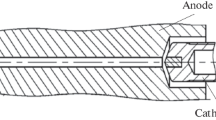
The paper presents the results of a study of the current-voltage characteristics and optical emission spectra of an atmospheric pressure pulsed discharge plasma at a frequency of several tens of kilohertz and a pulse duration of up to 10 μs in the mode of generation of plasma flows containing metal particles. The peculiarity of the plasma generator consists in a combination of the electrode design and the modes of the electric and gas supply to the discharge system. This combination allows a low-current (from 40 mA to 1 A) operation at a sufficiently high voltage of 150 to 200 V, without a transition to the arc discharge mode. These parameters make it possible to generate atomic flows from the melting cathode insert, which are blown out by a jet of working argon gas pumped at a flow rate of 1 l/min beyond the discharge system. The entry of a metal component into the gas-discharge plasma affects the discharge operation parameters and the properties of its optical emission. In the context of this phenomenon, the spectral distributions of the intensity of optical radiation corresponding to the lines of magnesium, indium, and zinc and their time dependence are investigated during the current pulse period as applied to identification of the physical features leading to a stable generation of metal atom flows at atmospheric pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Gascón-Garrido, N. Mainusch, H. Militz, et al., Eur. J. Wood Prod., 75, 315 (2017).
J. Hong, A. B. Murphy, B. Ashford, et al., Rev. Mod. Plasma Phys., 4, No. 1, 41614-019-0039-8 (2020).
G. E. Timuda, B. Hermanto, and T. Sudiro, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 1191, 012054 (2019).
Yu. G. Morozov, O. V. Belousova, M. V. Kuznetsov, et al., J. Mater. Chem., 22, 11214 (2012).
S. Sampath, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 19, No. 5, 921 (2010).
T. K. Sindhu, R. Sarathi, and S. R. Chakravarthy, Bull. Mater. Sci., 30, No. 2, 187 (2007).
S. Mitić, J. Philipps, and D. Hofmann, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 49, No. 2, 205202 (2016).
L. U. Pan, Dong-Wook Kim, Dong-Wha Park, Plasma Sci. Technol., 21, 044005 (2019).
K. Bobzin, F. Ernst, K. Richardt, et al., Surf. Coat. Technol., 202, 4438 (2008).
O. Galmiz, M. Stupavska, H. Wulff, et al., Open Chem., 13, No. 2, 198 (2015).
A. A. Efimov, G. N. Potapov, A. V. Nisan, and V. V. Ivanov, Results Phys., 7, 440 (2017).
W. Cheng, C. Hai-Chao, L. Wan-Wan, et al., Chin. Phys. B, 26, No. 2, 025202 (2017).
P. Siemroth, M. Laux, H. Pursch, et al., IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 47, No. 8, 3470 (2019).
I. G. Kesaev, Cathodic Processes of Electric Arc [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1962).
J. Kubásek, D. Dvorský, J. Šedý, et al., Materials, 12, 3745 (2019).
I. Kim, J. Yun, T. Baldoe, et al., Photon. Res., 8, No. 9, 1409 (2020).
W. Zhang, H. Li, W.Yu. William, and A. Y. Elezzabi, Light Sci. Appl., 9, 121 (2020).
K. P. Savkin, A. S. Bugaev, V. I. Gushenets, et al., Surf. Coat. Technol., 389, 125578 (2020).
B. B. Alchagirov, P. Kh Dadadshev, F. F. Dyshekova, and D. Z. Elimkhanov, TVT, 52, No. 6, 941 (2014).
Tables of Physical Quantities: reference book (Ed. I.K. Kikoin) [in Russian], Atomizdat, Moscow (1976).
A. Kramida, Yu. Ralchenko, J. Reader, and NIST ASD Team, NIST Atomic Spectra Database (ver. 5.9) (2021). Available at: https://physics.nist.gov/asd.
E. Carbone, N. Nader Sadeghi, E. Vos, et al., Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 24, 015015 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 11, pp. 11–18, November, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Beloplotov, D.V., Bugaev, A.S., Gushenets, V.I. et al. Low-Current Discharge in a Flow of Atmospheric-Pressure Argon Under the Formation of Metal Atoms: Electric and Optical Characteristics. Russ Phys J 65, 1804–1811 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-023-02834-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-023-02834-2