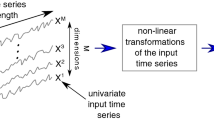
A description of the technique for studying the dynamic structure of the near-Earth orbital space using machine learning technology is presented. Artificial neural networks were used to process time series associated with the evolution of resonance characteristics that determine the dynamic structure of the near-Earth region up to 120 thousand km along the semi-major axis. The number of series processed has exceeded half a million, and their manual processing would be time consuming. The results of applying the technique to the analysis of the resonant structure of the selected area of space are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. S. Krasavin, A. G. Aleksandrova, and I. V. Tomilova, Russ. Phys. J., 63, No. 3, 426–431 (2020).
A. G. Aleksandrova, T. V. Bordovitsyna, and I. N. Chuvashov, Russ. Phys. J., 60, No. 1, 80-89 (2017).
A. G. Aleksandrova, V. A. Avdyushev, N. A. Popandopulo, and T. V. Bordovitsyna, Russ. Phys. J., 64, No. 8, 1566-1575(2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-021-02491-3
A. G. Aleksandrova, E. V. Blinkova, T. V. Bordovitsyna, N. A. Popandopulo, and I. V. Tomilova, Solar System Research, 55, No. 3, pp. 266–281 (2021).
A. G. Aleksandrova, T. V. Bordovitsyna, N. A. Popandopulo, et. al., Russ. Phys. J., 63, No. 1, 64-70 (2020).
C. M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, Springer, eBook, (2006).
I. Goodfellow, Y. Bengio, and A. Courville, Deep Learning, The MIT Press, eBook (2016). URL: http://www.deeplearnmgbook.orgcontents.TOChtml (05.12.2020).
K. V. Vorontsov, Mathematical Teaching Methods by Precedents (Machine Learning). Lecture course. URL: http://www.machinelearning.ru (05.12.2020)
Description of the Torch Library for Python. URL: https:/github.compytorchpytorch (05.12.2020).
Description of the nn Package of the Torch Library for the Python Language. URL: https://pytorch.orgdocsstablenn.html (06.12.2020).
Plas J. Vander, Python for Complex Problems: Data Science and Machine Learning, Piter, St. Petersburg (2018).
S. Rasсhka, Python and Machine Learning [Russian translation], DMK Press, Moscow (2017).
H. Ismail Fawaz, G. Forestier, J. Weber, et al., Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 33, Iss. 4, 917–963 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-019-00619-1.
M. T. Hagan, H. B. Demuth, M. Hudson Beale, and O. Jesús, Neural Network Design, 2nd Edition, eBook (2019). URL: https://hagan.okstate.edu/nnd.html (06.12.2019).
D. P. Kingma and M. Welling, An Introduction to Variational Autoencoders [Electronic resource], arXiv.org. 2019. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.02691.
L. McInnes, J. Healy, and S. Astels, Journal of Open Source Software, The Open Journal, 2(11), 205 (2017). https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.00205.
M. Ester, H.-P. Kriegel, J. Sander, and X. Xu, Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD-96), AAAI Press (1996), 226–231 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 10, pp. 38–43, October, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krasavin, D.S., Aleksandrova, A.G. & Tomilova, I.V. Application of Artificial Neural Networks in Studying the Dynamic Structure of the Near-Earth Orbital Space. Russ Phys J 64, 1824–1830 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-022-02528-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-022-02528-1