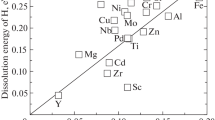
Mobile hydrogen, when dissolving in metals, redistributes due to the density gradients and elastic stresses, and enables destruction processes or phase transformations in local volumes of a solvent metal. It is rather important in solid state physics to investigate these interactions. The first-principle calculations performed in terms of the density functional theory, are used for thermodynamic simulation of the elastic stress effect on the energy of hydrogen dissolution in α-Fe crystal lattice. The paper presents investigations of the total energy of Fe–H system depending on the lattice parameter. As a result, the relation is obtained between the hydrogen dissolution energy and stress. A good agreement is shown between the existing data and simulation results. The extended equation is suggested for the chemical potential of hydrogen atom in iron within the local stress field. Two parameters affecting the hydrogen distribution are compared, namely local stress and phase transformations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. Shtremel’, Strength of Alloys. Pt. II: Lattice Defects [in Russian], MISiS, Мoscow (1997).
G. Alefeld and J. Völkl (Eds.), Hydrogen in Metals [Russian translation], Mir, Мoscow (1981).
Y. Fukai, The Metal-Hydrogen System. Heidelberg, Springer Verlag, Berlin (2005).
P. V. Gel'd and R. A. Ryabov, Hydrogen in Metals and Alloys [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Мoscow (1974).
D. A. Mirzaev, A. D. Shaburov, and A. O. Chernyavskii, Vestnik Yuzhno-Ural'skogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta. Ser. Metallurgiya, 14, No. 3, 40–45 (2014).
K. Schwarz, P. Blaha, and G. K.H. Madsen, Comput. Phys. Commun., 147, 71–76 (2002).
J. P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev. Lett., 77, 3865 (1996).
C. Elsasser, J. Zhu, S. G. Louie, et al. J. Phys.: Cond. Matter, 10, 5081–5111 (1998).
D. E. Jiang and E. A. Carter, Phys. Rev. В, 70, 064102 (2004).
M. A. Shtremel’, Strength of Alloys. Pt. II: Lattice Defects [in Russian], MISiS, Мoscow (1999)
J. C. M. Li, R. A. Oriani, and L. S. Darken, Z. Phys. Chem. Neue Folge, No. 49, 271–290 (5cy).
D. A. Mirzaev, A. A. Mirzoev, I. V. Kashukov, and K. Yu. Okishev, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 108, No. 5, 496-503 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 12, pp. 76–82, December, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakitin, M.S., Mirzoev, A.A. & Mirzaev, D.A. First-Principles and Thermodynamic Simulation of Elastiс Stress Effect on Energy of Hydrogen Dissolution in Alpha Iron. Russ Phys J 60, 2136–2143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-018-1337-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-018-1337-2