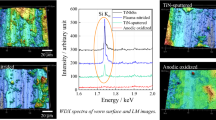
The results of an investigation of surface wettability of TiNi-based alloys by water and DMEM-medium are presented. A comparative analysis of the wetting angle is performed after processing the specimens by grinding, sand blasting, oxidation in air, etching in a solution of acids, processing by vapor, hydrogen peroxide, and detergent solution in an ultrasonic bath. It is shown that oxidation in air and etching in acids increase the surface hydrophilic property of TiNi-based alloys. The highest hydrophilic value with the water wetting angle about 30° is achieved in the case of vapor treatment following sand blasting and treatment of the oxidized specimens with hydrogen peroxide. The differing influence of treatments on the wetting angle is attributed to variations in the surface energy of TiNi-based alloy specimens, which is affected by the microrelief and structural-chemical characteristics of the surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. E. Gunther, KnE Mater. Sci., [S. l.] 1–9 (2017).
M. Es-Souni, M. Es-Souni, and H. Fischer-Brandies, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 381, Iss. 3, 557–567 (2005).
O. V. Kokorev, V. N. Khodorenko, G. A. Baigonakova, et al., Russ. Phys. J., 61, No. 9, 164–170 (2018).
R. A. Gittens, L. Scheideler, F. Rubb, et al., Acta Biomater., 10, No. 7, 2907– 2918 (2014).
M. R. Warocquier-Cleront, C. Legris, M. Degrange, and M. F. Sigot-Luizard, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 36, Iss. 1, 99–108 (1997).
E. Eisenbarth, J. Meyle, W. Nachtigall, and J. Breme, Biomaterials, 17, No. 14, 1399–1403 (1996).
T. Wassmann, S. Kreis, M. Behr, and R. Buergers, Int. J. Implant Dent., 3, No. 1, 32 (2017).
M. Lotfi, M. Nejib, and M. Naceur, Advances in Biomaterials Science and Biomedical Applications (Ed. R. Pignatello), Intech, Rijeka, Croatia (2013).
H. Liu and S. Wang, Sci. China Chem., 57(4), 552–557 (2014).
J. Schwartz, M. J. Avaltroni, M. P. Danahy, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 23, Iss. 3, 395–400 (2003).
Gu Hanyang, Wang Chi, Gong Shengjie, et al., Surf. Coatings Technol., 292, 72–77 (2016).
C. N.C. Lam, N. Kim, D. Hui, et al., Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 189, Iss. 1–3, 265–278 (2001).
M. Hilpert and A. Ben-David, Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 35, Iss. 3, 205–218 (2009).
F. Rupp, L. Scheideler, and J. Geis-Gerstorfer, Chem. Eng. Technol., 25, No. 9, 877–882 (2002).
K. S. Lee, N. Ivanova, V. M. Starov, et al., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 144, No. 1–2, 54–65 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 2, pp. 133–138, February, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasenchuk, Y.F., Gunther, S.V., Kokorev, O.V. et al. The Influence of Surface Treatment on Wettability of TiNi-Based Alloy. Russ Phys J 62, 333–338 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-019-01716-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-019-01716-w