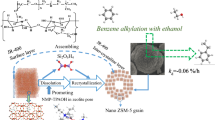
Abstract
Nanoscale polymer spherical and hollow structure HZSM-5 zeolites are prepared by hydrothermal and desilication–recrystallization methods. In addition, the crystallite size of two types of HZSM-5 can be easily controlled by changing H2O/Si mole ratio. The hollow structure HZSM-5 zeolite is formed, it is due to the 010 crystal plane is the most energetically favorable orientation in silicalite-1 and the Si species is first removed on this crystal plane. The properties of different morphology zeolites were characterized by means of XRD, SEM, TEM, NH3-TPD, N2 isothermal adsorption–desorption and TG, and the catalytic performance of these two types of HZSM-5 in MTA reaction was investigated in a fixed-bed differential reactor. The results showed that the multilevel pore structure and suitable acid strength and more acid density were obtained in the hollow structure HZSM-5 zeolite. Therefore, the hollow HZSM-5 zeolite exhibited that higher catalytic lifetime and selectivity of aromatics than nanoscale polymer spherical HZSM-5 zeolite in MTA reaction. Furthermore, the Al distribution on the 010 crystal plane may change slightly during the process of fabricating hollow mesoporous, which leads to higher selectivity of p-xylene over hollow HZSM-5 than nanoscale polymer spherical HZSM-5 zeolite.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi Y, Wang YL, Chen X et al (2014) Methanol aromatization over HZSM-5 catalysts modified with different zinc salts. Chin J Catal 35:1740–1751
Zhang N, Xu YR, Xu XL et al (2015) Study on the reaction conditions of methanol to aromatics over Zn/HZSM-5 catalyst. Nat Gas Chem 40:5–9
Pinilla-Herrero I, Borfecchia E, Holzinger J et al (2018) High Zn/Al ratios enhance dehydrogenation vs hydrogen transfer reactions of Zn-ZSM-5 catalytic systems in methanol conversion to aromatics. J Catal 362:146–163
Wang N, Qian WZ, Shen K et al (2016) Bayberry-like ZnO/MFI zeolite as high performance methanol-to-aromatics catalyst. Chem Commun 52:2011–2014
Zaidi HK, Pant KK (2004) Catalytic conversion of methanol to gasoline rang hydrocarbons. Catal Today 96:155–160
Baozhai H, Yang Y, Xu YY et al (2016) A review of the direct oxidation of methane to methanol. Chin J Catal 37:1206–1215
Xin AH, Sun Q (2013) Development progress of methanol to aromatics catalysts. Mod Chem Ind 33(29–32):34
Shen K, Wang N, Qian W et al (2014) Atmospheric pressure synthesis of nanosized ZSM-5 with enhanced catalytic performance for methanol to aromatics reaction. Catal Sci Technol 4:3840–3844
Li J, Liu S, Zhang H et al (2016) Synthesis and characterization of an unusual snowflake-shaped ZSM-5 zeolite with high catalytic performance in the methanol to olefin reaction. Chin J Catal 37:308–315
Wang XX, Zhang T, Zhang JF et al (2014) Synthesis of mesoporous HZnZSM-5 zeolite and its catalytic performance in methanol aromatization. Acta Pet Sin (Pet Process Sect) 30:336–342
Barber K, Bonino F, Bordiga S et al (2011) Structure–deactivation relationship for ZSM-5 catalysts governed by framework defects. J Catal 280:196–205
Wang L, Xu LX, Li J et al (2018) Studies on micro-bimodal mesoporous core-shell HZSM-5@BMMs catalyst for methanol to aromatics. Fine Chem 35:1562–1566
Wang Y, Tan L, Tan M et al (2019) Rationally designing bifunctional catalysts as an efficient strategy to boost CO2 hydrogenation producing value-added aromatics. ACS Catal 9:895–901
Hermann C, Hass J, Etting FF (1987) Effect of the crystal size on the activity of ZSM-5 catalysts in various reaction. Appl Catal A Gen 35:299–310
Wei Z, Xia T, Liu M et al (2015) Alkaline modification of ZSM-5 catalysts for methanol aromatization: the effect of the alkaline concentration. Front Chem Sci Eng 9:450–460
Bjørgen M, Joensen F, Holm MS et al (2008) Methanol to gasoline over zeolite H-ZSM-5: improved catalyst performance by treatment with NaOH. Appl Catal A Gen 345:43–50
Groen JC, Peffer LAA, Moulijn JA et al (2004) Mesoporosity development in ZSM-5 zeolite upon optimized desilication conditions in alkaline medium. Colloids Surf A 241:53–58
Groen JC, Bach T, Ziese U et al (2005) Creation of hollow zeolite architectures by controlled desilication of Al-zoned ZSM-5 crystals. J Am Chem Soc 127:10792–10793
Dai C, Zhang A, Li L et al (2013) Synthesis of hollow nanocubes and macroporous monoliths of silicalite-1 by alkaline treatment. Chem Mater 25:4197–4205
Shan ZC, Meng XJ, Liu SY et al (2011) Designed synthesis of TS-1 crystals with controllable b-oriented length. Chem Commun 47:1048–1050
Ma Z, Fu TJ, Wang YJ et al (2019) Silicalite-1 derivational desilication–recrystallization to prepare hollow nano-ZSM-5 and highly mesoporous micro-ZSM-5 catalyst for methanol to hydrocarbons. Ind Eng Chem Res 58(6):2146–2158
Persson AE, Schoeman BJ, Sterte J et al (1994) The synthesis of discrete colloidal particles of TPA-silicalite-1. Zeolite 14:557–567
Pérez-Ramírez J, Verboekend D, Bonilla A et al (2009) Zeolite catalysts with tunable hierarchy factor by pore-growth moderators. Adv Funct Mater 19:3972–3979
Abelló S, Bonilla A, Pérez-Ramírez J (2009) Mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts prepared by desilication with organic hydroxides and comparison with NaOH leaching. Appl Catal A Gen 364:191–198
Fojtíková PP, Mintova S, Zukal A et al (2006) Porosity of micro/mesoporous composites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 92:154–160
Viswanadham N, Kamble R, Singh M et al (2009) Catalytic properties of nano-sized ZSM-5 aggregates. Catal Today 141:182–186
Song W, Justice RE, Jones CA et al (2004) Size-dependent properties of nanocrystalline silicalite synthesized with systematically varied crystal sizes. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 20:4696–4702
Kang QQ (2018) Study on synthesis and modification of SAPO-34 and catalytic performance of butene cracking. https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:HXGJ.0.2018-04-008
Topsoe NJ, Pedersen K, Derouane EG (1981) Infrared and temperature-programmed desorption study of acidic properties of ZSM-5-type zeolites. J Catal 70:41–42
Gao Y, Zheng BH, Wu G et al (2016) Effect of the Si/Al ratio on the performance of hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites for methanol aromatization. RSC Adv 6:83581–83599
Nawaz Z, Tang XP, Zhang Q et al (2009) SAPO-34 supported Pt-Sn-based novel catalyst for propane dehydrogenation to propylene. Catal Commu 10:1925–1930
Dang S, Li SG, Yang CG et al (2019) Selective transformation of CO2 and H2 into lower olefins over In2O3-ZnZrOx/SAPO-34 bifunctional catalysts. ChemSusChem 12:3582–3591
Drago RS, Webster CE, Mcgilvray JM et al (1998) A multiple-process equilibrium analysis of silica gel and HZSM-5. J Am Chem Soc 120:538–547
Jung JS, Won Park J, Seo G (2005) Catalytic cracking of n-octane over alkali-treated MFI zeolites. Appl Catal A Gen 288:149–157
He Y, Liu M, Dai C et al (2013) Modification of nanocrystalline HZSM-5 zeolite with tetrapropylammonium hydroxide and its catalytic performance in methanol to gasoline reaction. Chin J Catal 34:1148–1158
Lin X, Fan Y, Liu Z et al (2007) A novel method for enhancing on-stream stability of fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) gasoline hydro-upgrading catalyst: post-treatment of HZSM-5 zeolite by combined steaming and citric acid leaching. Catal Today 125:185–191
Groen JC, Peffer LAA, Moulijin JA et al (2004) Mesoporosity development in ZSM-5 zeolite upon optimized desilication conditions in alkaline medium. Colloids Surf A 241:53–58
Miyake K, Hirota Y, Ono K et al (2016) Direct and selective conversion of methanol to para-xylene over Zn ion doped ZSM-5/silicalite-1 core-shell zeolite catalyst. J Catal 342:63–66
Zhang J, Qian W, Kong C et al (2015) Increasing para-xylene selectivity in making aromatics from methanol with a surface-modified Zn/P/ZSM-5 catalyst. ACS Catal 5:2982–2988
Bleken FL, Janssens TVW, Svelle S et al (2012) Product yield in methanol conversion over ZSM-5 is predominantly independent of coke content. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 164:190–198
Pérez-Ramírez J, Christensen CH, Egeblad D et al (2008) Hierarchical zeolites: enhanced utilisation of microporous crystals in catalysis by advances in materials design. Chem Soc Rev 37(11):2530–2542
Hu Z, Zhang H, Wang L et al (2014) Highly stable boron-modified hierarchical nanocrystalline ZSM-5 zeolite for the methanol to propylene reaction. Catal Sci Technol 4:2891–2895
Zhang H, Ma Y, Song K et al (2013) Nano-crystallite oriented self-assembled ZSM-5 zeolite and its LDPE cracking properties: effects of accessibility and strength of acid sites. J catal 302:115–125
Kim J, Choi M, Ryoo R (2010) Effect of mesoporosity against the deactivation of MFI zeolite catalyst during the methanol-to-hydrocarbon conversion process. J Catal 269:219–228
Kunieda T, Kim JH, Niwa M (1999) Source of selectivity of p-xylene formation in the toluene disproportionation over HZSM-5 zeolites. J Catal 188:431–433
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Youth Science and Technology Foundation of Gansu Province (20JR10RA107) and the Youth Teacher Research Group Foundation of Northwest Normal University (NWNU-LKQN-18-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Tian, H., Jiao, J. et al. Performance of HZSM-5 prepared by different methods for methanol to aromatics. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 133, 1045–1060 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02041-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02041-5