Abstract
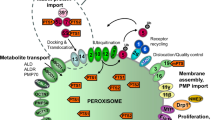
Intracellular organelles, peroxisomes, occur in cells of most eukaryotic species. Human severe congenital disorders are associated with defective assembly and functioning of peroxisomes, which partly explains the attention of researchers paid to peroxisome biogenesis. It has been shown that peroxisomes are involved in the realization of eukaryotic developmental programs (in particular, neuroblast differentiation and postembryonic development). Cytobiochemical and electron-microscopic studies of peroxisomal mutations showed that the primary role in peroxisome biogenesis is played by synthesis of specific proteins (peroxins) and their transport and incorporation into peroxisome membranes. More than 30 peroxin-encoding genes have been examined. These proteins are synthesized on free polysomes and transported into peroxisomes by means of specific signaling peptides, PTS1, PTS2, and PTS3. The import of matrix proteins depends on at least two shuttle receptor proteins, Pex5p and Pex7p. Some proteins regulating peroxisome proliferation in cells have been identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Breitling, R., Sharif, O., Hartman, M.L., and Krisans, S., Loss of Compartmentalization Cases Misregulation of Lysine Biosynthesis in Peroxisome-Deficient Yeast Cells, Eucaryotic Cells, 2002, vol. 1, no.6, pp. 978–986.
De Duve, C. and Baudhuin, P., Peroxisomes (Microbodies and Related Particles), Physiol. Rev., 1966, vol. 46, pp. 323–357.
Titorenko, V.I. and Rachubinski, R.A., The Life Cycle of the Peroxisome, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2001, vol. 2, pp. 357–368.
Van der Klei, I.J. and Veenhuis, M., Peroxisomes: Flexible and Dynamic Organelles, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 2002, vol. 14, pp. 500–505.
Gould, S. and Valle, D., Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders: Genetics and Cell Biology, Trends Genet., 2000, vol. 16, pp. 340–345.
Chandoga, J. and Petrovic, R., Peroxisomal Hereditary Metabolic Disorders, Cas. Lek. Cesk., 2001, vol. 140, no.21, pp. 651–657.
Depreter, M., Espeel, M., and Roels, F., Human Peroxisomal Disorders, Micr. Res. Tech., 2003, vol. 61, pp. 203–223.
Distel, B., Erdmann, R., Gould, S.J., et al., Unified Nomenclature for Peroxisome Biogenesis Factors, J.Cell Biol., 1996, vol. 135, pp. 1–3.
Purdue, P.E. and Lazarow, P.B., Peroxisome Biogenesis, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 2001, vol. 17, pp. 701–752.
Kunau, W.H., Peroxisome Biogenesis: From Yeast to Man, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 1998, vol. 1, pp. 232–237.
Tam, Y.Y.C., Torres-Guzman, J.C., Vizeacoumar, F.J., et al., Pex11-Related Proteins in Peroxisome Dynamics: A Role for the Novel Peroxin Pex27p in Controlling Peroxisome Size and Number in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2003, vol. 14, pp. 4089–4102.
Vizeacoumar, F.J., Torres-Guzman, J.C., Tam, Y.Y., et al., YHR150w and YDR479c Encode Peroxisomal Integral Membrane Proteins Involved in the Regulation of Peroxisome Number, Size, Distribution in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, J. Cell Biol., 2003, vol. 161, no.2, pp. 321–332.
Matsumoto, N., Tamura, S., and Fujuki, Y., The Patogenic Peroxin Pex26p Recruits the Pex1p–Pex6p AAA ATPase Complexes to Peroxisomes, Nat. Cell Biol., 2003, vol. 5, pp. 454–460.
Eckert, J.H. and Erdmann, R., Peroxisome Biogenesis, Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol., 2003, vol. 147, pp. 75–121.
Gould, S.J., Keller, G., Hosken, N., et al., A Conserved Tripeptide Sorts Proteins to Peroxisomes, J. Cell Biol., 1989, vol. 108, pp. 1657–1664.
Lametschwandtner, G., Brocard, C., Fransen, M., et al., The Difference in Recognition of Terminal Tripeptides As Peroxisomal Targeting Signal 1 between Yeast and Human Is Due to Different Affinities of Their Receptor Pex5p to the Cognate Signal and to Residues Adjacent to It, J. Biol. Chem., 1998, vol. 273, pp. 33 635–33 643.
Swinkels, B.W., Gould, S.J., Bodnar, A.G., et al., A Novel, Cleavable Peroxisomal Targeting Signal at the Amino-Terminus of the Rat 3-Ketoacyl-CoA Thiolase, EMBO J., 1991, vol. 10, pp. 3255–3262.
Chudzik, D.M., Michels, P.A., de Walque, S., and Hol, W.G., Structures of Type 2 Peroxisomal Targeting Signals in Two Trypanosomatid Aldolases, J. Mol. Biol., 2000, vol. 300, pp. 697–707.
McCollum, D., Monosov, E., and Subramani, S., The pas8 Mutant of Pichia pastoris Exhibits the Peroxisomal Protein Import Deficiencies of Zellweger Syndrome Cells: The PAS8 Protein Binds to the COOH-Terminal Tripeptide Peroxisomal Targeting Signal and Is a Member of the TPR Protein Family, J. Cell Biol., 1993, vol. 121, pp. 761–774.
Marzioch, M., Erdmann, R., Veenhuis, M., and Kunau, W.H., PAS7 Encodes a Novel Yeast Member of the WD-40 Protein Family Essential for Import of 3-Oxoacyl-CoA Thiolase, a PTS2-Containing Protein, into Peroxisomes, EMBO J., 1994, vol. 13, pp. 4908–4918.
Brocard, C., Kragler, F., Simon, M.M., et al., The Tetratricopeptide Repeat Domain of the PAS10 Protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Is Essential for Binding the Peroxisomal Targeting Signal-SKL, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1994, vol. 204, pp. 1016–1022.
Fransen, M., Brees, C., Baumgart, E., et al., Identification and Characterization of the Putative Human Peroxisomal C-Terminal Targeting Signal Import Receptor, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, vol. 270, pp. 7731–7736.
Terlecky, S.R., Nuttley, W.M., McCollum, D., et al., The Pichia pastoris Peroxisomal Protein PAS8p Is the Receptor for the C-Terminal Tripeptide Peroxisomal Targeting Signal, EMBO J., 1995, vol. 14, pp. 3627–3634.
Szilard, R.K. and Rachubinski, R.A., Tetratricopeptide Repeat Domain of Yarrowia lipolytica Pex5p Is Essential for Recognition of the Type 1 Peroxisomal Targeting Signal but Does Not Confer Full Biological Activity on Pex5p, Biochem. J., 2000, vol. 346, pp. 177–184.
Dodt, G., Braverman, N., Wong, A., et al., Mutations in the PTS1 Receptor Gene, PXR1, Define Complementation Group 2 of the Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders, Nat. Genet., 1995, vol. 9, pp. 115–125.
Van der Klei, I.J., Hilbrands, R.E., Swaving, G.J., et al., The Hansenula polymorpha PER3 Gene Is Essential for the Import of PTS1 Proteins into the Peroxisomal Matrix, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, vol. 270, pp. 17 229–17 236.
Szilard, R.K., Titorenko, V.I., Veenhuis, M., and Rachubinski, R.A., Pay32p of the Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica Is an Intraperoxisomal Component of the Matrix Protein Translocation Machinery, J. Cell Biol., 1995, vol. 131, pp. 1453–1469.
Zhang, J.W. and Lazarow, P.B., PEB1 (PAS7) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Encodes a Hydrophilic, Intra-Peroxisomal Protein That Is a Member of the WD Repeat Family and Is Essential for the Import of Thiolase into Peroxisomes, J. Cell Biol., 1995, vol. 129, pp. 65–80.
Elgersma, Y., Elgersma-Hooisma, M., Wenzel, T.J., et al., A Mobile PTS2 Receptor for Peroxisomal Protein Import in Pichia pastoris, J. Cell Biol., 1998, vol. 140, pp. 807–820.
Dammai, V. and Subramani, S., The Human Peroxisomal Targeting Signal Receptor, Pex5p, Is Translocated Into the Peroxisomal Matrix and Recycled to the Cytosol, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 2001, vol. 20, pp. 187–196.
Hunt, J.E. and Trelease, R., Sorting Pathway and Molecular Targeting Signals for the Arabidopsis Peroxin 3, Biochem. Biophis. Res. Commun., 2004, vol. 314, pp. 586–596.
Small, G.M., Szabo, L.J., and Lazarow, P.B., Acyl-CoA Oxidase Contains Two Targeting Sequences Each of Which Can Mediate Protein Import into Peroxisomes, EMBO J., 1988, vol. 7, pp. 1167–1173.
Klein, A., Barnett, P., Bottger, G., et al., Recognition of Peroxisomal Targeting Signal Type 1 by the Import Receptor Pex5p, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, pp. 15 034–15 041.
Gould, S., Kalish, J., Morrell, J., et al., Pex13p Is an SH3 Protein of the Peroxisome Membrane and a Docking Factor for the Predominantly Cytoplasmic PTS1 Receptor, J. Cell Biol., 1996, vol. 135, pp. 85–95.
Komori, M., Rasmussen, S.W., Kiel, J.A.K.W., et al., The Hansenula polymorpha PEX14 Gene Encodes a Novel Peroxisomal Membrane Protein Essential for Peroxisome Biogenesis, EMBO J., 1997, vol. 16, pp. 44–53.
Will, G.K., Soukupova, M., Hong, X., et al., Identification and Characterization of the Human Orthologue of Yeast Pex14p, Mol. Cell. Biol., 1999, vol. 19, pp. 2265–2277.
Huhse, B., Rehling, P., Albertini, M., et al., Pex17p of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Is a Novel Peroxin and Component of the Peroxisomal Protein Translocation Machinery, J. Cell Biol., 1998, vol. 140, pp. 49–60.
Elgersma, Y., Kwast, L., Klein, A., et al., The SH3 Domain of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Peroxisomal Membrane Protein Pex13p Functions As a Docking Site for Pex5p, a Mobile Receptor for the Import of PTS1-Containing Proteins, J. Cell Biol., 1996, vol. 135, pp. 97–109.
Girzalsky, W., Rehling, P., Stein, H., et al., Involvement of Pex13p in Pex14p Localization and Peroxisomal Targeting Signal 2-Dependent Protein Import into Peroxisomes, J. Cell Biol., 1999, vol. 144, pp. 1151–1162.
Fransen, M., Terlecky, S.R., and Subramani, S., Identification of a Human PTS1 Receptor Docking Protein Directly Required for Peroxisomal Protein Import, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, vol. 95, pp. 8087–8092.
Shimizu, N., Itoh, R., Hirono, Y., et al., The Peroxin Pex14p: cDNA Cloning by Functional Complementation on a Chinese Hamster Ovary Cell Mutant, Characterization, and Functional Analysis, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, vol. 274, pp. 12 593–12 604.
Albertini, M., Rehling, P., Erdmann, R., et al., Pex14p, a Peroxisomal Membrane Protein Binding Both Receptors of the Two PTS-Dependent Import Pathways, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1997, vol. 89, pp. 83–92.
Salomons, F.A., Kiel, J.A.K.W., Faber, K.N., et al., Overproduction of Pex5p Stimulates Import of Alcohol Oxidase and Dihydroxyacetone Synthase in a Hansenula polymorpha PEX14 Null Mutant, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, vol. 275, pp. 12 603–12 611.
Bellu, A.R., Komori, M., van der Klei, I.J., et al., Peroxisome Biogenesis and Selective Degradation Converge at Pex14p, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, pp. 44 570–44 574.
Elgersma, Y., Kwast, L., Berg, M., et al., Overexpression of Pexl5p, a Phosphorylated Peroxisomal Integral Membrane Protein Required for Peroxisome Assembly in S. cerevisiae, Causes Proliferation of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane, EMBO J., 1997, vol. 16, pp. 7326–7341.
Komori, M., Kiel, J.A.K.W., and Veenhuis, M., The Peroxisomal Membrane Protein Pexl4p of Hansenula polymorpha Is Phosphorylated in Vivo, FEBS Lett., 1999, vol. 457, pp. 397–399.
Subramani, S., Koller, A., and Snyder, W.B., Import of Peroxisomal Matrix and Membrane Proteins, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 2000, vol. 69, pp. 399–418.
Tsukamoto, T., Miura, S., and Fujiki, Y., Restoration by a 35K Membrane Protein of Peroxisome Assembly in a Peroxisome-Deficient Mammalian Cell Mutant, Nature, 1991, vol. 350, pp. 77–81.
Chang, C.C., Warren, D.S., Sacksteder, K.A., and Gould, S.J., PEX12 Interacts with PEX5 and PEX10 and Acts Downstream of Receptor Docking in Peroxisomal Matrix Protein Import, J. Cell Biol., 1999, vol. 147, pp. 761–774.
Okumoto, K., Abe, I., and Fujiki, Y., Molecular Anatomy of the Peroxin Pex12p, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, vol. 275, pp. 25 700–25 710.
Brul, S., Wiemer, E.A., Westerveld, A., et al., Kinetics of the Assembly of Peroxisomes after Fusion of Complementary Cell Lines from Patients with the Cerebro-Hepato-Renal (Zellweger) Syndrome and Related Disorders, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1988, vol. 152, pp. 1083–1089.
McNew, J.A. and Goodman, J.M., The Targeting and Assembly of Peroxisomal Proteins: Some Old Rules Do Not Apply, Trends Biochem. Sci., 1996, vol. 21, pp. 54–58.
Titorenko, V.I., Smith, J.J., Szilard, R.K., and Rachubinski, R.A., Pex20p of the Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica Is Required for the Oligomerization of Thiolase in the Cytosol and for Its Targeting to the Peroxisome, J. Cell Biol., 1998, vol. 142, pp. 403–420.
Glover, J., Andrews, D., Subramani, S., and Rachubinski, R., Mutagenesis of the Amino Targeting Signal of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 3-Ketoacyl-CoA Thiolase Reveals Conserved Amino Acids Required for Import into Peroxisomes in Vivo, J. Biol. Chem., 1994, vol. 269, pp. 7558–7563.
Van der Klei, I.J. and Veenhuis, M., Peroxisomes: Flexible and Dynamic Organelles, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 2002, vol. 14, pp. 500–505.
Walton, P.A., Hill, P.E., and Subramani, S., Import of Stably Folded Proteins into Peroxisomes, Mol. Biol. Cell, 1995, vol. 6, pp. 675–683.
Erdmann, R., Wiebel, F., Flessau, A., et al., PAS1, a Yeast Gene Required for Peroxisome Biogenesis, Encodes a Member of a Novel Family of Putative ATPases, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1991, vol. 64, pp. 499–510.
Faber, K.N., Heyman, J.A., and Subramani, S., Two AAA Family Peroxins, PpPex1p and PpPex6p, Interact with Each Other in an ATP-Dependent Manner and Are Associated with Different Subcellular Membranous Structures Distinct from Peroxisomes, Mol. Cell. Biol., 1998, vol. 18, pp. 936–943.
Kiel, J.A.K.W., Hilbrands, R.E., van der Klei, I.J., et al., Hansenula polymorpha Pex1p and Pex6p Are Peroxisome-Associated AAA Proteins That Functionally and Physically Interact, Yeast, 1999, vol. 15, pp. 1059–1078.
Yahraus, T., Braverman, N., Dodt, G., et al., The Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorder Group 4 Gene, PXAAA1, Encodes a Cytoplasmic ATPase Required for Stability of the PTS1 Receptor, EMBO J., 1996, vol. 15, pp. 2914–2923.
Tamura, S., Shimozawa, N., Suzuki, Y., et al., A Cytoplasmic AAA Family Peroxin, Pex1p, Interacts with Pex6p, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1998, vol. 245, pp. 883–886.
Imanaka, T., Small, G., and Lazarow, P., Translocation of Acyl-CoA Oxidase into Peroxisomes Requires ATP Hydrolysis but Not a Membrane Potential, J. Cell Biol., 1987, vol. 105, pp. 2915–2922.
Wendland, M. and Subramani, S., Presence of Cytoplasmic Factors Functional in Peroxisomal Protein Import Implicates Organelle-Associated Defects in Several Human Peroxisomal Disorders, J. Clin. Invest., 1993, vol. 92, pp. 2462–2468.
Dodt, G. and Gould, S.J., Multiple PEX Genes Are Required for Proper Subcellular Distribution and Stability of Pex5p, the PTS1 Receptor: Evidence That PTS1 Protein Import Is Mediated by a Cycling Receptor, J. Cell Biol., 1996, vol. 135, pp. 1763–1774.
Titorenko, V.I. and Rachubinski, R.A., Mutants of the Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica Defective in Protein Exit from the Endoplasmic Reticulum Are Also Defective in Peroxisome Biogenesis, Mol. Cell. Biol., 1998, vol. 18, pp. 2789–2803.
Titorenko, V.I. and Rachubinski, R.A., Peroxisomal Membrane Fusion Requires Two AAA Family ATPases, Pex1p and Pex6p, J. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 150, pp. 881–886.
Collins, C., Kalish, J., Morrell, J., et al., The Peroxisome Biogenesis Factors Pex4p, Pex22p, Pex1p, and Pex6p Act in the Terminal Steps of Peroxisomal Matrix Protein Import, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2000, vol. 20, pp. 7516–7526.
Liu, H., Tan, X., Russell, K.A., et al., PER3, a Gene Required for Peroxisome Biogenesis in Pichia pastoris, Encodes a Peroxisomal Membrane Protein Involved in Protein Import, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, vol. 270, pp. 10 940–10 951.
Rehling, P., Skaletz-Rorowski, A., Girzalsky, W., et al., Pex8p, an Intraperoxisomal Peroxin of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Required for Protein Transport into Peroxisomes Binds the PTS1 Receptor Pex5p, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, vol. 275, pp. 3593–3602.
Waterham, H.R., Titorenko, V.I., Haima, P., et al., The Hansenula polymorpha PER1 Gene Is Essential for Peroxisome Biogenesis and Encodes a Peroxisomal Matrix Protein with Both Carboxy-and Amino-Terminal Targeting Signals, J. Cell Biol., 1994, vol. 127, pp. 737–749.
Van der Klei, I.J., Hilbrands, R.E., Kiel, J.A.K.W., et al., The Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme Pex4p of Hansenula polymorpha Is Required for Efficient Functioning of the PTS1 Import Machinery, EMBO J., 1998, vol. 77, pp. 3608–3618.
Koller, A., Snyder, W., Faber, K.N., et al., Pex22p of Pichia pastoris, Essential for Peroxisomal Matrix Protein Import, Anchors the Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme, Pex4p, on the Peroxisomal Membrane, J. Cell Biol., 1999, vol. 146, pp. 99–112.
Faber, K.N., Keizer-Gunnink, I., Pluim, D., et al., The N-Terminus of Amine Oxidase of Hansenula polymorpha Contains a Peroxisomal Targeting Signal, FEBS Lett., 1995, vol. 357, pp. 115–120.
De Vet, E.C.J.M., Ijist, L., Oostheim, W., et al., Alkyl-Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate Synthase: Fate in Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders and Identification of the Point Mutation Underlying a Single Enzyme Deficiency, J. Biol. Chem., 1998, vol. 273, pp. 10 296–10 301.
Wanders, R.J.A. and Romeijn, G.J., Cholesterol Biosynthesis, Peroxisomes and Peroxisomal Disorders: Mevalonate Kinase Is Not Only Deficient in Zellweger Syndrome but Also in Rhizomelic Chondrodysplasia Punctata, J. Inherit. Metab. Dis., 1998, vol. 21, pp. 309–312.
Jansen, G., Ofman, R., Ferdinandusse, S., et al., Refsum Disease Is Caused by Mutations in the Phytanoyl-CoA Hydroxylase Gene, Nat. Genet., 1997, vol. 2, pp. 190–193.
Ledakis, J. and Terlecky, S., PTS2 Protein Import into Mammalian Peroxisomes, Traffic, 2001, vol. 2, pp. 252–260.
Purdue, P.E., Yang, X., and Lazarow, P.B., Pex18p and Pex21p, a Novel Pair of Related Peroxins Essential for Peroxisomal Targeting by the PTS2 Pathway, J. Cell Biol., 1998, vol. 143, pp. 1859–1869.
Braverman, N., Dodt, G., Gould, S.J., and Valle, D., An Isoform of Pex5p, the Human PTS1 Receptor, Is Required for the Import of PTS2 Proteins into Peroxisomes, Hum. Mol. Genet., 1998, vol. 7, pp. 1195–1205.
Smith, J.J. and Rachubinski, R.A., A Role for the Peroxin Pex8p in Pex20p-Dependent Thiolase Import into Peroxisomes of the Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, pp. 1618–1625.
Motley, A.M., Hettema, E.H., Ketting, R., et al., Caenorhabditis elegans Has a Single Pathway to Target Matrix Proteins to Peroxisomes, EMBO Rep., 2000, vol. 1, pp. 40–46.
Birdsey, M., Lewin, J., Cunningham, A., et al., Differential Enzyme Targeting As an Evolutionary Adaptation to Herbivory in Carnivora, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2004, vol. 21, no.4, pp. 632–646.
Adoutte, A., Balavoilne, G., Lartillot, N., Lespinet, O., et al., The New Animal Phylogeny: Reliability and Implications, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2000, vol. 97, pp. 4453–4456.
Baerends, R.J.S., Faber, K.N., Kiel, J.A.K.W., et al., Sorting and Function of Peroxisomal Membrane Proteins, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2000, vol. 24, pp. 291–301.
Lazarow, P. and Fujiki, Y., Biogenesis of Peroxisomes, Annu. Rev. Cell Biol., 1985, vol. 1, pp. 489–530.
Purdue, P.E. and Lazarow, P.B., Peroxisome Biogenesis, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 2001, vol. 17, pp. 701–752.
Veldhoven, P.P. and Mannaerts, G.P., Assembly of the Peroxisomal Membrane, Subcellular Biochemistry, vol. 22: Membrane Biogenesis, Maddy, A.H. and Harris, J.R., Eds., New York: Plenum, 1994, pp. 231–261.
Horiguchi, H., Yurimoto, H., Kato, N., and Sakai, Y., Antioxidant System within Yeast Peroxisome: Biochemical and Physiological Characterization of CbPmp20in the Methylotrophic Yeast Candida boidinii, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, pp. 14 279–14 288.
Schrader, M., Burkhardt, J.K., Baumgart, E., et al., Interaction of Microtubules with Peroxisomes: Tubular and Spherical Peroxisomes in HepG2 Cells and Their Alterations Induced by Microtubule-Active Drugs, Eur. J. Cell Biol., 1996, vol. 69, pp. 24–35.
Wiemer, E.A.C., Wenzel, T., Deerinck, T.J., et al., Visualization of the Peroxisomal Compartment in Living Mammalian Cells: Dynamic Behavior and Association with Microtubules, J. Cell Biol., 1997, vol. 136, pp. 71–80.
Huber, C., Saffrich, R., Anton, M., et al., A Heterotrimeric G Protein-Pho-Pholipase A2 Signaling Cascade Is Involved in the Regulation of Peroxisomal Motility in CHO Cells, J. Cell Sci., 1997, vol. 110, pp. 2955–2968.
Kiel, J.A.K.W., Rechinger, K.B., van der Klei, I.J., et al., The Hansenula polymorpha PDD1 Gene Product, Essential for the Selective Degradation of Peroxisomes, Is a Homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Vps34p, Yeast, 1999, vol. 15, pp. 741–754.
Hettema, E. and Tabak, H., Transport of Fatty Acids and Metabolites across the Peroxisomal Membrane, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2000, vol. 1486, pp. 18–27.
Elgersma, Y. and Tabak, H., Proteins Involved in Peroxisome Biogenesis and Functioning, Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 1996, vol. 1286, pp. 269–283.
Fujiki, Y., Rachubinski, R.A., and Lazarow, P.B., Synthesis of a Major Integral Membrane Polypeptide of Rat Liver Peroxisomes on Free Polysomes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1984, vol. 81, pp. 7127–7131.
Just, W. and Diestelkotter, P., Protein Insertion into the Peroxisomal Membrane, Ann. New York Acad. Sci., 1996, vol. 804, pp. 60–75.
Sulter, G., Looyenga, L., Veenhuis, M., and Harder, W., Occurrence of Peroxisomal Membrane Proteins in Methylotrophic Yeasts Grown under Different Conditions, Yeast, 1990, vol. 6, pp. 35–43.
Salomons, F.A., van der Klei, I.J., Kram, et al., Brefeldin A Interferes with Peroxisomal Protein Sorting in the Yeast Hansenula polymorpha, FEBS Lett., 1997, vol. 411, pp. 133–139.
Imanaka, T., Shiina, Y., Takano, T., et al., Insertion of the 70-kDa Peroxisomal Membrane Protein into Peroxisomal Membranes in Vivo and in Vitro, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, vol. 271, pp. 3706–3713.
Just, W., and Hartl, F.-U., in Peroxisomes in Biology and Medicine, Fahimi, H.D. and Sie, H., Eds., Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 1987, pp. 402–416.
Dyer, J.M., McNew, J.A., and Goodman, J.M., The Sorting Sequence of the Peroxisomal Integral Membrane Protein PMP47 Is Contained within a Short Hydrophilic Loop, J. Cell Biol., 1996, vol. 133, pp. 269–280.
Wiemer, E.A.C., Luers, G.H., Faber, K.N., et al., Isolation and Characterization of Pas2p, a Peroxisomal Membrane Protein Essential for Peroxisome Biogenesis in the Methylotrophic Yeast Pichia pastoris, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, vol. 271, pp. 18 973–18 980.
Kammerer, S., Holzinger, A., Welsch, U., and Roscher, A., Cloning and Characterization of the Gene Encoding the Human Peroxisomal Assembly Protein Pex3p, FEBS Lett., 1998, vol. 429, pp. 53–60.
Jones, J.M., Morrell, J.C., and Gould, S.J., Multiple Distinct Targeting Signals in Integral Peroxisomal Membrane Proteins, J. Cell Biol., 2001, vol. 153, pp. 1141–1150
Erdmann, R., Veenhuis, M., and Kunau, W.-H., Peroxisomes: Organelles at the Crossroads, Trends Cell Biol., 1997, vol. 7, pp. 400–407.
Snyder, W., Faber, K., Wenzel, T., et al., Pex19p Interacts with Pex3p and Pex10p and Is Essential for Peroxisome Biogenesis in Pichia pastoris, Mol. Biol. Cell, 1999, vol. 10, pp. 1745–1761.
Soukupova, M., Sprenger, C., Gorgas, K., et al., Identification and Characterization of the Human Peroxin PEX3, Eur. J. Cell Biol., 1999, vol. 78, pp. 357–374.
Snyder, W., Koller, A., Choy, A., et al., Pex17p Is Required for Import of Both Peroxisome Membrane and Lumenal Proteins and Interacts with Pex19p and the Peroxisome Targeting Signal-Receptor Docking Complex in Pichia pastoris, Mol Biol. Cell, 1999, vol. 10, pp. 4005–4019.
Eitzen, G., Szilard, R., and Rachubinski, R., Enlarged Peroxisomes Are Present in Oleic Acid-Grown Yarrowia lipolytica Overexpressing the PEX16 Gene Encoding an Intraperoxisomal Peripheral Membrane Peroxin, J. Cell Biol., 1997, vol. 137, pp. 1265–1278.
Kunau, W. and Erdmann, R., Peroxisome Biogenesis: Back to the Endoplasmic Reticulum?, Curr. Biol., 1998, vol. 8, pp. 299–302.
Titorenko, V.I., Chan, H., and Rachubinski, R.A., Fusion of Small Peroxisomal Vesicles in Vitro Reconstructs an Early Step in the in Vivo Multistep Peroxisome Assembly Pathway of Yarrowia lipolytica, J. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 148, pp. 29–43.
Titorenko, V.I. and Rachubinski, R.A., Dynamics of Peroxisome Assembly and Function, Trends Cell Biol., 2001, vol. 11, pp. 22–29.
Heinemann, P. and Just, W., Peroxisomal Protein Import, FEBS Lett., 1992, vol. 300, pp. 179–182.
Wilcke, M., Hultenby, K., and Alexson, S.E.H., Novel Peroxisomal Populations in Subcellular Fractions from Rat Liver: Implications for Peroxisome Structure and Biogenesis, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, vol. 270, pp. 6949–6958.
Titorenko, V.I., Eitzen, G.A., and Rachubinski, R.A., Mutations in the PAY5 Gene of the Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica Cause the Accumulation of Multiple Subpopulations of Peroxisomes, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, vol. 271, pp. 20 307–20 314.
South, S.T. and Gould, S.J., Peroxisome Synthesis in the Absence of Preexisting Peroxisomes, J. Cell Biol., 1999, vol. 144, pp. 255–266.
Honsho, M., Hiroshige, T., and Fujiki, Y., The Membrane Biogenesis Peroxin Pex16p-Topogenesis and Functional Roles in Peroxisomal Membrane Assembly, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, vol. 277, pp. 44 513–44 524.
South, S., Sacksteder, K., Li, X., et al., Inhibitors of COPI and COPII Do Not Block PEX3-Mediated Peroxisome Synthesis, J. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 149, pp. 1345–1360.
Faber, K.N., Haan, G.J., Baerends, R.J., et al., Normal Peroxisome Development from Vesicles Induced by Truncated Hansenula polymorpha Pex3p, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, vol. 277, pp. 11 026–11 033.
Marshall, P.A., Dyer, J.M., Quick, M.E., and Goodman, J.M., Redox-Sensitive Homodimerization of Pex11p: A Proposed Mechanism to Regulate Peroxisomal Division, J. Cell Biol., 1996, vol. 135, pp. 123–137.
Subramani, S., Protein Import into Peroxisomes and Biogenesis of the Organelle, Annu. Rev. Cell Biol., 1993, vol. 9, pp. 445–478.
Veenhuis, M. and Goodman, J.M., Peroxisomal Assembly: Membrane Proliferation Precedes the Induction of the Abundant Matrix Proteins in the Methylotrophic Yeast Candida boidinii, J. Cell Sci., 1990, vol. 96, pp. 583–590.
Tan, X., Waterham, H.R., Veenhuis, M., and Cregg, J.M., The Hansenula polymorpha PER8 Gene Encodes a Novel Peroxisomal Integral Membrane Protein Involved in Proliferation, J. Cell Biol., 1995, vol. 128, pp. 307–319.
Erdmann, R. and Blobel, G., Giant Peroxisomes in Oleic Acid-Induced Saccharomyces cerevisiae Lacking the Peroxisomal Membrane Protein Pmp27p, J. Cell Biol., 1995, vol. 128, pp. 509–523.
Marshall, P., Krimkevich, Y., Lark, R., et al., Pmp27 Promotes Peroxisomal Proliferation, J. Cell Biol., 1995, vol. 129, pp. 345–355.
Schrader, M., Reuber, B.E., Morrell, J.C., et al., Expression of PEX11 Mediates Peroxisome Proliferation in the Absence of Extracellular Stimuli, J. Biol. Chem., 1998, vol. 273, pp. 29 607–29 614.
Abe, I. and Fujiki, Y., cDNA Cloning and Characterization of a Constitutively Expressed Isoform of the Human Peroxin Pex11p, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1998, vol. 252, pp. 529–533.
Abe, I., Okumoto, K., Tamura, S., and Fujiki, Y., Clofibrate-Inducible, 28-kDa Peroxisomal Integral Membrane Protein Is Encoded by PEX11, FEBS Lett., 1998, vol. 431, pp. 468–472.
Lorenz, P., Maier, A., Baumgart, E., et al., Elongation and Clustering of Glycosomes in Trypanosoma brucei Overexpressing the Glycosomal Pex11p, EMBO J., 1998, vol. 17, pp. 3542–3555.
Maier, A., Schulreich, S., Bremser, M., and Clayton, C., Binding of Coatomer by the PEX11 C-Terminus Is Not Required for Function, FEBS Lett., 2000, vol. 484, pp. 82–86.
Van Roermund, C.W.T., Tabak, H.F., Berg, M., et al., Pex11p Plays a Primary Role in Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation, a Process That Affects Peroxisome Number and Size in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, J. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 150, pp. 489–497.
Van Roermund, C.W., Drissen, R., van Den Berg, M., et al., Identification of a Peroxisomal ATP Carrier Required for Medium-Chain Fatty Acid β-Oxidation and Normal Peroxisome Proliferation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2001, vol. 21, pp. 4321–4329.
Hoepfner, D., Berg, M., Philippsen, P., et al., A Role for Vps1p, Actin, the Myo2p Motor in Peroxisome Abundance and Inheritance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, J.Cell Biol., 2001, vol. 155, pp. 979–990.
Smith, J.J., Marelli, M., Christmas, R.H., et al., Transcriptome Profiling to Identify Genes Involved in Peroxisome Assembly and Function, J. Cell Biol., 2002, vol. 158, pp. 259–271
Yoon, Y., Pitts, K.R., Dahan, S., and McNiven, M.A., A Novel Dynamin-Like Protein Associates with Cytoplasmic Vesicles and Tubules of the Endoplasmic Reticulum in Mammalian Cells, J. Cell Biol., 1998, vol. 140, pp. 779–793.
Pitts, K.R., Yoon, Y., Krueger, E.W., and McNiven, M.A., The Dynamin-Like Protein DLP1 Is Essential for Normal Distribution and Morphology of the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria in Mammalian Cells, Mol. Biol. Cell, 1999, vol. 10, pp. 4403–4417.
Koch, A., Thiemann, M., Grabenbauer, M., et al., The Dynamin-Like Protein DLP1 Is Involved in Peroxisomal Fission, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, p. M211761200.
Li, X. and Gould, S.J., The Dynamin-Like GTPase DLP1 Is Essential for Peroxisome Division and Is Recruited to Peroxisomes in Part by PEX11, J. Biol. Chem., 2003, vol. 278, pp. 17 012–17 020.
Tabak, H., Murk, J., Braakman, I., and Geuze, H.J., Peroxisomes Start Their Life in the Endoplasmic Reticulum, Traffic, 2003, vol. 4, pp. 512–518.
Nunnari, J. and Walter, P., Regulation of Organelle Biogenesis, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1996, vol. 84, pp. 389–394.
Warren, G. and Wickner, W., Organelle Inheritance, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1996, vol. 84, pp. 395–400.
Yaffe, M.P., Dynamic Mitochondria, Nat. Cell Biol., 1999, vol. 1, pp. E149–E150.
Titorenko, V. and Rachubinski, R., The Peroxisome: Orchestrating Important Developmental Decisions from Inside the Cell, J. Cell Biol., 2004, vol. 164, pp. 641–645.
Gould, S., Valle, D., and Raymond, J., The Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders, The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S., and Valle, D., Eds., New York: McGraw-Hill, 2001, pp. 3181–3217.
Petriv, O.I., Pilgrim, D.B., Rachubinski, R.A., and Titorenko, V.I., RNA Interference of Peroxisome-Related Genes in C. elegans: A New Model for Human Peroxisomal Disorders, Physiol. Genomics, 2002, vol. 10, pp. 79–91.
Thines, E., Weber, R.W.S., and Talbot, N.J., MAP Kinase and Protein Kinase A-Dependent Mobilization of Triacylglycerols and Glycogen during Appressorium Turgor Generation by Magnaporthe grisea, Plant Cell, 2000, vol. 12, pp. 1703–1718.
Kimura, A., Takano, Y., Furusawa, I., and Okuno, T., Peroxisomal Metabolic Function Is Required for Appressorium-Mediated Plant Infection by Colletotrichum lagenarium, Plant Cell, 2001, vol. 13, pp. 1945–1957.
Titorenko, V.I., Ogrydziak, D.M., and Rachubinski, R.A., Four Distinct Secretory Pathways Serve Protein Secretion, Cell Surface Growth, and Peroxisome Biogenesis in the Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica, Mol. Cell. Biol., 1997, vol. 17, pp. 5210–5226.
Titorenko, V.I. and Rachubinski, R.A., Mutants of the Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica Defective in Protein Exit from the Endoplasmic Reticulum Are Also Defective in Peroxisome Biogenesis, Mol. Cell. Biol., 1998, vol. 18, pp. 2789–2803.
Gavva, N., Wen, S., Daftari, P., et al., NAPP2, a Peroxisomal Membrane Protein, Is Also a Transcriptional Corepressor, Genomics, 2002, vol. 79, pp. 423–431.
Lin, Y., Sun, L., Nguyen, L.V., et al., The Pex16p Homolog SSE1 and Storage Organelle Formation in Arabidopsis Seeds, Science, 1999, vol. 284, pp. 328–330.
Sarmiento, C., Ross, J.H.E., Herman, E., and Murphy, D.J., Expression and Subcellular Targeting of a Soybean Oleosin in Transgenic Rapeseed: Implications for the Mechanism of Oil-Body Formation in Seeds, Plant J., 1997, vol. 11, pp. 783–796.
Footitt, S., Slocombe, S., Larner, V., et al., Control of Germination and Lipid Mobilization by COMATOSE, the Arabidopsis Homologue of Human ALDP, EMBO J., 2002, vol. 21, pp. 2912–2922.
Berteaux-Lecellier, V., et al., A Mammalian Homolog of the PAF1 Gene Zellweger Syndrome Discovered As a Gene Involved in Karyogamy in the Fungus Podospora anserina, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1995, vol. 81, pp. 1043–1051.
Baumgartner, M.R. and Saudubray, J.M., Peroxisomal Disorders, Semin. Neonatol., 2002, vol. 7, pp. 85–94.
Walter, C., Gootjes, J., Mooijer, P.A., et al., Disorders of Peroxisome Biogenesis Due to Mutations in PEX1: Phenotypes and PEX1 Protein Levels, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2001, vol. 69, pp. 35–48.
Imamura, A., Shimozawa, N., Suzuki, Y., et al., Temperature-Sensitive Mutation of PEX6 in Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders in Complementation Group C (CG-C): Comparative Study of PEX6 and PEX1, Pediatric. Res., 2000, vol. 48, no.4, pp. 234–240.
Imamura, A., Tamura, S., Shimozawa, N., et al., Temperature-Sensitive Mutation in PEX1 Moderates the Phenotypes of Peroxisome Deficiency Disorders, Hum. Mol. Genet., 1998, vol. 7, pp. 2089–2094.
Imamura, A., Tsukamoto, T., Shimozawa, N., et al., Temperature-Sensitive Phenotypes of Peroxisome Assembly Processes Represent the Milder Forms of Human Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 1998, vol. 62, pp. 1539–1543.
Matsumoto, N., Tamura, S., Furuki, S., et al., Mutations in Novel Peroxin Gene PEX26 That Cause Peroxisome-Biogenesis Disorders of Complementation Group 8 Provide a Genotype-Phenotype Correlation, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2003, vol. 73, pp. 233–246.
Collins, C.S. and Gould, S.J., Identification of a Common PEX1 Mutation in Zellweger Syndrome, Hum. Mutat., 1999, vol. 14, pp. 45–53.
Tamura, S., Matsumoto, N., Imamura, A., et al., Phenotype-Genotype Relationships in Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders of PEX1-Defective Complementation Group 1 Are Defined by Pex1p–Pex6p Interaction, Biochem. J., 2001, vol. 357, pp. 417–426.
Shimozawa, N., Tsukamoto, T., Nagase, T., et al., Identification of a New Complementation Group of the Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders and PEX14 As the Mutated Gene, Hum. Mutat., 2004, vol. 23, no.6, pp. 552–558.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Genetika, Vol. 41, No. 2, 2005, pp. 149–165.
Original Russian Text Copyright © 2005 by Kurbatova, Dutova, Trotsenko.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurbatova, E.M., Dutova, T.A. & Trotsenko, Y.A. Structural, functional and genetic aspects of peroxisome biogenesis. Russ J Genet 41, 97–111 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11177-005-0032-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11177-005-0032-x