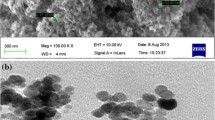
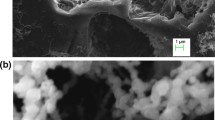
Abstract
The present research aims to optimize the removal of phosphate (PO4 3−) from aqueous solution by Fe3O4 stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles (Fe3O4–ZVINPs). A three-factor, three-level, Box–Behnken design combined with response surface methodology was applied to design the experiments, to develop a mathematical model, and for evaluating the individual and also the interactive effects of the operating variables like pH, temperature, and PO4 3− concentration on removal efficiency. The analysis of variance has been used to evaluate the adequacy of the developed mathematical model in order to predict the optimal conditions of independent process variables, and to get maximum removal efficiency. Three-dimensional response surface plots were constructed to visualize the simultaneous interactive effects between two process variables. All three factors had a significant impact on removal of PO4 3−. The predicted value of the model (166.0 mg g−1PO4 3−) was in good agreement with the experimental value (164.92 mg g−1 PO4 3−) under the optimum conditions of temperature 49.2 °C; pH 3.5; and PO4 3− concentration 79.8 mg L−1. The removal of PO4 3− in the presence of environmental matrix (other ions) was also investigated at optimum conditions as predicted by the model. The results suggest that the presence of these ions had no significant effect on PO4 3− removal. In addition, the adsorbed PO4 3− can be effectively desorbed at higher pH of the solution. The findings suggest that removal of PO4 3− from aqueous solution using Fe3O4–ZVINPs can be an effective method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Choi, S.Y. Lee, S.H. Lee, K.B. Lee, D.J. Kim, S.W. Hong, Adsorption of phosphate by amino-functionalized and Co-condensed SBA-15. Water Air Soil Pollut. 223(2012), 2551–2562 (2012)
T. Almeelbi, A. Bezbaruah, Aqueous phosphate removal using nanoscale zero-valent iron. J. Nanoparticle Res. 14, 1–14 (2012)
G. Zhang, H. Liu, R. Liu, J. Qu, Removal of phosphate from water by a Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 335, 168–174 (2009)
D. Donnert, M. Salecker, Elimination of phosphorous from waste water by crystallization. Environ. Technol. 20, 735–742 (1999)
E.M. Van Voorthuizen, A. Zwijnenburg, M. Wessling, Nutrient removal by NF and RO membranes in a decentralized sanitation system. Water Res. 39, 3657–3667 (2005)
M. Gouider, N. Mlaik, M. Feki, S. Sayadi, Integrated physicochemical and biological treatment process for fluoride and phosphorus removal from fertilizer plant wastewater. Water Environ. Res. 83, 731–738 (2011)
D. Mohan, C.U. Jr, Pittman, activated carbons and low cost adsorbents for remediation of tri and hexavalent chromium for water. J. Hazard. Mater. 137, 762–811 (2006)
V.K. Gupta, I. Ali, Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat. Protoc. 1, 2661–2667 (2007)
A. Mittal, J. Mittal, A. Malviya, D. Kaur, V.K. Gupta, Decoloration treatment of a hazardous triarylmethane dye, light green SF (yellowish) by waste material adsorbents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 342, 518–527 (2010)
Q. Yue, Y. Zhao, Q. Li, W. Li, B. Gao, S. Han, Y. Qi, H. Yu, Research on the characteristics of red mud granular adsorbents (RMGA) for phosphate removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 176, 741–748 (2010)
S. Hussain, H.A. Aziz, M.H. Isa, A. Ahmad, J. Van Leeuwen, L. Zou, S. Beecham, M. Umar, Orthophosphate removal from domestic wastewater using limestone and granular activated carbon. Desalination 271, 265–272 (2011)
R. Chitrakar, S. Tezuka, A. Sonoda, K. Sakane, K. Ooi, T. Hirotsu, Phosphate adsorption on synthetic goethite and akaganeite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 298, 602–608 (2006)
X. Lv, J. Xu, G. Jiang, J. Tang, X. Xu, Highly active nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI)–Fe3O4 nanocomposites for the removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 369, 460–469 (2012)
Y. Wu, J. Zhang, Y. Tong, X. Xu, Chromium (VI) reduction in aqueous solutions by Fe3O4-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 172, 1640–1645 (2009)
K.P. Singh, A.K. Singh, S. Gupta, Optimization of nitrate reduction by EDTA catalyzed zero-valent bimetallic nanoparticles in aqueous medium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 19, 3914–3924 (2012)
A.K. Singh, K.P. Singh, Response surface optimization of nitrite removal from aqueous solution by Fe3O4 stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles using a three-factor, three-level Box–Behnken Design. Res. Chem. Inter. 42, 2247–2265 (2016)
K.P. Singh, A.K. Singh, S. Gupta, S. Sinha, Optimization of Cr(VI) reduction by zero-valent bimetallic nanoparticles using the response surface modeling approach. Desalination 270, 275–284 (2011)
K.P. Singh, A.K. Singh, S. Gupta, P. Rai, Modeling and optimization of reductive degradation of chloramphenicol in aqueous solution by zero-valent bimetallic nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 19, 2063–2078 (2012)
S. Bajpai, S.K. Gupta, A. Dey, M.K. Jha, V. Bajpai, S. Joshi, A. Gupta, Application of central composite design approach for removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution using weakly anionic resin: modeling, optimization and study of interactive variables. J. Hazard. Mater. 227–228, 436–444 (2012)
A.R. Khataee, G. Dehghan, Optimization of biological treatment of a dye solution by macroalgae Cladophora sp. using response surface methodology. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 42, 26–33 (2011)
K.P. Singh, A.K. Singh, U.V. Singh, P. Verma, Optimizing removal of ibuprofen from water by magnetic nanocomposite using Box–Behnken design. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 19, 724–738 (2012)
X. Lv, Y. Hu, J. Tang, T. Sheng, G. Jiang, X. Xu, Effects of co-existing ions and natural organic matter on removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI)-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 218, 55–64 (2013)
D. Wu, Y. Shen, A. Ding, M. Qiu, Q. Yang, S. Zheng, Phosphate removal from aqueous solutions by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Technol. 34, 2663–2669 (2013)
S.R. Chowdhury, E.K. Yanful, Arsenic and chromium removal by mixed magnetite–maghemite nanoparticles and the effect of phosphate on removal. J. Environ. Manag. 91, 2238–2247 (2010)
J. Hu, I.M.C. Lo, G. Chen, Performance and mechanism of chromate (VI) adsorption by δ-FeOOH-coated maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles. Sep. Pur. Technol. 58, 76–82 (2007)
R. Chen, C. Zhi, H. Yang, Y. Bando, Z. Zhang, N. Sugiur, D. Golberg, Arsenic (V) adsorption on Fe3O4 nanoparticle-coated boron nitride nanotubes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 359, 261–268 (2011)
M. Iram, C. Guo, Y. Guan, A. Ishfaq, H. Liu, Adsorption and magnetic removal of neutral red dye from aqueous solution using Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 181, 1039–1050 (2010)
Q. Wang, S. Snyder, J. Kim, H. Choi, Aqueous ethanol modified nanoscale zero-valent iron in bromate reduction: synthesis, characterization and reactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 3292–3299 (2009)
A. Sowmya, S. Meenakshi, Effective removal of nitrate and phosphate anions from aqueous solutions using functionalised chitosan beads, Desalin. Water Treat. 52(13–15), 2583–2593 (2014)
B. Pan, J. Wu, B. Pan, L. Lv, W. Zhang, L. Xiao, X. Wang, X. Tao, S. Zheng, Development of polymer-based nanosized hydrated ferric oxides (HFOs) for enhanced phosphate removal from waste effluents. Water Res. 43, 4421–4429 (2009)
A. Rajeswari, A. Amalraj, A, Pius, Removal of phosphate using chitosan–polymer composites. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 3, 2331–2341 (2015)
F. Ogata, D. Imai, M. Toda, M. Otani, N. Kawasaki, Adsorption of phosphate ion in aqueous solutions by calcined cobalt hydroxide at different temperatures. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 3, 1570–1577 (2015)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the director, CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research, Lucknow (India) for his keen interest in this work and for providing the necessary facilities. Arun K. Singh gratefully acknowledges CSIR (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research) for awarding the senior research fellowship to him.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A.K., Singh, K.P. Evaluation of phosphate removal capacity of Fe3O4–ZVINPs from aqueous solution: optimization using response surface analysis. Res Chem Intermed 42, 7397–7415 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-016-2543-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-016-2543-6