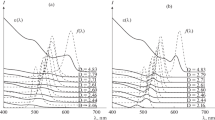
Frequency dependences of the dipole polarizabilities of clusters consisting of two solid conducting spherical nanoparticles and double-layer metal nanoparticles are investigated versus the geometrical parameters of the system with taking into account the degeneracy of electron gas of its metallic components. It is established that the spectra of the dynamic polarizabilities and absorption cross-sections of clusters have a complex multiresonant structure and strong dependence on the configuration parameters of the cluster, the degree of degeneracy of the metal, and kinetic characteristics of its electron gas. Spectral transformations of the absorption cross-sections of nanoclusters are illustrated under variation of the radii of particles or theirs nuclei, characteristic lengths of the Thomas-Fermi screening, and frequency of electron collisions. The anisotropic nature of absorption of electromagnetic field energy by a cluster is established: it is shown that the value of the absorption cross section depends on the direction of the electric field strength vector relative to the axis of the cluster.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. V. Klimov, Nanoplasmonics [in Russian], Fizmatlit, Moscow (2009).
M. G. Kucherenko and V. M. Nalbandyan, Vestnik OGU, 162, No. 1, 118–126 (2014).
V. I. Sugakov and G. V. Vertsimakha, Phys. Rev. B, 81, 235308 (2010).
V. P. Krainov and M. B. Smirnov, Usp. Fiz. Nauk, 170, No. 9, 969–990 (2000).
M. G. Kucherenko, Vestnik OGU, 137, No. 1, 141–149 (2012).
O. N. Gadomskii and A. S. Shalin, Zh. Exp. Teor. Fiz, 137, No. 5, 5–13 (2007).
S. J. Oldenburg, R. D. Averitt, S. L. Westcott, and N. J. Halas, Chem. Phys. Lett., 288, 243–247 (1998).
V. S. Lebedev, A. S. Medvedev, D. N. Vasil’ev, et al., Kvant. Elektron., 40, No. 3, 246–253 (2010).
Ken-Tye Yong, Yudhisthira Sahoo, Mark T. Swihart, and Paras N. Prasad, Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 290, 89–105 (2006).
Paulina Dobrowolska, et al., Materials, 8, 2849–2862 (2015).
Antonio M. Brito-Silva, et al., Langmuir, 29, 4366−4372 (2013).
Da Jian Wu, et al., Gold Bull., 45, 197–201 (2012).
B. N. Khlebtsova and N. G. Khlebtsov, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer, 106, 154–169 (2007).
Tanabe Katsuaki, J. Phys. Chem. C, 112, 15721–15728 (2008).
T. M. Chmereva and M. G. Kucherenko, Russ. Phys. J., 57, No. 10, 1428–1435 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 9, pp. 87–93, September, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kucherenko, M.G., Nalbandyan, V.M. Dipole Polarizabilities and Absorption Cross Sections of Two-Particle Nanoclusters of Conductive Homogeneous and Layered Particles with the Degenerate Electron Gas. Russ Phys J 59, 1425–1432 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-017-0926-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-017-0926-9