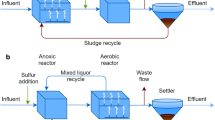
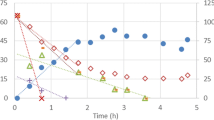
Abstract
Sulphide generated during anaerobic treatment of S-containing wastewaters represents an environmental problem. Adding limited amounts of oxygen or nitrate (or nitrite) to biologically (or chemically) oxidise sulphide forms a simple process-level strategy to control this problem. This short review evaluates the feasibility and limitations of this strategy on the basis of the results of bioreactor studies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akunna JC, Bizeau C, Moletta R (1992) Denitrification in anaerobic digesters: possibilities and influence of waste water COD/N-NOx ratio. Environ Technol 13(9):825–836
Annachhatre AP, Suktrakoolvait S (2001) Biological sulphide oxidation in a fluidized bed reactor. Environ Technol 22(6):661–672
Balderston WL, Payne WJ (1976) Inhibition of methanogenesis in salt marsh sediments and whole-cell suspensions of methanogenic bacteria by nitrogen oxides. Appl Environ Microbiol 32(2):264–269
Basu SK, Mino T (1993) Domestic waste-water treatment using microaerophilic upflow sludge bed reactor. Environ Technol 14(5):413–422
Basu SK, Mino T, Oleszkiewicz JA (1995) Novel application of sulphur metabolism in domestic wastewater treatment. Can J Civ Eng 22:1217–1223
Bentzen G, Smith AT, Bennett D, Webster NJ, Reinholt F, Sletholt E, Hobson J (1995) Controlled dosing of nitrate for prevention of H2S in a sewer network and the effects on the subsequent treatment processes. Water Sci Technol 31(7):293–302
Brüser T, Lens PNL, Trüper HG (2000) The biological sulphur cycle. In: Lens PNL, Hulshoff Pol LW (eds) Environmental technologies to treat sulfur pollution – principles and engineering. IWA Publishing, London, pp 47–85
Buisman CJN, Lettinga G (1990) Sulphide removal from anaerobic waste treatment of a paper mill. Water Res 24(3):313–319
Buisman CJN, Geraats BG, Ijspeert P, Lettinga G (1990) Optimization of sulphur production in a biotechnological sulphide-removing reactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:50–56
Burgess JE, Parsons SA, Stuetz RM (2001) Developments in odour control and waste gas treatment biotechnology: a review. Biotechnol Adv 19:35–63
Cardoso RB, Sierra-Alvarez R, Rowlette P, Razo-Flores E, Gómez J, Field JA (2006) Sulfide oxidation under chemolithoautotrophic denitrifying conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng 95(6):1148–1157
Chen KC, Lin YF (1993) The relationship between denitrifying bacteria and methanogenic bacteria in a mixed culture system of acclimated sludges. Water Res 27(12):1749–1759
Chuang SH, Pai TY, Horng RY (2005) Biotreatment of sulfate-rich wastewater in an anaerobic/micro-aerobic bioreactor system. Environ Technol 26(9):993–1001
Clancy PB, Venkataraman N, Lynd LR (1992) Biochemical inhibition of sulfate reduction in batch and continuous anaerobic digesters. Water Sci Technol 25(7):51–60
Daniels L, Belay N, Rajagopal BS (1986) Assimilatory reduction of sulfate and sulfite by methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:703–709
Dannenberg S, Kroder M, Dilling W, Cypionka H (1992) Oxidation of H2, organic compounds and inorganic sulfur compounds coupled to reduction of O2 or nitrate by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Arch Microbiol 158:93–99
Dewaters JE, Zander AK, Grimberg SJ (1999) The use of ferric salts for controlling sulfide odors in high-strength pulp and paper manufacturing wastes. Environ Eng Sci 16(6):441–450
Fox P, Venkatasubbiah V (1996) Couple anaerobic/aerobic treatment of high-sulfate wastewater with sulfate reduction and biological sulfide oxidation. Water Sci Technol 34(5–6):359–366
Gadekar S, Nemati M, Hill GA (2006) Batch and continuous biooxidation of sulphide by Thimicrospira sp. CVO: reaction kinetics and stoichiometry. Water Res 40(12):2436–2446
Garuti A, Giordano A, Pirozzi F (2001) Full-scale ANANOX® system performance. Water SA 27(2):189–198
Gommers PJF, Bijleveld W, Kuenen JG (1988) Simultaneous sulphide and acetate oxidation in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor-I start-up and reactor performance. Water Res 22(9):1075–1083
González-Sanchéz A, Revah S (2007) The effect of chemical oxidation on the biological sulfide oxidation by an alkaliphilic sulfoxidizing bacterial consortium. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:292–298
Hagen CE, Hartung RW (1997) New chemical treatment method controls wastewater system odor. Pulp Pap 71(11):81–89
Hanselmann KW (1991) Microbial energetics applied to waste repositories. Experientia 47:645–687
Hendriksen HV, Ahring BK (1996) Integrated removal of nitrate and carbon in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor: operating performance. Water Res 30(6):1451–1458
Hossain F (2004) Activated sludge bulking: a review of causes and control strategies. J Instn Engrs (India) 85:1–6
Hulshoff Pol LW, Lens PNL, Stams AJM, Lettinga G (1998) Anaerobic treatment of sulphate-rich wastewaters. Biodegradation 9:213–224
Im J-H, Woo H-J, Choi M-W, Han K-B, Kim C-W (2001) Simultaneous organic and nitrogen removal from municipal landfill leachate using an anaerobic-aerobic system. Water Res 35(10):2403–2410
Isa MH, Anderson GK (2005) Molybdate inhibition of sulphate reduction in two-phase anaerobic digestion. Process Biochem 40(6):2079–2089
Jacksonmoss CA, Duncan JR (1990) Anaerobic-digestion at high sulphate concentrations. J Am Leather Chem As 85(10):376–382
Janssen AJH, Sleyster R, van der Kaa C, Jochemsen A, Bontsema J, Lettinga G (1995) Biological sulphide oxidation in a fed-batch reactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 47:327–333
Janssen AJH, Meijer S, Bontsema J, Lettinga G (1998) Application of the redox potential for controlling a sulfide oxidizing bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 60(2):147–155
Jin P, Bhattacharya SK, Williams CJ, Zhang C (1998) Effects of sulphide addition on copper inhibition in methanogenic systems. Water Res 32(4):977–988
Kalyuzhnyi S, Gladchenko M, Mulder A, Versprille B (2006a) DEAMOX – new biological nitrogen removal process based on anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupled to sulphide-driven conversion of nitrate into nitrite. Water Res 40(19):3637–3645
Kalyuzhnyi S, Gladchenko M, Mulder A, Versprille B (2006b) DEAMOX – new anaerobic process of nitrogen removal. Water Sci Technol 54(8):163–170
Kalyuzhnyi S, Gladchenko M, Mulder A, Versprille B (2007) Comparison of quasisteady-state performance of the DEAMOX process under intermittent and continuous feeding and different nitrogen loading rates. Biotechnol J 2:894–900
Kaspar HF, Tiedje JM, Firestone RB (1981) Denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in digested sludge. Can J Microbiol 27(9):878–885
Kato MT, Field JA, Lettinga G (1993) High tolerance of methanogens in granular sludge to oxygen. Biotechnol Bioeng 42(11):1360–1366
Khanal SK, Huang JC (2003a) Anaerobic treatment of high sulfate wastewater with oxygenation to control sulfide toxicity. J Environ Eng 129(12):1104–1111
Khanal SK, Huang JC (2003b) ORP-based oxigenation for sulfide control in anaerobic treatment of high sulfate wastewater. Water Res 37:2053–2062
Khanal SK, Huang JC (2006) Online oxygen control for sulfide oxidation in anaerobic treatment of high-sulfate wastewater. Water Environ Res 78(4):397–308
Kleerebezem R, Mendez R (2002) Autotrophic denitrification for combined hydrogen sulfide removal from biogas and post-denitrification. Water Sci Technol 45(10):349–356
Koster IW, Rinzema A, de Vegt AL, Lettinga G (1986) Sulfide inhibition of the methanogenic activity of granular sludge at different pH levels. Water Res 21(12):1561–1567
Krishnakumar B, Manilal VB (1999) Bacterial oxidation of sulphide under denitrifying conditions. Biotechnol Lett 21(5):437–440
Lau GN, Sharma KR, Chen GH, van Loosdrecht MCM (2006) Integration of sulphate reduction, autotrophic denitrification and nitrification to achieve low-cost excess sludge minimisation for Hong Kong sewage. Water Sci Technol 53(3):227–325
Lens PNL, Visser ANL, Janssen AJH, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lettinga G (1998) Biotechnological treatment of sulfate-rich wastewaters. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 28(1):41–88
Lens PNL, Sipma J, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lettinga G (2000) Effect of nitrate on acetate degradation in a sulfidogenic staged reactor. Water Res 34(1):31–42
Little BJ, Ray RI, Pope RK (2000) Corrosion and sulfur bacteria. In: Lens PNL, Hulshoff Pol LW (eds) Environmental technologies to treat sulfur pollution – principles and engineering, 1st edn. IWA Publishing, London, pp 491–513
Mahmood Q, Zheng P, Cai J, Wu D, Hu B, Li J (2007) Anoxic sulphide biooxidation using nitrite as electron acceptor. J Hazard Mater (in press), corrected proof
Mathioudakis VL, Vaiopoulou E, Aivasidis A (2006) Addition of nitrate for odor control in sewer networks: laboratory and field experiments. Global NEST J 8(1):37–42
Noyola A, Morgan-Sagastume JM, López-Hernández JE (2006) Treatment of biogas produced in anaerobic reactors for domestic wastewater: odor control and energy/resource recovery. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 5(1):93–114
Núñez LA, Martínez B (2001) Evaluation of an anaerobic/aerobic system for carbon and nitrogen removal in slaughterhouse wastewater. Water Sci Technol 44(4):271–277
Ochi T, Kitagawa M, Tanaka S (1998) Controlling sulphide generation in force mains by air injection. Water Sci Technol 37(1):87–95
O’Reilly C, Colleran E (2005) Toxicity of nitrite toward mesophilic and thermophilic sulphate-reducing, methanogenic and syntrophic populations in anaerobic sludge. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 32(2):46–52
Oude Elferink SJWH, Visser A, Hulshoff Pol LW, Stams AJM (1994) Sulfate reduction in methanogenic bioreactors. FEMS Microbiol Rev 15:119–136
Peddie CC, Maviniv DS, Jenkins DJ (1990) Use of ORP for monitoring and control of aerobic sludge digestion. J Environ Eng 116(3):461–471
Percheron G, Michaud S, Bernet N, Moletta R (1998) Nitrate and nitrite reduction of a sulphide-rich environment. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 72:213–220
Pott BM, Mattiasson B (2004) Separation of heavy metals from water solutions at the laboratory scale. Biotechnol Lett 26(5):451–456
Reyes-Avila J, Razo-Flores E, Gomez J (2004) Simultaneous biological removal of nitrogen, carbon and sulfur by denitrification. Water Res 38(14–15):3313–3321
Rinzema A (1988) Anaerobic treatment of wastewater with high concentrations of lipid or sulphate. PhD thesis, Wageningen Agricultural University, the Netherlands
Rittmann BE, McCarty PL (eds) (2000) Environmental biotechnology principles and application. McGraw-Hill Companies Inc., New York, pp 340–347
Roy R, Conrad R (1999) Effect of methanogenic precursors (acetate, hydrogen, propionate) on the suppression of methane production by nitrate in anoxic rice field soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 28(1):49–61
Sierra-Alvarez R, Guerrero F, Rowlette P, Freeman S, Field JA (2005) Comparison of chemo-, hetero- and mixotrophic denitrification in laboratory-scale UASBs. Water Sci Technol 52(1–2):337–342
Shin HS, Jung JY, Bae BU, Paik BC (1995) Phase-separated anaerobic toxicity assays for sulfate and sulfide. Water Environ Res 67:802–806
Smet E, Lens P, Van Langenhove H (1998) Treatment of waste gases contaminated with odorous sulfur compounds. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 28(1):89–117
Steudel R (1996) Mechanism for the formation of elemental sulfur from aqueous sulfide in chemical and microbiological desulfurization processes. Ind Eng Chem Res 35:1417–1423
Tai CS, Singh KS, Grant SR (2006) Combined removal of carbon and nitrogen in an integrated UASB-jet loop reactor bioreactor system. J Environ Eng 132(6):624–637
Tanimoto Y, Tasaki M, Okamura K, Yamaguchi M, Minami K (1989) Screening growth inhibitors of sulfate-reducing bacteria and their effects on methane fermentation. J Ferment Bioeng 68(5):353–359
Tilche A, Bortone G, Forner G, Indulti M, Stante L, Tesini O (1994) Combination of anaerobic digestion and denitrification in a hybrid upflow anaerobic filter integrated in a nutrient removal treatment plant. Water Sci Technol 30(12):405–414
Tugtas AE, Pavlostathis SG (2007) Inhibitory effects of nitrogen oxides on a mixed methanogenic culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 96(3):444–455
Tursman JF, Cork DJ (1989) Influence of sulphate and sulfite-reducing bacteria on anaerobic digestion technology. In: Biological waste treatment. Alan R Liss Inc., New York, pp 273–281
Vaiopoulou E, Melidis P, Aivasidis A (2005) Sulphide removal in wastewater from petrochemical industries by autotrophic denitrification. Water Res 39(17):4101–4109
van der Zee FP, Villaverde S, Garcia PA, Fdz-Polanco F (2007) Sulfide removal by moderate oxygenation of anaerobic sludge environments. Bioresour Technol 98:518–524
Van Haandel AC, Monroy O, Celis B, Rustrian E, Cervantes FJ (2006) Principles and process design for industrial wastewater treatment systems. In: Cervantes FJ, Pavlostathis SG, van Haandel AC (eds) Advanced biological treatment processes for industrial wastewaters – principles and applications. IWA Publishing, London, pp 118–132
Visser A, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lettinga G (1996) Competition of methanogenic and sulfidogenic bacteria. Water Sci Technol 33(3):99–110
Wang Z, Banks CJ (2006) Anaerobic digestion of a sulphate-rich high-strength landfill leachate: the effect of differential dosing with FeCl3. Waste Manag Res 24:289–293
Wellinger A, Lindeberg A (eds) (1999) Biogas upgrading and utilization. Task 24: energy from biological conversion of organic wastes. IEA Bioenergy, Winterthur, pp 1–19
Yadav VK, Archer DB (1989) Sodium molybdate inhibits sulphate reduction in the anaerobic treatment of high-sulphate molasses wastewater. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31(1):103–106
Zhang D, Verstraete W (2001) The anaerobic treatment of nitrite containing wastewater using an expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactor. Environ Technol 22(8):905–913
Zhou W, Imai T, Ukita M, Li F, Yuasa A (2007) Effect of limited aeration on the anaerobic treatment of evaporator condensate from a sulfite pulp mill. Chemosphere 66:924–929
Zitomer DH, Shrout JD (2000) High-sulfate, high-chemical oxygen demand wastewater treatment using aerated methanogenic fluidised beds. Water Environ Res 72(1):90–97
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science (project CTM 2005-02967/TECNO) for financial support and P. Wheeler, AEA Technology Environment, A. Wellinger, Nova Energie, O. Jönsson, The Swedish Gas Centre and T. Al Seadi, University of Southern Denmark, for their help with the implementation in practice of micro-aerobic conditions in anaerobic bioreactors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cirne, D.G., van der Zee, F.P., Fernandez-Polanco, M. et al. Control of sulphide during anaerobic treatment of S-containing wastewaters by adding limited amounts of oxygen or nitrate. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7, 93–105 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-008-9128-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-008-9128-9