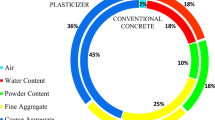
Results are provided for a study of the properties of SiC refined by different methods (milling and disintegration) on morphology of the particles obtained. It is established that SiC refinement by disintegration in an amount of 10 – 20% within the composition of heat-resistant concrete compared with a similar amount of milled SiC improves concrete mechanical properties after hardening and firing from 11 to 23%, reduces its shrinkage by up to 25%, and improves thermal shock resistance by up to 20%.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. P. Luz, M. Huger, and V. C. Pandolfelli, “Hot elastic modulus of Al2O3–SiC–SiO2–C castables,” Ceram. Internat., 37, 2335 – 2345 (2011).
S. Goberis, I. Pundene, V. Antonovich, and R. Stonis,”Physicomechanical properties of medium-cement refractory castables containing chamotte-silicon carbide fillers tested for practical applications,” Refract. Indust. Ceram., 46(5), 333 – 337 (2005).
V. A. Kamenskikh, I. D. Kashcheev, N. A. Mityushov, et al., “Silicon carbide refractory castables,” Refract. Indust. Ceram., 46(6), 333 – 337 (2005).
C. Durmus, R. Mingu, and S. Ozgen, “ Evaluation of SiC additives in alumina based castable refractories,” Conference on Refractory Castables, Praha, 23 – 24 November (2001).
M. H. Amin, M. A. Ebrahimabadi, and M. R. Rahimipour, “The effect of nanosized carbon black on the physical and thermomechanical properties of Al2O3–SiC–SiO2–C composite,” J. Nanomaterials — Special issue on nanocomposites for engineering applications, 2009, 1 – 5 (2009).
A. P. Luz, F. A. O. Valenzuela, V. G. Domiciano, et al., “Thermo-mechanical-chemical characterization of high-carbon-containing refractory castables,” J. Technical Association of Refractories, Japan. 29(2), 3 – 7 (2009).
A. M. Hundere, B. Myhre, B. Sandberg, et al.], “Norway castables for kiln furniture,” Proc. of 3rd International Symposium on Refractories (1998).
O. Bahloul, T. Chotard, M. Huger, et al., “Young’s modulus evolution at high temperature of SiC refractory castables,” J. Mater. Sci., 45, 3652 – 3660 (2010).
E. Karamian and A. Monshi, “Influence of additives on nano-SiC whisker formation in alumina silicate–SiC–C monolithic refractories,” Ceram. Internat., 36, 811 – 816 (2010).
A. Shishkin, A. Korjakins, and V. Mironovs, “Using of cavitation disperser, for porous ceramic and concrete material preparation,” World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Environmental, Chemical, Ecological, Geological and Geophysical Engineering, 9(5), 540 – 543 (2015).
P. Peetsalu, D. Goljandin, P. Kulu, et al., “Micropowders produced by disintegrator milling,” Powder Metall., 3, 99 – 110 (2003).
Alcoa Calcium Aluminate Cement test Methods Brochure. Revision 5. Frankfurt: Available through Alcoa Industrial Chemicals (1999).
V. Antonovich, M. Shyukshta, I. Pundene, and R. Stonis, “Procedural elements in estimation of the thermal shock resistance of different types of refractory concrete based on chamotte filler,” Refract. Indust. Ceram., 52(1), 70 – 74 (2011).
S. Otroj, M. A. Bahrevar, F. Mostarzadeh, et al., “The effect of deflocculants on the self-flow characteristics of ultra-low-cement castables in Al2O3–SiC–C system,” Ceram. Internat., 31, 647 – 653 (2005).
S. P. Mehrotra, T. C. Alex, G. Greifzu, et al., “Mechanical activation of gibbsite and boehmite: new findings and their implications,” Trans. Indian Institute of Metals, 69(1), 51 – 59 (2016).
K. Terada and E. Yonemochi, “Physicochemical properties and surface free energy of ground talc,” Solid State Ionics, 172, 459 – 462 (2004).
J. Cao, Y. Fang, R. Fan, et al., “Influence of mechanochemical effect on physical properties of boiler bottom slag,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 23(4), 111 – 114 (2015).
G. Bumanis and D. Bajarea, “Compressive strength of cement mortar affected by sand microfiller obtained with collision milling in disintegrator,” Procedia Engineering, 172, 149 – 156 (2017).
V. N. Sokov and V. V. Sokov, “High temperature heat insulation of a new generation,” Industrial heat insulation. Use and production: Sci.-Tech. Conf., Moscow (2004), OAO Teploproekt (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Novye Ogneupory, No. 3, pp. 50 – 56, March, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pundiene, I., Prantskevichene, I. & Kairite, A. Effect of SiC-Filler Refinement by Different Methods on Heat-Resistant Medium-Cement Concrete Properties. Refract Ind Ceram 59, 156–162 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11148-018-0198-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11148-018-0198-0