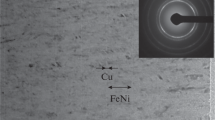
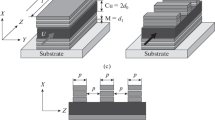
Using numerical micromagnetic modeling, we have investigated the development of domain structure and magnetization reversal in multilayer thin-film structures. The permalloy (Ni80Fe20) magnetic layers had the inplane uniaxial and perpendicular magnetic anisotropy. We found that as the thickness of nonmagnetic interlayers decreases, the in-plane configuration of magnetic moments in the permalloy layers transforms from a single domain state to stripe domains, which is caused by the increase of magnetostatic interaction between layers. In structures with “thick” interlayers, even weak magnetostatic interaction enforces the neighboring single domain permalloy layers to have opposite orientations of magnetic moments. The saturation field of such samples increases linearly with the number of layers. By analyzing the dynamic characteristics of multilayers, we determined the optimum number of layers ensuring the maximum conversion efficiency of wideband microwave microstrip sensors of weak magnetic fields.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Herzer, Acta Mater., 61, 718–734 (2013).
E. C. Stoner and E. P. Wohlfarth, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc., A240, 599–644 (1948).
J. P. Volkerts, Magnetic Thin Films: Properties, Performance and Applications, Nova Science Publishers (2011).
J. Petzold, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 242–245, 84–89 (2002).
I. Fergen, K. Seemann, A. V. D. Weth, and A. Schüppen, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 242–245, 146–151 (2002).
S. Tumanski, Handbook of Magnetic Measurements, CRC Press (2011).
N. Smith and P. Arnett, IEEE Trans. Magn., 38, 32–37 (2002).
W. F. Egelhoff, J. Bonevich, P. Pong, et al., J. Appl. Phys., 105, 013921 (2009).
C. Tannous and J. Gieraltowski, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 15, 125–133 (2004).
A. N. Babitskii, B. A. Belyaev, G. V. Skomorokhov, et al., Tech. Phys. Lett., 41, 324–327 (2015).
A. N. Babitskii, B. A. Belyaev, N. M. Boev, and A. V. Izotov, IEEE Sensors 2017: Conf. Proc. 316–318 (2017).
N. Saito, H. Fujiwara, and Y. Sugita, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 19, 1116–1125 (1964).
Y. Sugita, H. Fujiwara, and T. Sato, Appl. Phys. Lett., 10, 229–231 (1967).
J. Wei, Z. Zhu, H. Feng, et al., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 48, 465001 (2015).
D. Cao, L. Pan, X. Cheng, et al., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 51, 025001 (2018).
Y. Murayama, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 21, 2253–2266 (1966).
A. V. Svalov, I. R. Aseguinolaza, A. Garcia-Arribas, et al., IEEE Trans. Magn., 46, 333–336 (2010).
P. N. Solovev, A. V. Izotov, and B. A. Belyaev, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 429, 45–51 (2017).
N. Kataoka, T. Shima, and H. Fujimori, J. Appl. Phys., 70, 6238 (1991).
K. Ikeda, K. Kobayashi, and M. Fujimoto, J. Appl. Phys., 92, 5395–5400 (2002).
H. Greve, C. Pochstein, H. Takele, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 89, 242501 (2006).
B. A. Belyaev, A. V. Izotov, and An. A. Leksikov, Phys. Solid State, 52, 1664–1672 (2010).
B. A. Belyaev and A. V. Izotov, Phys. Solid State, 55, 2491–2500 (2013).
A. V. Izotov, B. A. Belyaev, P. N. Solovev, and N. M. Boev, Phys. B, 556, 42–47 (2019).
K. M. Lebecki, M. J. Donahue, and M. W. Gutowski, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 41, 175005 (2008).
B. A. Belyaev, A. V. Izotov, G. V. Skomorokhov, and P. N. Solovev, Mater. Res. Express., 6, 116105 (2019).
B. A. Belyaev, A. V. Izotov, G. V. Skomorokhov, and P. N. Solovev, Russ. Phys. J., 63, No. 5, 837–843 (2020).
P. N. Solovev, A. V. Izotov, B. A. Belyaev, and N. M. Boev, Phys. B, 604, 412699 (2021).
A. Hubert and R. Schäfer, Magnetic Domains, Springer, Berlin (1998).
A. N. Babitskii, B. A. Belyaev, N. M. Boev, et al., Instrum. Exp. Tech., 59, 425–432 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 6, pp. 170–176, June, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belyaev, B.A., Boev, N.M., Izotov, A.V. et al. Domain Structure and Magnetization Reversal in Multilayer Structures Consisting of Thin Permalloy Films Separated with Nonmagnetic Interlayers. Russ Phys J 64, 1160–1167 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-021-02436-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-021-02436-w