Abstract
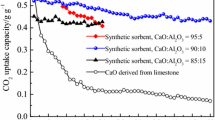
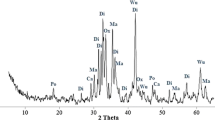
A new method of carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) by sodium humate (HA–Na) and Ca(OH)2 from carbide slag (CS) solution was proposed. The effects of various operating parameters, such as the additive amount of HA–Na, pH, temperature, gas flow rate, CO2 inlet concentration, and stirring rate on both the Ca ion concentration and Ca conversion rate were investigated in a lab-scale bubbling reactor. The synergistic mechanism of HA–Na and Ca(OH)2 from CS on CCS is also put forward and demonstrated. The experimental results indicate that HA–Na may improve significantly the CCS capability of CS since the Ca conversion rate of CS is increased 10% by HA–Na additive. The pH is a key factor for the CO2 absorption process and HA–Na may lower the rate of pH decrease of Ca(OH)2 solution. The increasing temperature, stirring rate, and CO2 inlet concentration are favorable to CO2 capture, as well as low gas flow rate. Ca(OH)2 from CS mixed with HA–Na solution shows good performance in CO2 uptake, and the Ca conversion rate reaches 99% with 100 mL of Ca(OH)2 (1.5 g/L) solution mixed with 0.1 g HA–Na at 40 °C, a gas flow rate of 0.1 L/min, and an inlet CO2 concentration of 100% at ambient pressure. Moreover, calcite CaCO3 is is identified as the main product of CO2 capture by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy analysis.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Freund, Geological Storage of Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) (Woodhead, Cambridge, 2013)
Q. Wang, J.Z. Luo, Z.Y. Zhong, A. Borgna, Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 42 (2011)
E.R. Bobicki, Q.X. Liu, Z.H. Xu, H.B. Zeng, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 38, 302 (2012)
A. Sanna, M. Uibu, G. Caramanna, R. Kuusik, M.M. Maroto-Valer, Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 8049 (2014)
M.E. Boot-Handford, J.C. Abanades, E.J. Anthony, M.J. Blunt, S. Brandani, N. Mac Dowell, J.R. Fernández, M.C. Ferrari, R. Gross, J.P. Hallett, R.S. Haszeldine, P. Heptonstall, A. Lyngfelt, Z. Makuch, E. Mangano, R.T.J. Porter, M. Pourkashanian, G.T. Rochelle, N. Shah, J.G. Yao, P.S. Fennell, Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 130 (2014)
A. Kaithwas, M. Prasad, A. Kulshreshtha, S. Verma, Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 90, 1632 (2012)
C.W. Zhao, X.P. Chen, E.J. Anthony, X. Jiang, L.B. Duan, Y. Wu, W. Dong, C.S. Zhao, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 39, 515 (2013)
Z.R. He, Y.J. Li, X.T. Ma, W. Zhang, C.Y. Chi, Z.Y. Wang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 41, 4296 (2016)
Y.J. Li, R.Y. Sun, C.T. Liu, H.L. Liu, C.M. Lu, Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control 9, 117 (2012)
W. Zhang, Y.J. Li, L.B. Duan, X.T. Ma, Z.Y. Wang, C.M. Lu, Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 109, 806 (2016)
Y.J. Li, R.Y. Sun, J.L. Zhao, C.T. Liu, C.M. Lu, Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 38, 13655 (2013)
C.T. Liu, Y.J. Li, R.Y. Sun, S.M. Wu, Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 9, 678 (2014)
Y.J. Li, M.Y. Su, X. Xie, S.M. Wu, C.T. Liu, Appl. Energy 145, 60 (2015)
X.T. Ma, Y.J. Li, L. Shi, Z.R. He, Z.Y. Wang, Appl. Energy 168, 85 (2016)
J. Sun, W.Q. Liu, Y.C. Hu, J.Q. Wu, M.K. Li, X.W. Yang, W.Y. Wang, M.H. Xu, Chem. Eng. J. 285, 293 (2016)
A.G. De-Melo, F.L. Motta, M.H. Santana, Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 62, 967 (2016)
Z.G. Sun, H.Y. Gao, G.X. Hu, Y.H. Li, Environ. Eng. Sci. 26, 1249 (2009)
G.X. Hu, Z.G. Sun, H.Y. Gao, Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 6712 (2010)
Z.G. Sun, Y. Zhao, H.Y. Gao, G.X. Hu, Energy Fuels 24, 1013 (2010)
Z.G. Sun, B. Tang, H.Y. Xie, Energy Fuels 29, 1269 (2015)
Z.G. Sun, J.T. Yang, L. Zhang, H.Y. Xie, NANO 11, 1650070 (2016)
Z.G. Sun, H.Y. Xie, L. Yang, Y.T. Zhu. CN. Patent 201210365138.2. (2012)
O. Rahmani, R. Junin, M. Tyrer, R. Mohsin, Energy Fuels 28, 5953 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (nos. 15ZR1416900, 16ZR1412600), State Key Laboratory for Modification of Chemical Fibers and Polymer Materials, Donghua University (no. LK1518), Cultivate Discipline Fund of Shanghai Second Polytechnic University (no. XXKPY1601), and Postgraduate Foundation of Shanghai Second Polytechnic University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Feng, R., Zhang, L. et al. CO2 capture and sequestration by sodium humate and Ca(OH)2 from carbide slag. Res Chem Intermed 44, 3613–3627 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3328-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3328-x