Abstract
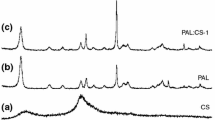
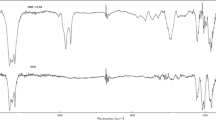
Clays are widely used in controlled drug delivery systems due to their strong adsorption properties and natural origin. In this study, a drug carrier was prepared using chitosan, a natural polymer, mixed with bentonite clay. Then, poly(acrylic acid) was added to improve its swelling properties. Pantoprazole was chosen as the model drug. The swelling properties of the prepared samples were investigated at two different temperatures: 25 and 37 °C. The prepared samples were examined by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The controlled release of the pantoprazole from the drug carriers indicated that the release of the pantoprazole is temperature-sensitive. In order to study the effect of bentonite on the drug carrier system, drug release was also investigated in the samples without adding clay. It was observed that the drug release profiles of the prepared sample containing bentonite fitted better than the sample without clay. The release kinetics analysis showed that the first-order and the Korsmeyer-Peppas models fit the best, and that pantoprazole was transported via Fickian diffusion. The prepared samples showed the capability of pantoprazole loading and, thus, its possibility to be used in drug delivery systems.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao Y, Zhou Y, Liu L et al (2020) Nanoparticle-based drug delivery in cancer therapy and its role in overcoming drug resistance. Front Mol Biosci 7:193. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMOLB.2020.00193/BIBTEX
Meyler’s side effects of drugs - 16th Edition. https://www.elsevier.com/books/meylers-side-effects-of-drugs/aronson/978-0-444-53717-1. Accessed 6 Dec 2021
Giacomini KM, Krauss RM, Roden DM et al (2007) When good drugs go bad. Nat. https://doi.org/10.1038/446975a
Odiba A, Ukegbu C, Anunobi O et al (2016) Making drugs safer: Improving drug delivery and reducing the side effect of drugs on the human biochemical system. Nanotechnol Rev 5:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1515/NTREV-2015-0055/MACHINEREADABLECITATION/RIS
Tryfonidou MA, de Vries G, Hennink WE, Creemers LB (2020) “Old Drugs, New Tricks”—Local controlled drug release systems for treatment of degenerative joint disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 160:170–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ADDR.2020.10.012
Li R, Peng F, Cai J et al (2020) Redox dual-stimuli responsive drug delivery systems for improving tumor-targeting ability and reducing adverse side effects. Asian J Pharm Sci 15:311–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AJPS.2019.06.003
Rohani Shirvan A, Bashari A, Hemmatinejad N (2019) New insight into the fabrication of smart mucoadhesive buccal patches as a novel controlled-drug delivery system. Eur Polym J 119:541–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURPOLYMJ.2019.07.010
Qiu M, Wang D, Liang W et al (2018) Novel concept of the smart NIR-light-controlled drug release of black phosphorus nanostructure for cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:501–506. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.1714421115/-/DCSUPPLEMENTAL
Wu X, Liu J, Yang L, Wang F (2019) Photothermally controlled drug release system with high dose loading for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy of multidrug resistance cancer. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 175:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFB.2018.11.088
Aroguz AZ, Baysal K, Tasdelen B, Baysal BM (2011) Preparation, characterization, and swelling and drug release properties of a crosslinked chitosan-polycaprolactone gel. J Appl Polym Sci 119:2885–2894. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.33074
Gref R, Domb A, Quellec P et al (1995) The controlled intravenous delivery of drugs using PEG-coated sterically stabilized nanospheres. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 16:215–233
Heng PWS (2018) Controlled release drug delivery systems. Pharm Dev Technol 23:833
Kumar R, Mondal K, Panda PK et al (2020) Core-shell nanostructures: perspectives towards drug delivery applications. J Mater Chem B 8:8992–9027
Amiri M, Khazaeli P, Salehabadi A, Salavati-Niasari M (2021) Hydrogel beads-based nanocomposites in novel drug delivery platforms: recent trends and developments. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 288:102316
Mottaghitalab F, Farokhi M, Shokrgozar MA et al (2015) Silk fibroin nanoparticle as a novel drug delivery system. J Control Release 206:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCONREL.2015.03.020
Chou SF, Carson D, Woodrow KA (2015) Current strategies for sustaining drug release from electrospun nanofibers. J Control Release 220:584–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCONREL.2015.09.008
Wu J, Zhang Z, Gu J et al (2020) Mechanism of a long-term controlled drug release system based on simple blended electrospun fibers. J Control Release 320:337–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCONREL.2020.01.020
Mehraz L, Nouri M, Namazi H (2018) Electrospun silk fibroin/β-cyclodextrin citrate nanofibers as a novel biomaterial for application in controlled drug release. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 69:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2018.1552865
Goyanes A, Wang J, Buanz A et al (2015) 3D Printing of medicines: engineering novel oral devices with unique design and drug release characteristics. Mol Pharm 12:4077–4084. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.MOLPHARMACEUT.5B00510
Kyobula M, Adedeji A, Alexander MR et al (2017) 3D inkjet printing of tablets exploiting bespoke complex geometries for controlled and tuneable drug release. J Control Release 261:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCONREL.2017.06.025
Saadeh Y, Vyas D (2014) Nanorobotic applications in medicine: current proposals and designs. Am J Robot Surg 1:4–11. https://doi.org/10.1166/AJRS.2014.1010
Hu M, Ge X, Chen X et al (2020) Micro/nanorobot: a promising targeted drug delivery system. Pharmaceutics 12:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/PHARMACEUTICS12070665
Pan X, Veroniaina H, Su N et al (2021) Applications and developments of gene therapy drug delivery systems for genetic diseases. Asian J Pharm Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AJPS.2021.05.003
Sung YK, Kim SW (2019) Recent advances in the development of gene delivery systems. Biomater Res 231(23):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/S40824-019-0156-Z
Tewabe A, Abate A, Tamrie M et al (2021) Targeted drug delivery; from magic bullet to nanomedicine: principles, challenges, and future perspectives. J Multidiscip Healthc 14:1711–1724. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S313968
Benhabbour SR, Kovarova M, Jones C et al (2019) Ultra-long-acting tunable biodegradable and removable controlled release implants for drug delivery. Nat Commun 101(10):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12141-5
Gomes CSF, Rautureau M, Gomes JHC, Silva EAF (2021) Interactions of clay and clay minerals with the human health. Miner latu sensu Hum Heal. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65706-2_7
Nizam El-Din HM, Ibraheim DM (2021) Biological applications of nanocomposite hydrogels prepared by gamma-radiation copolymerization of acrylic acid (AAc) onto plasticized starch (PLST)/montmorillonite clay (MMT)/chitosan (CS) blends. Int J Biol Macromol 192:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2021.09.196
Selvasudha N, Dhanalekshmi U-M, Krishnaraj S et al (2020) Multifunctional clay in pharmaceuticals. Clay Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.5772/INTECHOPEN.92408
García-Villén F, Carazo E, Borrego-Sánchez A, et al (2019) Clay minerals in drug delivery systems. In: Modified Clay and Zeolite Nanocomposite Materials. Elsevier, pp 129–166
Ghadiri M, Chrzanowski W, Rohanizadeh R (2015) Biomedical applications of cationic clay minerals. RSC Adv 5:29467–29481. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA16945J
Kaplan Can H, Şahin Ö (2015) Design, Synthesis and Characterization of 3,4-Dihydro-2H-pyran containing copolymer/clay nanocomposites. 52:465–475. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2015.1029372
Zhao D, Yu S, Sun B et al (2018) Biomedical applications of chitosan and its derivative nanoparticles. Polym 10:462. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM10040462
Lin KF, Hsu CY, Huang TS et al (2005) A novel method to prepare chitosan/montmorillonite nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 98:2042–2047. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.22401
Qian L (2018) Cellulose-based composite hydrogels: preparation, structures, and applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-76573-0_23-1
Aguzzi C, Cerezo P, Viseras C, Caramella C (2007) Use of clays as drug delivery systems: possibilities and limitations. Appl Clay Sci 36:22–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2006.06.015
Surya R, Mullassery MD, Fernandez NB, Thomas D (2019) Synthesis and characterization of a clay-alginate nanocomposite for the controlled release of 5-Flurouracil. J Sci Adv Mater Devices 4:432–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2019.08.001
Wang Y, Wang J, Yuan Z et al (2017) Chitosan cross-linked poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels: drug release control and mechanism. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 152:252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFB.2017.01.008
Bashir S, Teo YY, Ramesh S et al (2018) Rheological behavior of biodegradable N-succinyl chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid) hydrogels and their applications as drug carrier and in vitro theophylline release. Int J Biol Macromol 117:454–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2018.05.182
Aroğuz AZ, Teofilovic V, Budinski-Simendic JCH (2017) Highly swollen composite hydrogel for investigation of pantoprazole release profile. In: IUPAC-FAPS 2017. p 118
Aguilera-Castro L, Martín-de-Argila-dePrados C, Albillos-Martínez A (2016) Practical considerations in the management of proton-pump inhibitors. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 108:145–153
Teofilović V, Pavličević J, Erceg T et al (2021) Modification of Tokat Resadiye Bentonite with Cationic Surfactant. In: Čupić Ž (ed) Physical Chemistry 2021. The Society of Physical Chemists of Serbia, Belgrade, pp 489–491
Pentrák M, Hronský V, Pálková H et al (2018) Alteration of fine fraction of bentonite from Kopernica (Slovakia) under acid treatment: a combined XRD, FTIR, MAS NMR and AES study. Appl Clay Sci 163:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLAY.2018.07.028
Timofeeva MN, Panchenko VN, Krupskaya VV et al (2017) Effect of nitric acid modification of montmorillonite clay on synthesis of solketal from glycerol and acetone. Catal Commun 90:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATCOM.2016.11.020
Korsmeyer RW, Gurny R, Doelker E et al (1983) Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int J Pharm 15:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(83)90064-9
Peppas NA (1985) Analysis of Fickian and non-Fickian drug release from polymers. Pharm Acta Helv 60:110–111
Shaikh HK, Kshirsagar RV, Patil SG (2015) Mathematical models for drug release characterization: a review. Shaikh al World J Pharm Res 4:324
Mahdavinia GR, Pourjavadi A, Hosseinzadeh H, Zohuriaan MJ (2004) Modified chitosan 4. Superabsorbent hydrogels from poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) grafted chitosan with salt- and pH-responsiveness properties. Eur Polym J 40:1399–1407. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURPOLYMJ.2004.01.039
Lente G (2015) Deterministic Kinetics in Chemistry and Systems Biology. Springer International Publishing, Cham
D’Ottone L, Ochonogor EC (2017) Error analysis of absolute rate coefficient extrapolated under pseudo-first order conditions. J Turkish Chem Soc Sect A Chem 5:29–40
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Fund of the Istanbul University-Cerrahpaşa. Project code: BAP-22775, and by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (Grant no. 451-03-9/2021-14/200134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design, material preparation, data collection, and analysis. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AZ Aroguz and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teofilović, V., Agan, B., Pavličević, J. et al. Synthesis, characterization and kinetics of sustained pantoprazole release studies of interpenetrated poly(acrylic acid)-chitosan-bentonite hydrogels for drug delivery systems. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 135, 1423–1437 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02209-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02209-7