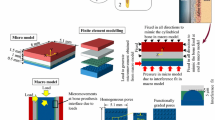
Hip and knee replacement operations mostly utilize the cementing procedure, which determines the biocompatibility relevance of bone cement, a porous material, which is filled with the body fluid after surgery. The paper proposes a computer model of the bone cement mechanical behavior with explicit and implicit analyses of different-size pores, including isolated macropores. The multilevel simulation utilizes the movable cellular automaton method. The mechanical behavior of test samples, both dry and containing the body fluid, is studied under uniaxial compression and four-point bending. Nonlinear porosity dependences are detected for elastic and strength properties of bone cement during compression tests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. E. Khramov, M. A. Makarov, S. A. Makarov, et al., Nauchno-prakticheskaya revmatologiya, 55, No. 5, 549–554 (2017).
M. R. Whitehouse, N. S. Atwal, M. Pabbruwe, et al., Eur. Cells Mater., 27, 50–62 (2014). https://doi.org/10.22203/ecm.v027a05
A. Sas, B. Helgason, S. J. Ferguson, Lenthe G. H. van, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 115, 104247 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2020.104247.
H. A. Shirazi, A. Asnafi, H. M. Navidbakhs, et al., Mater. Res. Express., 6, 125422 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab66f5.
J. Slane, J. Vivanco, D. Ebenstein, et al., J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 37, 141–152 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.05.015.
I. Lambrescu, C. Teodoriu, and M. Amani, Materials, 14, No. 23, 7235 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237235.
B. Cimatti, M. A. Santos, M. S. Dos Brassesco, et al., J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 106, No. 2, 649–658 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.33870.
S. Cavalu, KEM, 745, 39–49 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.745.39.
H. Asgharzadeh Shirazi, M. R. Ayatollahi, M. Navidbakhsh, and A. Asnafi, Nanomaterials for Advanced Biological Applications. Advanced Structured Materials, Vol. 104, M. Rahmandoust, M. Ayatollahi, eds., Springer, Cham (2019), pp. 209–224 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10834-2_8.
K. J. Messick, M. A. Miller, L. A. Damron, et al., J. Bone Joint Surg. Br., 89 B, No. 8, 1115–1121 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.89B8.19129.
A. Machrowska, J. Szabelski, R. Karpiński, et al., Materials, 13, 5419 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235419.
M. R. Whitehouse, N. S. Atwal, M. Pabbruwe, et al., Eur. Cells Mater., 27, 50–62 (2014). https://doi.org/10.22203/ecm.v027a05.
A. Yu. Smolin, E. V. Shilko, S. V. Astafurov, et al., Def. Technol., 14, 643–656 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2018.09.003.
E. V. Shilko, A. S. Grigoriev, and A. Yu. Smolin, FU Mech. Eng., 19, 7–22 (2021). https://doi.org/10.22190/FUME201221012S.
A. S. Grigoriev, A. V. Zabolotskiy, E. V. Shilko, et al., Materials, 14, 7376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237376.
A. Yu. Smolin, G. M. Eremina, and S. Yu. Korostelev, Russ. Phys. J., 62, No. 8, 1445–1454 (2019).
S. G. Psakhie, A. V. Dimaki, E. V. Shilko, and S. V. Astafurov, Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng., 106, 623–643 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.5134
G. Eremina and A. Smolin, Materials, 14, No. 24, 7678 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247678.
G. Eremina and A. Smolin, Procedia Struct. Integr., 35, 115–123 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostr.2021.12.055.
N. Dunne, Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials, Orthopaedic Bone Cements, Sanjukta Deb, ed., Woodhead Publishing (2008), pp. 233–264. https://doi.org/10.1533/9781845695170.3.233.
A. C. Jones and R. K. Wilcox, Med. Eng. Phys., 30, No. 10, 1287–304 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2008.09.006
H. Khellafi, M. M. Bouziane, A. Djebli, et al., JBBBE, 41, 37–48 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/JBBBE.41.37.
G. X. Qu, Z. M. Ying, C. C. Zhao, et al., Int. J. Med. Sci, 15, No. 13, 1458−1465 (2018). https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.27759.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 6, pp. 83–88, June, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Smolin, A.Y., Eremina, G.M. & Martyshina, I.P. Mechanical Properties of Bone Cement Affected by Porosity. Russ Phys J 65, 998–1003 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-022-02724-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-022-02724-z