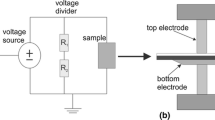
Breakdown delay times are measured and velocities of forming a conductive channel in aluminum oxide based porous ceramic materials impregnated with transformer oil are determined for pulsed electrical breakdown initiated by nanosecond pulses at a voltage of 140 kV. The breakdown delay times are also measured in monolithic aluminum oxide ceramics and leuco-sapphire single crystals. It is demonstrated that in porous ceramics, the average velocity of breakdown channel propagation decreases with increasing volume of the sample occupied by the liquid dielectric in comparison with single crystal and monolythic ceramics; it makes 50% of the velocity of breakdown channel propagation in leuco-sapphire and exceeds 3 times the corresponding value in transformer oil measured at the same voltage and pulse duration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu. V. Koritskii, V. V. Pasynkov, and B. M. Tareev, Handbook on Electrical Engineering Materials, Vol. 1 [in Russian], Energoizdat, Moscow (1986).
A. S. Lipilin, Altern. Energ. Ekol., No. 9, 139–152 (2009).
S. D. Grishin and L. V. Leskov, Electric Rocket Engines of Space Vehicles [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1989).
C. A. Scharlemann, T. M. York, and P. J. Turchi, in: Proc. 38th AIAA Joint Propulsion Conference, Indianapolis, Indiana, AIAA-2002-4270 (2002).
G. A. Mesyats, Pis’ma Zh. Tekhn. Fiz., 31, No. 24, 51–59 (2005).
A. S. Gilev, R. V. Emlin, and I. F. Punanov, in: Abstracts of Reports Presented at the 8th Int. Conf. “Aviation and Cosmonautics-2009,” Moscow (2009), p. 170.
R. V. Emlin, A. S. Gilev, S. R. Korzhenevskii, et al., in: Abstracts of Reports Presented at the 7th Int. Conf. “Aviation and Cosmonautics-2008,” Moscow (2008), p. 195.
W. Y. Ching, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc., 73, 3135–3160 (1991).
A. A. Vorob’ev and E. K. Zavadovskaya, Electric Strength of Solid Dielectrics [in Russian], State Technical and Theoretical Press, Moscow (1956).
I. E. Balygin, in: Electric Properties of Solid Dielectrics [in Russian], Energiya, Leningrad (1974), pp. 70–88.
G. A. Mesyats, Pulse Power and Electronics [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (2004).
All-Union State Standard 2409-95. Refractories. Method of Determining the Apparent Density, Open and General Porosity, and Water Absorption [in Russian], PPC Standard Publishing House, Minsk (2002).
Z. Yu. Gotra, Technologies of Microelectronic Devices: A Handbook [in Russian], Radio i Svyaz’, Moscow (1991).
Yu. N. Vershinin, Electronic-Thermal and Detonation Processes in Dielectrics [in Russian], Publishing House of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Ekaterinburg (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 1, pp. 57–60, January, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Punanov, I.F., Emlin, R.V., Morozov, P.A. et al. Investigation of breakdown in porous ceramics initiated by nanosecond pulses. Russ Phys J 55, 191–194 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-012-9794-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-012-9794-5