Abstract
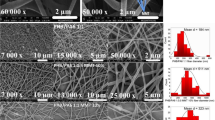
A novel polyacrylonitrile (PAN)–titanium oxide (TiO2) nanofiber adsorbent functionalized with aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) was fabricated by electrospinning. The adsorbent was characterized by SEM, FTIR, TEG and BET analyses. The pore diameter and surface area of the adsorbent were 3.1 nm and 10.8 m2 g−1, respectively. The effects of several variables, such as TiO2 and amine contents, pH, interaction time, initial concentration of metal ions, ionic strength and temperature, were studied in batch experiments. The kinetic data were analyzed by pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order and double-exponential models. Two isotherm models, namely Freundlich and Langmuir, were used for analysis of equilibrium data. The maximum adsorption capacities of Th(IV), Ni(II) and Fe(II) by Langmuir isotherm were found to be 250, 147 and 80 mg g−1 at 45 °C with pH of 5, 6 and 5, respectively, and greater adsorption of Th(IV) could be justified with the concept of covalent index and free energy of hydration. Calculation of ΔG°, ΔH° and ΔS° demonstrated that the nature of the Th(IV), Ni(II) and Fe(II) metal ions adsorption onto the PAN–TiO2–APTES nanofiber was endothermic and favorable at a higher temperature. The negative values of ΔG° for Th(IV) showed that the adsorption process was spontaneous, but these values for Ni(II)and Fe(II) were positive and so the adsorption process was unspontaneous. Increasing of ionic strength improved the adsorption of Ni(II) and Fe(II) on nanofiber adsorbent but decreased the adsorption capacity of Th(IV). The adsorption capacity was reduced slightly after six cycles of adsorption–desorption, so the nanofiber adsorbent could be used on an industrial scale. The inhibitory effect of Ni(II) and Fe(II) on the adsorption of Th(IV) was increased with an increase in the concentration of inhibitor metal ions.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Barakat, New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 4, 361–377 (2011)
M. Metaxas, Thorium removal by different adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 97, 71–82 (2003)
Y.C. Sharma, Economic treatment of cadmium (II)-rich hazardous waste by indigenous material. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 173, 66–70 (1995)
M. Kilic, C. Kirbiyik, Ö. Cepeliogullar, A.E. Pütün, Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by bio-char, a by-product of pyrolysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 283, 856–862 (2013)
S. Yari, S. Abbasizadeh, S.E. Mousavi, M.S. Moghaddam, A.Z. Moghaddam, Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution by an electrospun CeO2 nanofiber adsorbent functionalized with mercapto groups. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 94, 159–171 (2015)
M.R. Moghaddam, S. Fatemi, A. Keshtkar, Adsorption of lead (Pb2+) and uranium cations by brown algae; experimental and thermodynamic modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 231, 294–303 (2013)
R. Kumar, A.M. Isloor, Preparation and evaluation of heavy metal rejection properties of polysulfone/chitosan, polysulfone/N-succinyl chitosan and polysulfone/N-propylphosphonyl chitosan blend ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 350, 102–108 (2014)
W.P. Zhu, S.P. Sun, Dual-layer polybenzimidazole/polyethersulfone (PBI/PES) nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for heavy metals removal from wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 456, 117–127 (2014)
S.Y. Huang, C.S. Fan, C. Hou, Electro-enhanced removal of copper ions from aqueous solutions by capacitive deionization. J. Hazard. Mater. 278, 8–15 (2014)
A.M. Shoushtari, M. Zargaran, M. Abdouss, Preparation and characterization of high efficiency ion-exchange cross linked acrylic fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 101, 2202–2209 (2006)
A.B. Resterna, R. Cierpiszewski, K. Prochaska, Kinetic and equilibrium studies of the removal of cadmium ions from acidic chloride solutions by hydrophobic pyridinecarboxamide extractants. J. Hazard. Mater. 179, 828–833 (2010)
M. Visa, C. Bogatu, A. Duta, Simultaneous adsorption of dyes and heavy metals from multicomponent solutions using fly ash. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 5486–5491 (2010)
D. Humelnicu, L. Bulgariu, M. Macoveanu, On the retention of uranyl and thorium ions from radioactive solution on peat moss. J. Hazard. Mater. 174, 782–787 (2010)
A. Dastbaz, A. Keshtkar, Adsorption of Th4+, U6+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution by a novel modified polyacrylonitrile composite nanofiber adsorbent prepared by electrospinning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 293, 336–344 (2014)
D. Türkmen, E. Yılmaz, N. Ozturk, V. Akgol, A. Denizli, Poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) nanobeads containing imidazole groups for removal of Cu(II) ions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 29, 2072–2078 (2009)
X. Liu, Q. Hu, Z. Fang, X. Zhang, B. Zhang, Magnetic chitosan nanocomposites: a useful recyclable tool for heavy metal ion removal. Langmuir 25, 3–8 (2009)
K. Saeed, S. Haidera, T.J. Oh, S.Y. Park, Preparation of amidoxime-modified polyacrylonitrile (PAN-oxime) nano-fibers and their applications to metal ions adsorption. J. Membr. Sci. 322, 400–405 (2008)
S. Abbasizadeh, A.R. Keshtkar, M.A. Mousavian, Preparation of a novel electrospun polyvinyl alcohol/titanium oxide nanofiber adsorbent modified with mercapto groups for uranium(VI) and thorium(IV) removal from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 220, 161–171 (2013)
H. Reneker, A.L. Yarin, Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer 49, 2387–2425 (2008)
A.K. Gupta, D.K. Paliwal, P. Bajaj, Polyacrilonitryle structure. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 70, 2703–2709 (1998)
M. Hua, S. Zhang, B. Pan, W. Zhang, L. Lv, Q. Zhang, Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 211–212, 317–331 (2012)
X. Guan, J. Du, X. Meng, Y. Sun, B. Sun, Q. Hu, Application of titanium dioxide in arsenic removal from water: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 215–216, 1–16 (2012)
X. Qu, P.J.J. Alvarez, Q. Li, Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Water Res. 47, 3931–3946 (2013)
X. Zhao, L. Lv, B. Pan, W. Zhang, S. Zhang, Q. Zhang, Polymer-supported nanocomposites for environmental application: a review. Chem. Eng. J. 170, 381–394 (2011)
A.R. Ladhea, P. Frailiea, D. Huab, M. Darsillob, D. Bhattacharyya, Thiol functionalized silica–mixed matrix membranes for silver capture from aqueous solutions: experimental results and modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 326, 460–471 (2009)
G. Socrates, The theory of vibrational spectroscopy and its application to polymeric materials. Mater. Des. 3, 646–647 (1982)
S. Deng, R. Bai, J.P. Chen, Aminated polyacrylonitrile fibers for lead and copper removal. Langmuir 19, 5058–5064 (2003)
S. Mallakpour, A. Barat, Efficient preparation of hybrid nanocomposite coatings based on poly(vinyl alcohol) and silane coupling agent modified TiO2 nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 71, 391–398 (2011)
L. Ji, X. Zhang, Ultrafine polyacrylonitrile/silica composite fibers via electrospinning. J. Mater. Lett. 62, 2161–2164 (2008)
C. Xiong, C. Yao, L. Wang, J. Ke, Adsorption behavior of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions onto geltype weak acid resin. Hydrometallurgy 98, 318–324 (2009)
M. Irani, A. Keshtkar, M.A. Mousavian, Removal of cadmium from aqueous solution using mesoporous PVA/TEOS/APTES composite nanofiber prepared by sol–gel/electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 200–202, 192–201 (2012)
F. Rashidi, R.S. Sarabi, Z. Ghasemi, A. Seif, Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies for the removal of lead(II) and copper(II) ions from aqueous solutions by nanocrystalline TiO2. Superlattices Microstruct. 48, 577–591 (2010)
N. Chiron, R. Guilet, E. Deydier, Adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) onto a grafted silica, isotherms and kinetic models. Water Res. 37, 3079–3086 (2003)
K.T. Noa, Description of hydration free energy density as a function of molecular physical properties. Biophys. Chem. 78, 127–145 (2005)
A. Zayed, M. Badruddozaa, Fe3O4/cyclodextrin polymer nanocomposites for selective heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater. Carbohydr. Polym. 91, 322–332 (2013)
L.M. Zhou, Y.P. Wang, Z.R. Liu, Q.W. Huang, Characteristics of equilibrium, kinetics studies for adsorption of Hg(II), Cu(II), and Ni(II) ions by thiourea-modified magnetic chitosan microspheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 161, 995–1002 (2009)
A. Taha, Y. Wu, H. Wang, F. Li, Preparation and application of functionalized cellulose acetate/silica composite nanofibrous membrane via electrospinning for Cr(VI) ion removal from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Manag. 112, 10–16 (2012)
F.A. Dawodu, K.G. Akpomie, Simultaneous adsorption of Ni(II) and Mn(II) ions from aqueous solution onto a Nigerian kaolinite clay. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 3, 129–141 (2014)
T. Jong, D.L. Parry, Adsorption of Pb(II), Cu(II), Cd(II), Zn(II), Ni(II), Fe(II), and As(V) on bacterially produced metal sulfides. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 275, 61–71 (2004)
S. Abbasizadeh, A.R. Keshtkar, M.A. Mousavian, Sorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by a novel cast PVA/TiO2 nanohybrid adsorbent functionalized with amine groups. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 1656–1664 (2014)
A. Kamari, S.N.M. Yusoff, F. Abdullah, W.P. Putra, Biosorptive removal of Cu(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions using coconut dregs residue: adsorption and characterisation studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2, 1912–1919 (2014)
R. Akkaya, Removal of radioactive elements from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto polyacrylamide–expanded perlite: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic study. Desalination 321, 3–8 (2013)
M.K. Nazal, M.A. Albayyari, F.I. Khalili, Effect of high ionic strength on the extraction of uranium(VI) ions. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 18, 59–67 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokhtari, M., Keshtkar, A.R. Removal of Th(IV), Ni(II)and Fe(II) from aqueous solutions by a novel PAN–TiO2 nanofiber adsorbent modified with aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Res Chem Intermed 42, 4055–4076 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2258-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2258-0