Abstract
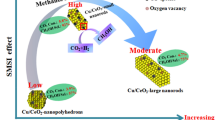
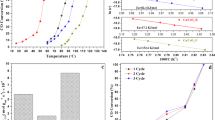
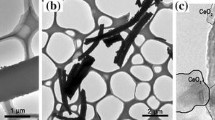
Cu loaded on different morphologies of CeO2 were synthesized and tested by SEM and CO catalytic oxidation experiment, the results indicated that with the same Cu load, nanorod-like Cu/CeO2 performed the best catalytic activity than 3D flower-like Cu/CeO2 and gear-like Cu/CeO2. Then nanorod-like Cu/CeO2 were chose to explore the best Cu load on CeO2 nanorods for CO oxidation. Cu/CeO2 nanorods were characterized by TEM, XRD, XPS as well as physical and chemical adsorption. The results indicate that 0.15Cu/CeO2 nanorods have the best catalytic activity because of more reducing copper species (Cu+), adsorbed oxygen (Oads) and Ce3+ species on the catalysts surface, which can achieve 99% CO conversion at 100 °C. The effect of CO2 and water vapor on catalytic activity was also examined.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebenstein A, Fan M, Greenstone M, He G, Zhou M (2017) New evidence on the impact of sustained exposure to air pollution on life expectancy from China's Huai River Policy. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114:10384–10389
Sandilands EA, Bateman DN (2016) Carbon monoxide. Medicine 44:151–152
Guo M, Lu J, Wu Y, Wang Y, Luo M (2011) UV and visible Raman studies of oxygen vacancies in rare-earth-doped ceria. Langmuir 27:3872–3877
Zhang J, Yang H, Wang S, Liu W, Liu X, Guo J, Yang Y (2014) Mesoporous CeO2 nanoparticle sassembled by hollow nanostructures: formation mechanism and enhanced catalytic properties. Cryst Eng Comm 16:8777–8785
Haruta M, Yamada N, Kobayashi T, Iijima S (1989) Gold catalysts prepared by coprecipitation for low-temperature oxidation of hydrogen and of carbon monoxide. J Catal 115:301–309
Newton MA, Ferri D, Smolentsev G, Marchionni V, Nachtegaal M (2016) Room-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide by oxygen over Pt/Al2O3 using combined, time-resolved XAFS, DRIFTS, and mass spectrometry. J Am Chem Soc 138:13930–13940
Campbell CT, Peden CHF (2005) Oxygen vacancies and catalysis on ceria surfaces. Science 309:713–714
Li Z, Han F, Li C, Jiao X, Chen D (2016) Hollow CeO2 dodecahedrons: one-step template synthesis and enhanced catalytic performance. RSC Adv 6:60975–60982
Qu Z, Yu F, Zhang X, Wang Y, Gao J (2013) Support effects on the structure and catalytic activity of mesoporous Ag/CeO2 catalysts for CO oxidation. Chem Eng J 229:522–532
Bao H, Zhang Z, Hua Q, Huang W (2014) Compositions, structures, and catalytic activities of CeO2@Cu2O nanocomposites prepared by the template-assisted method. Langmuir 30:6427–6436
Zou W, Ge C, Lu M, Wu S, Wang Y, Sun J, Pu Y, Tang C, Gao F, Dong L (2015) Engineering the NiO/CeO2 interface to enhance the catalytic performance for CO oxidation. RSC Adv 5:98335–98343
Hossain ST, Azeeva E, Zhang K, Zell ET, Bernard DT, Balaz S, Wang R (2018) A comparative study of CO oxidation over Cu-O-Ce solid solution and CuO/CeO2 nanorods catalysts. Appl Surf Sci 455:132–143
Lykaki M, Pachatouridou E, Carabineiro SAC, Iliopoulou E, Andriopoulou C, Kallithrakas-Kontos N, Boghosian S, Konsolakis M (2018) Ceria nanoparticles shape effects on the structural defects and surface chemistry: implications in CO oxidation by Cu/CeO2 catalysts. Appl Catal B 230:18–28
Jampaiah D, Venkataswamy P, Coyle VE, Reddy BM, Bhargava SK (2016) Low-temperature CO oxidation over manganese, cobalt, and nickel doped CeO2 nanorods. RSC Adv 6:80541–80548
Chen XY, Wu CL, Guo ZZ (2019) Synthesis of efficient Cu/CoFe2O4 catalysts for low temperature CO oxidation. Catal Lett 149:399–409
Si R, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M (2008) Shape and crystal-plane effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au-CeO2 catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:2884
Zhong LS, Hu JS, Cao AM, Liu Q, Song WG, Wan LJ (2007) 3D flowerlike ceria micro/nanocomposite structure and its application for water treatment and CO removal. Chem Mater 19:1648–1655
Zhang C, Meng F, Wang L, Zhang M, Ding Z (2014) Morphology-selective synthesis method of gear-like CeO2 microstructures and their optical properties. Mater Lett 130:202–205
Trovarelli A (1996) Catalytic properties of ceria and CeO2-containing materials. Catal Rev Sci Eng 38:439–520
Gong X, Liu B, Kang B, Xu G, Wang Q, Jia C, Zhang J (2017) Microwave enhanced catalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution over CuO/CeO2 catalyst in the absence and presence of H2O2. Mol Catal 436:90–99
Alla SK, Kollu P, Mandal RK, Prasad NK (2018) Formation of uniform CuO nanorods by spontaneous aggregation: selective synthesis of CuO, Cu2O and Cu nanoparticles by a solid-liquid phase arc discharge process. Ceram Int 44:7221–7227
Xu D, Cheng F, Lu Q, Dai P (2014) Nanoshaped CuO/CeO2 materials: effect of the exposed ceria surfaces on catalytic activity in N2O decomposition reaction. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:2625–2632
Yao WT, Yu SH, Zhou Y, Jiang J, Wu QS, Zhang L, Jiang J (2005) Boosting Cu-Ce interaction in CuxO/CeO2 nanocube catalysts for enhanced catalytic performance of preferential oxidation of CO in H2-rich gases. J Phys Chem B 109:14011–14016
Zabilskiy M, Djinović P, Tchernychova E, Tkachenko OP, Kustov LM, Pintar A (2015) Magnetic properties of Cu doped CeO2 nanostructures prepared by microwave refluxing technique. ACS Catal 5:5357–5365
Carabineiro SAC, Silva AMT, Dražić G, Tavares PB, Figueiredo JL (2010) Gold nanoparticles on ceria supports for the oxidation of carbon monoxide. Catal Today 154:21–30
Wang J, Zhong L, Lu J, Chen R, Lei Y, Chen K, Han C, He S, Wan G, Luo Y (2017) A solvent-free method to rapidly synthesize CuO-CeO2 catalysts to enhance their CO preferential oxidation: effects of Cu loading and calcination temperature. Mol Catal 443:241–252
Liotta LF, Carlo DG, Pantaleo G, Venezia AM (2006) Co3O4/CeO2 composite oxides for methane emissions abatement: relationship between Co3O4-CeO2 interaction and catalytic activity. Appl Catal B Environ 66:217–227
Moretti E, Storaro L, Talon A, Riello P, Molina AI (2015) 3-D flower like Ce-Zr-Cu mixed oxide systems in the CO preferential oxidation (CO-PROX): effect of catalyst composition. Appl Catal B Environ 168–169:385–395
Avgouropoulos G, Ioannides T (2006) Effect of synthesis parameters on catalytic properties of CuO-CeO2. Appl Catal B Environ 67:1–11
Polster CS, Nair H, Baertsch CD (2009) Study of active sites and mechanism responsible for highly selective CO oxidation in H2 rich atmospheres on a mixed Cu and Ce oxide catalyst. J Catal 266:308–319
Aranda A, Agouram S, López JM, Mastral AM, Sellick DR, Solsona B, Taylor SH, García T (2012) Oxygen defects: the key parameter controlling the activity and selectivity of mesoporous copper-doped ceria for the total oxidation of naphthalene. Appl Catal B Environ 127:77–88
Santos VP, Carabineiro SAC, Bakker JJW, Soares OSGP, Chen X, Pereira MFR, Órfão JJM, Figueiredo JL, Gascon J, Kapteijn F (2014) Stabilized gold on cerium-modified cryptomelane: highly active in low-temperature CO oxidation. J Catal 309:58–65
Luo JY, Meng M, Li X, Li XG, Zha YQ, Hu TD, Xie YN, Zhang J (2008) Mesoporous Co3O4-CeO2 and Pd/Co3O4-CeO2 catalysts: synthesis, characterization and mechanistic study of their catalytic properties for low-temperature CO oxidation. J Catal 254:310–324
Liu J, Zhao Z, Wang J, Xu C, Duan A, Jiang G, Yang Q (2008) The highly active catalysts of nanometric CeO2-supported cobalt oxides for soot combustion. Appl Catal B Environ 84:185–195
Guo X, Zhou R (2016) A new insight into the morphology effect of ceria on CuO/CeO2 catalysts for CO selective oxidation in hydrogen-rich gas. Catal Sci Technol 6:3862–3871
Aboukaïs A, Skaf M, Hany S, Cousin R, Aouad S, Labaki M, Abi-Aad E (2016) A comparative study of Cu, Ag and Au doped CeO2 in the total oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Mater Chem Phys 177:570–576
Saw ET, Oemar U, Tan XR, Du Y, Borgna A, Hidajat K, Kawi S (2014) Bimetallic Ni-Cu catalyst supported on CeO2 for high temperature water-gas shift reaction: methane suppression via enhanced CO adsorption. J Catal 314:32–46
Shen W, Mao D, Luo Z, Yu J (2017) CO oxidation on mesoporous SBA-15 supported CuO-CeO2 catalyst prepared by a surfactant assisted impregnation method. RSC Adv 7:27689
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2019XKQYMS70), and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT17R103).
Funding
Funding was provided by the National Key R&D Program of China (2019XKQYMS70) and Science and Technology Innovative Research Team in Higher Educational Institutions of Hunan Province (CN) (IRT17R103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Guo, Z., Chen, X. et al. Cu/CeO2 as efficient low-temperature CO oxidation catalysts: effects of morphological structure and Cu content. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 131, 691–706 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01870-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01870-0