Abstract
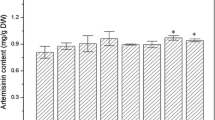
The contents of artemisinin and artemisinic acid were monitored in the Artemisia annua plants treated with GA3 at vegetative and flowering initiation stages. The highest artemisinin content was observed at full bloom. The decrease in artemisinic acid content occurred during the transition from the vegetative stage to the beginning of flowering. Endogenous GA3 content in the leaves peaked at full bloom. At the vegetative stage, in plants treated with various concentrations of GA3 , the content of artemisinin increased while that of artemisinic acid decreased. Apparently, the rate-limiting step in artemisinin biosynthesis was from artemisinic acid to artemisinin. The “bottleneck” of artemisinin biosynthesis was probably unlocked during the flowering or in the vegetative plants treated with GA3 , which triggered off the conversion of artemisinic acid to artemisinin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DMAPP:
-
dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
- FPP:
-
farnesyl pyrophosphate
- GA3 :
-
gibberellic acid
- GGPP:
-
geranyl geranyl pyrophosphate
- GPP:
-
geranyl pyrophosphate
- IPP:
-
isopentenyl pyrophosphate
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
REFERENCES
D.L. Klayman (1985) ArticleTitleQinghaosu (Artemisinin), an Antimalarial Drug from China Science 228 1049–1055
E. Geldre ParticleVan A. Vergauwe E. Eeckhout Particlevan den (1997) ArticleTitleState of the Production of the Antimalarial Compound Artemisinin in Plants Plant. Mol. Biol. 33 199–209
R. Lierch H. Soicke C. Stehr H.U. Tullner (1986) ArticleTitleFormation of Artemisinin in Artemisia annua during One Vegetation Period Planta Med. 52 387–390
N. Pras J.F. Visser S. Batterman H.J. Woerdenbag T.M. Malingre C.B. Lugt (1991) ArticleTitleLaboratory Selection of Artemisia annua for High Artemisinin Yielding Types Phytochem. Anal. 2 80–83
A. Singh R.A. Vishwakarma A. Husain (1988) ArticleTitleEvaluation of Artemisia annua Strains for Higher Artemisinin Production Planta Med. 54 475–476
M.R. Morales D.J. Charles J.E. Simon (1993) ArticleTitleSeasonal Accumulation of Artemisinin in Artemisia annua Acta Horticult. 334 416–420
D.P. Fulzele A.T. Sipahimalani M.R. Heble (1995) ArticleTitleTissue Cultures of Artemisia annua L. Plantlet Cultures in Bioreactor J. Biotechnol. 40 139–143
N.B. Paniego A.M. Giulietti (1996) ArticleTitleArtemisinin Production by Artemisia annua L.-Transformed Organ Cultures Enzyme Microbiol. Technol. 18 526–530
H.J. Bouwmeester E.T. Wallaart M. Janssen H.A. Jansen B. Loo Particlevan B.J.M. Jansen M.A. Posthumus C.O. Schmidt J.-W. Kraker Particlede W.A. König M.C.R. Franssen (1999) ArticleTitleAmorpha-4,11-Diene Synthase Catalyses the First Probable Step in Artemisinin Biosynthesis Phytochemistry 52 843–854
M. Jung H.N. Elsohly J.D. McChesney (1990) ArticleTitleArtemisinic Acid: A Versatile Chiral Synthon and Bioprecursor to Natural Products Planta Med. 56 624
R.J. Roth N. Acton (1987) ArticleTitleIsolation of Arteannuic Acid from Artemisia annua Planta Med. 53 501–502
S.S. Zhao M.Y. Zeng (1986) ArticleTitleDetermination of Qinghaosu in Artemisia annua L. by High Performance Liquid Chromatography Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 6 3–5
S.C. Vonwiller R.K. Haynes G. King H.-J. Wang (1993) ArticleTitleAn Improved Method for the Isolation of Qinghao Acid from Artemisia annua Planta Med. 59 562–563
H.J. Woerdenbag N. Pras N.G. Chan B.T. Bang W.V. Uden V.Y. Pham V.B. Nguyen S. Batterman B.L. Charles (1994) ArticleTitleArtemisinin, Related Sesquiterpenes, and Essential Oil in Artemisia annua during a Vegetation Period in Vietnam Planta Med. 60 272–275
T.E. Wallaart N. Pras A.C. Beekman W.J. Quax (2000) ArticleTitleSeasonal Variation of Artemisinin and Its Biosynthetic Precursors in Plants of Artemisia annua of Different Geographical Origin: Proof for the Existence of Chemotypes Planta Med. 66 57–62
P. Hedden W.M. Proebsting (1999) ArticleTitleGenetic Analysis of Gibberellin Biosynthesis Plant Physiol. 119 365–370
T.E. Wallaart H.J. Bouwmeester J. Hille L. Poppinga N.C.A. Maijers (2001) ArticleTitleAmorpha-4,11-Diene Synthase: Cloning and Functional Expression of a Key Enzyme in the Biosynthetic Pathway of the Novel Antimalarial Drug Artemisinin Planta 212 460–465
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
From Fiziologiya Rastenii, Vol. 52, No. 1, 2005, pp. 68–73.
Original English Text Copyright © 2005 by Zhang, Ye, Liu, Wang, Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y.S., Ye, H.C., Liu, B.Y. et al. Exogenous GA3 and flowering induce the conversion of artemisinic acid to artemisinin in Artemisia annua plants. Russ J Plant Physiol 52, 58–62 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11183-005-0009-6
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11183-005-0009-6