of Academic Integrity. International Center for Academic Integrity. https://academicintegrity.org/images/pdfs/20019_ICAI-Fundamental-Values_R12.pdf
Johnstone, D. B., Arora, A., & Experton, W. (1998). The financing and management of higher education: A status report on worldwide reforms. World Bank, Human Development Network, Education.
Khadka, N. (1997). Foreign aid to Nepal: Donor motivations in the post-cold war period. Asian Survey, 37(11), 1044–1061.
King, D. A. (2004). The scientific impact of nations. Nature, 430(6997), 311–316. https://doi.org/10.1038/430311a
Knevel, R. J. M., Gussy, M. G., Farmer, J., & Karimi, L. (2015). Nepalese dental hygiene and dental students’ career choice motivation and plans after graduation: A descriptive cross-sectional comparison. BMC Medical Education, 15(1), 219. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-015-0500-5
Lakomý, M., Hlavová, R., Machackova, H., Bohlin, G., Lindholm, M., Bertero, M. G., & Dettenhofer, M. (2020). The motivation for citizens’ involvement in life sciences research is predicted by age and gender. PLoS ONE, 15(8), e0237140. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0237140
Lam, A. (2011). What motivates academic scientists to engage in research commercialization: ‘Gold’, ‘ribbon’ or ‘puzzle’? Research Policy, 40(10), 1354–1368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2011.09.002
Langer, A., Díaz-Olavarrieta, C., Berdichevsky, K., & Villar, J. (2004). Why is research from developing countries underrepresented in international health literature, and what can be done about it? Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 82(10), 2.
Lauchlan, E. (2019). NATURE PhD SURVEY 2019 (pp. 1–38).
Maestre, F. T. (2019). Ten simple rules towards healthier research labs. PLOS Computational Biology, 15(4), e1006914. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006914
Man, J. P., Weinkauf, J. G., Tsang, M., & Sin, J. H. D. D. (2003). Why do some countries publish more than others? An international comparison of research funding, English proficiency and publication output in highly ranked general medical journals. European Journal of Epidemiology, 19(8), 811–817. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EJEP.0000036571.00320.b8
Marks, M. S., Marsh, M., Schroer, T. A., & Stevens, T. H. (2013). Misuse of journal impact factors in scientific assessment. Traffic, 14(6), 611–612. https://doi.org/10.1111/tra.12075
Masum, A. K. M., Azad, M. A. K., & Beh, L.-S. (2015). Determinants of academics’ job satisfaction: Empirical evidence from private universities in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE, 10(2), e0117834. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117834
Metz, J. J. (1995). Development in Nepal: Investment in the status quo. GeoJournal, 35(2), 175–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00814063
MoEST. (2019). National Science, Technology and Innovation Policy, 2019 (Policy document). Kathmandu, Nepal: Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Government of Nepal.
Nature Index. (2024). Nature Index (1 October 2022–30 September 2023). Country/territory tables. https://www.nature.com/nature-index/country-outputs/generate/all/global
Nosek, B. A., Alter, G., Banks, G. C., Borsboom, D., Bowman, S. D., Breckler, S. J., et al. (2015). Promoting an open research culture. Science, 348(6242), 1422–1425.
Nour OM, S. S. (2005Sep). Science and technology development indicators in the Arab region: A comparative study of Arab Gulf and Mediterranean countries. Science, Technology and Society, 10(2), 249–274.
NPC. (2019). First Five Year Plan (Working Paper). Karnali Province Planning Commission, Karnali Province Governmet.
OECD. (2002). Changing Government Policies for Public Research. https://doi.org/10.1787/sti_outlook-2002-7-en
Ogle, D. (2019). FSA: Fisheries Stock Assessment. R package version 0.8.24, http://www.RForge.net/FSA.
Oshagbemi, T. (1997). The influence of rank on the job satisfaction of organizational members. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 12(8), 511–519. https://doi.org/10.1108/02683949710189111
Oshagbemi, T. (2000). How satisfied are academics with their primary tasks of teaching, research and administration and management? International Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education, 1(2), 124–136. https://doi.org/10.1108/1467630010371876
Oso, O., Adebayo, K., & George, F. (2017). Communication satisfaction and organizational commitment of agriculture researchers in South-West Nigeria: Mediating role of job satisfaction. Agriculturae Conspectus Scientificus, 82(4), 403–408.
Panday, D. R. (2012). The legacy of Nepal’s failed development. In S. von Einsiedel, D. M. Malone, & S. Pradhan (Eds.), Nepal in transition: From people’s war to fragile peace. (Vol. 81). Cambridge University Press.
Paudel, P. K., Baniya, S., Sharma, S., Bhandari, S., & Pokharel, M. (2023). Half century in biodiversity and conservation research in Nepal: A review. Biodiversity and Conservation, 32(8), 2611–2636.
Pradhan, R., & Shrestha, A. (2005). Ethnic and caste diversity: Implications for development. Asian Development Bank.
R Core Team. (2018). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/.
Regmi, K. D. (2021). Higher education in Nepal: A handmaiden of neoliberal instrumentalism. Higher Education Policy, 34(2), 393–411. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41307-019-00138-0
Reif, L. R. (2017). How to maintain America’s edge: Increase funding for basic science. Foreign Affairs, 96, 95.
Ruedin, D. (2016). agrmt: Calculate Agreement or Consensus in Ordered Rating Scales. R Package, version 1.40.4. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/agrmt/index.html.
Salager-Meyer, F. (2008). Scientific publishing in developing countries: Challenges for the future. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 7(2), 121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2008.03.009
Schulz, J. (2013). The impact of role conflict, role ambiguity and organizational climate on the job satisfaction of academic staff in research-intensive universities in the UK. Higher Education Research & Development, 32(3), 464–478. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2012.680209
SCImago. (2024). SCImago Journal & Country Rank. Scimago Journal & Country Rank (Metrics based on Scopus® data as of April 2023). Retrieved February 27, 2024, from https://www.scimagojr.com/countryrank.php.
Sharma, K. (2011). Foreign aid, governance and economic development in Nepal. Asia Pacific Journal of Public Administration, 33(2), 95–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/23276665.2011.10779380
Shields, R., & Rappleye, J. (2008). Uneven terrain: Educational policy and equity in Nepal. Asia Pacific Journal of Education, 28(3), 265–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/02188790802270237
Simkhada, P., & Van Teijlingen, E. (2010). Higher education in Nepal: Several challenges ahead. Diaspora, 3(1), 44–47.
Singh, M. P., Malla, S. B., Rajbhandari, S. B., & Manandhar, A. (1979). Medicinal plants of Nepal—Retrospects and prospects. Economic Botany, 33(2), 185–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02858287
Slusser, M. S. (1996). Water Conduits in the Kathmandu Valley. JSTOR. https://www.jstor.org/stable/3250110. Accessed 25 January 2024
Sponholz, G. (2000). Teaching scientific integrity and research ethics. Forensic Science International, 113(1–3), 511–514.
Sulo, T. K., & Kosgei, R. (2012). Factors affecting research productivity in public universities of Kenya: The case of Moi University, Eldoret. Journal of Emerging Trends in Economics and Management Sciences (JE TEMS), 3(5), 475–478.
Sylwester, K. (2001). R&D and economic growth. Knowledge, Technology & Policy, 13(4), 71–84.
Szromek, A. R., & Wolniak, R. (2020). Job satisfaction and problems among academic staff in higher education. Sustainability, 12(12), 4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124865
Tol, W. A., Kohrt, B. A., Jordans, M. J. D., Thapa, S. B., Pettigrew, J., Upadhaya, N., & de Jong, J. T. V. M. (2010). Political violence and mental health: a multi-disciplinary review of the literature on Nepal. Social Science & Medicine (1982), 70(1), 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2009.09.037
Tolani, M. A., Ahmed, M., Ojewola, R. W., Abdulwahab-Ahmed, A., Abdulkadir, A., Mbaeri, T. U., et al. (2020). Assessment of health-care research and its challenges among medical doctors in Nigeria. Nigerian Medical Journal: Journal of the Nigeria Medical Association, 61(4), 218.
UGC Nepal. (2016). Openings for HERP-funded Academic Excellence Based Tenure-Track Positions in Tribhuvan University. Openings for HERP-funded Academic Excellence Based Tenure-Track Positions in Tribhuvan University. Notice. Retrieved July 10, 2021, from https://www.ugcnepal.edu.np/singleNotice/1/233.
van Dijk, H., & van Zelst, M. (2020). Comfortably numb? Researchers’ satisfaction with the publication system and a proposal for radical change. Publications, 8(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications8010014
Van Doren, C. L. (1992). A history of knowledge: Past, present, and future. Random House Digital Inc.
Vose, P. B., & Cervellini, A. (1983). Problems of scientific research in developing countries. IAEA Bulletin, 2, 37–40.
Wagner, M., Schaltegger, S., Hansen, E. G., & Fichter, K. (2019). University-linked programmes for sustainable entrepreneurship and regional development: How and with what impact? Small Business Economics, 56, 1141–1158.
Ward, S. C. (2012). Neoliberalism and the global restructuring of knowledge and education. Routledge. Retrieved January 25, 2024, from https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=6ujGBQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT9&dq=+Neoliberalism+and+the+Global+Restructuring+of+Knowledge+and+Education+&ots=jrLxVXWZqd&sig=5m4AaOzocHyvgChUli-yFkfa1Ps.
Weise, K. (2013). Revisiting Kathmandu: safeguarding living urban heritage. In Proceeding of an international symposium, Kathmandu valley (pp. 25–29).
Wickham, H., & Chang, W. (2008). ggplot2: An implementation of the Grammar of Graphics. R package version 0.7. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggplot2.
Yamin, A. B., & Luna, F. (2016). Brain Drain, the Consequence of Globalization and Future Development: A Study on Bangladesh, 24–28.
Zhou, P., & Leydesdorff, L. (2006). The emergence of China as a leading nation in science. Research Policy, 35(1), 83–104.
Acknowledgements
PKP acknowledges Simrik Singh Bhandari, Shreeya Shrestha and Shreeya Manandhar for their help in collecting and reviewing relevant literature.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PKP: conceptualization; methodology; software; funding; formal analysis; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing; visualization. BG: questionnaire revision; writing—review and editing.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval for the survey was obtained from Kathmandu Institute of Applied Sciences Research Ethics Committee (decision letter number: RE-17-01). The first page of the survey form included objectives of the survey. Respondents were clearly informed about the anonymity of data and reporting only in aggregate form in scientific reports (e.g., journal articles, research communication, and policy notes, etc.). Respondents who agreed provided their consent by clicking the “Agree” button and proceeded to the questions.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Paudel, P.K., Giri, B. Carrying out research in Nepal: perceptions of scholars about research environment and challenges. Scientometrics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-024-04989-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-024-04989-2