Abstract
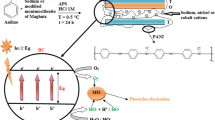
The performance of Co2+-doped ZnO nanoparticles, prepared using the sol–gel method, for 2-chlorophenol degradation under direct solar radiation was investigated. Various parameters were investigated during the degradation process, namely solar intensity, Co2+ ion concentration, loading concentrations of Co2+-doped ZnO, and pH. The photocatalytic degradation efficiency increased when the initial concentration of 2-chlorophenol decreased; the optimum concentration was 50 mg/L under similar experimental conditions. Moreover, optimum values, established on a sunny day, were 0.75 wt% of Co2+, a 1 g/L loading concentration, and a pH of 6.0, respectively. The highest degradation efficiency observed was 95 %, after only 90 min of solar light irradiation. The mechanism of visible photocatalytic degradation using Co2+-doped ZnO was explained as a strong electronic interaction between Co2+, Co3+ and ZnO, and a promotion in the charge separation, which enhanced the degradation performance. The fragmentation of 2-chlorophenol under the optimal conditions was investigated using HPLC, comparing standards of all intermediate compounds. The pathway of the fragmentation was proposed as involving hydroxyhydroquinone, catechol, and phenol formation, which were then converted to non-toxic compounds such as oxalic acid and acetic acid with further decomposition to CO2 and H2O.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Roques, Chemical Water Treatment (VCH Verlag, Weinheim, Germany, 1996)
K.M. Parida, S. Parija, Photocatalytic degradation of phenol under solar radiation using microwave irradiated zinc oxide. Sol. Energy 80, 1048–1054 (2006)
U. Gaya, Heterogeneous Photocatalysis Using Inorganic Semiconductor Solids (Springer, New York, 2013)
M. Czaplicka, Photo-degradation of chlorophenols in the aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 134, 45–59 (2006)
D.N. Moza, K. Fytianos, V. Samanidou, F. Korte, Photodecomposition of chlorophenols in aqueous medium in presence of hydrogen peroxide. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 41, 678–682 (1988)
M.M. Häggblom, D. Janke, M.S. Salkinoja-Salonen, Degradation and transformation of chlorinated phenolic compounds by strain of Rhodococcus and Mycobaterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 555, 16–519 (1989)
X.W. Zhang, M.H. Zhou, L.C. Lei, TiO2 photocatalyst deposition by MOCVD on activated carbon. Carbon 44, 325–333 (2006)
J.M. Herrmann, Heterogeneous photocatalysis: fundamentals and applications to the removal of various types of aqueous pollutants. Catal. Today 53, 115–129 (1999)
G. Ganapathy Selvam, K. Sivakumar, Phycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye using silver (Ag) nanoparticles synthesized from Hypnea musciformis (Wulfen) J.V. Lamouroux. Appl. Nanosci. 5, 617–622 (2015)
Y.T. Chung, M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.W. Mohammad, N.H.H. Hairom, A. Benamor, Synthesis of minimal-size ZnO nanoparticles through sol–gel method: Taguchi design optimisation. Mater. Des. 87, 780–787 (2015)
E. Mahmoudi, L.Y. Ng, M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.W. Mohammad, Novel nanohybrid polysulfone membrane embedded with silver nanoparticles on graphene oxide nanoplates. Chem. Eng. J. 277, 1–10 (2015)
A. Shafaei, M. Nikaza, M. Arami, Photocatalytic degradation of terephthalic acid using titania and zinc oxide photocatalysts: comparative study. Desalin. 252, 8–16 (2010)
M.A. Behnajady, N. Modirshahla, R. Hamzavi, Kinetic study on photocatalytic degradation of C.I. Acid Yellow 23 by ZnO photocatalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. B 133, 226–232 (2006)
S. Sakthivel, H. Kish, Photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical properties of N-doped titanium dioxide. Chem. Phys. Chem. 4, 487–490 (2003)
M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.A.H. Kadhum, A.A. Al-Amiery, A.B. Mohamad, M.S. Takriff, Toxicity evaluation for low concentration of chlorophenols under solar radiation using zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 7, 48–52 (2012)
M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.A.H. Kadhum, A.B. Mohamad, M.S. Takriff, K. Sopian, Synthesis and catalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles for photochemical oxidation of concentrated chlorophenols under direct solar radiation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7, 4871–4888 (2012)
M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.A.H. Kadhum, A.B. Mohamad, M.S. Takriff, R.T.T. Jalgham, Synthesis and catalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles for photochemical oxidation of concentrated chlorophenols under direct solar radiation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7, 11363–11376 (2012)
J. Huo, L. Fang, Y. Lei, G. Zeng, H, Zeng, Facile preparation of yttrium and aluminum codoped ZnO via a sol-gel route for photocatalytic hydrogen production. J. Mater. Chem A. 2, 11040–11044 (2014)
M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.A.H. Kadhum, A.B. Mohamad, M.S. Takriff, K. Sopian, Visible light photocatalytic activity of Fe3+-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared via sol–gel technique. Chemosphere 91, 1604–1611 (2013)
M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.A.H. Kadhum, A.B. Mohamad, M.S. Takriff, K. Sopian, The effect of process parameters on the size of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized via the sol–gel technique. J. Alloys Compd. 550, 63–70 (2013)
M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.A.H. Kadhum, A.B. Mohamad, M.S. Takriff, K. Sopian, Optimization of process parameters using D-optimal design for synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles via sol–gel technique. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 19, 99–105 (2013)
M. Ram, E.S. Andreescu, D. Hanming, Nanotechnology for Environmental Decontamination (McGraw Hill Professional, New York, 2011)
S. Ahmed, M.G. Rasul, R. Brown, M.A. Hashib, Influence of parameters on the heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of pesticides and phenolic contaminants in wastewater: a short review. J. Environ. Manage. 92, 311–330 (2011)
R. Ullah, J. Dutta, Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes with manganese-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Haza. Mater. 156, 194–200 (2008)
Q. Xiao, J. Zhang, C. Xiao, X. Tan, Photocatalytic decolorization of methylene blue over Zn1 − xCoxO under visible light irradiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 142, 121–125 (2007)
K.S. Yu, J.Y. Shi, Z.L. Zhang, Y.M. Liang, W. Liu, Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalysis of ZnO and Er-doped ZnO. J. Nanomater. 2013, 372951–372956 (2013)
M.G. Nair, M. Nirmala, K. Rekha, A. Anukaliani, Structural, optical, photo catalytic and antibacterial activity of ZnO and Co doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 65, 1797–1800 (2011)
M. Zhou, J. Yu, B. Cheng, Effects of Fe-doping on the photocatalytic activity of mesoporous TiO2 powders prepared by an ultrasonic method. J. Hazard. Mater. 137, 1838–1847 (2006)
U.I. Gaya, A.H. Abdullah, M.Z. Hussein, Z. Zainal, Photocatalytic removal of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol from water exploiting commercial ZnO powder. Desalin 263, 176–182 (2010)
E. Evgenidou, K. Fytianos, I. Poulios, Semiconductor-sensitized photodegradation of dichlorvos in water using TiO2 and ZnO as catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 59, 81–89 (2005)
Z.M. El-Bahyb, A.A. Ismaila, R.M. Mohamed, Enhancement of titania by doping rare earth for photodegradation of organic dye (Direct Blue). J. Hazard. Mater. 166, 138–143 (2009)
M.A. Behnajady, N. Modirshala, R. Hamazavi, Kinetic study on photocatalytic degradation of C.I. Acid Yellow 23 by ZnO photocatalyst. J. Hazard Mat. 133, 226–232 (2006)
C. Karunakaran, R. Dhanalakshmi, Semiconductor-catalyzed degradation of phenols with sunlight. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 92, 1315–1321 (2008)
M.M. Hassan, A.S. Ahmed, M. Chaman, W. Khan, A.H. Naqvi, A. Azam, Structural and frequency dependent dielectric properties of Fe3+doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 3952–3958 (2012)
C.H. Patterson, Role of defects in ferromagnetism in Zn1−xCoxO: a hybrid density-functional study. Matter. Mater. Phys. 74, 144432–144435 (2006)
N.N. Rao, A.K. Dubey, S. Mohanty, P. Khare, R. Jain, S.N. Kaul, Photocatalytic degradation of 2-chlorophenol: a study of kinetics. Intermediates and biodegradability. J. Hazard. Mater. 101, 301–314 (2003)
M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.A.H. Kadhum, A.B. Mohamad, M.S. Takriff, K. Sopian, Photocatalytic degradation of chlorophenols under direct solar radiation in the presence of ZnO catalyst. Res. Chem. Intermed. 39, 1981–1996 (2013)
E.R. Bandala, C.A. Arancibia-Bulnes, S.L. Orozco, C.A. Estrada, Solar photoreactors comparison based on oxalic acid photocatalytic degradation. Sol. Energy 77, 503–512 (2004)
T. Xia, Y. Zhao, T. Sager, S. George, S. Pokhrel, N. Li, D. Schoenfeld, H. Meng, S. Lin, X. Wang, M. Wang, Z. Ji, J.I. Zink, L. Mädler, V. Castranova, S. Lin, A.E. Nel, Decreased dissolution of ZnO by iron doping yields nanoparticles with reduced toxicity in the rodent lung and zebrafish embryos. ACS Nano. 5, 1223–12235 (2011)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Research Centre for Sustainable Process Technology (CESPRO), Faculty of Engineering and Built Environment, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia for support this study under project iconic-2014-004. Also, one of the authors (M. M. Ba-Abbad) is grateful to the Hadhramout University of Science and Technology, Yemen, for their financial support for his PhD study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ba-Abbad, M.M., Takriff, M.S. & Mohammad, A.W. Enhancement of 2-chlorophenol photocatalytic degradation in the presence Co2+-doped ZnO nanoparticles under direct solar radiation. Res Chem Intermed 42, 5219–5236 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2352-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2352-3