Abstract
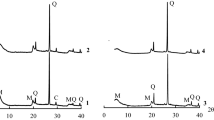
The Pd–Cu/attapulgite clay catalysts were synthesized using a deposition–precipitation method with different precipitants. The as-synthesized catalysts were characterized by ICP-AES, N2-physisorption, XRD, FT-IR, TEM and TPR. Their catalytic activities for CO oxidation were tested by a fixed-bed continuous flow reactor at room temperature and in humid circumstances. The results illustrated that the activity of CO oxidation strongly depended on the precipitant. The best catalytic performance is achieved by using NH3·H2O (PC-AH) or NH4HCO3 (PC-AHC) as precipitants. The crystalline phase of PC-AH and PC-AHC comprised of Cu2Cl(OH)3 and CuO, while the catalysts prepared with NaOH (PC-SH) or NaHCO3 (PC-SHC) as precipitants were mainly CuO. Combined with FT-IR and TEM results, it could be found that Cu2Cl(OH)3 on PC-AH and PC-AHC possessed higher stability than that on PC-SH and PC-SHC due to the different formation process and morphology of Cu2Cl(OH)3 species. The TPR results showed that the Cu2Cl(OH)3 had a strong interaction with Pd species and enhanced reducibility. Moreover, the residual sodium ions on PC-SH and PC-SHC may have adverse effect on the catalytic activity. A suitable precipitant resulted in the most efficient CO oxidation catalyst at room temperature and in humid circumstances.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doggali P, Kusaba H, Einaga H et al (2011) Low-cost catalysts for the control of indoor CO and PM emissions from solid fuel combustion. J Hazard Mater 186:796–804
Yang X, Yang L, Lin S et al (2014) Effects of the addition of small quantities of ceria on the catalytic behavior of Pd-only close-coupled catalysts during automobile exhaust elimination. Chin J Catal 35:1267–1280
Chang BK, Tatarchuk BJ (2006) Microfibrous entrapment of small catalyst particulates for high contacting efficiency removal of trace CO from practical reformates for PEM H2-O2 fuel cells. J Mater Eng Perform 15:453–456
Du N, Zhang H, Ma X et al (2008) Homogeneous coating of Au and SnO2 nanocrystals on carbon nanotubes via layer-by-layer assembly a new ternary hybrid for a room-temperature CO gas sensor. Chem Commun 48:6182–6184
Cai LL, Lu GZ, Zhan WC et al (2011) The effect of preparation method on the activities of Pd-Fe-Ox/Al2O3 catalysts for CO oxidation. J Mater Sci 46:5639–5644
Ali Bumajdad, Shaimaa Al-Ghareeb, Metwally Madkour et al (2017) Synthesis of MgO nanocatalyst in water-in-oil microemulsion for CO oxidation. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 122:1213–1229
Dhahri M, Munõz MA, Yeste MP et al (2016) Preparation of manganese-impregnated aluminapillared bentonite, characterization and catalytic oxidation of CO. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 118:655–668
Wang C, Wen C, Lauterbach J (2017) Superior oxygen transfer ability of Pd/MnOx-CeO2 for enhanced low temperature CO oxidation activity. Appl Catal B: Environ 206:1–8
Leunga E, Shimizua A, Barmakb K (2017) Copper oxide catalyst supported on niobium oxide for CO oxidation at low temperatures. Catal Commun 97:42–46
Zhang XD, Li HX, Hou FL (2017) Synthesis of highly efficient Mn2O3 catalysts for CO oxidation derived from Mn-MIL-100. Appl Surf Sci 411:27–33
Nemec V, Kaper H, Petaud G (2017) Impact of Mg2+ ion incorporation on the phase development of ZrO2-type solid solutions and their application in the catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide. J Mol Struct 1140:127–141
Piumetti M, Bensaid S, Fino D (2016) Nanostructured ceria-zirconia catalysts for CO oxidation: study onsurface properties and reactivity. Appl Catal B 197:35–46
Venkataswamy P, Jampaiah D, Mukherjee D (2016) Mn-doped ceria solid solutions for CO oxidation at lower temperatures. Catal Lett 146:2105–2118
Gürdag Gülten, Boz Ismail, Ebiller Sibel, Gürkaynak Mehmet Ali (2004) Room temperature carbon monoxide oxidation over Pt/Co2SnO4 and Pt/(Co3O4 + SnO2) catalysts. React Kinet Catal Lett 83:47–54
Santos VP, Carabineiro SAC, Bakker JJW et al (2014) Stabilized gold on cerium-modified cryptomelane: highly active in low-temperature CO oxidation. J Catal 309:58–65
Tseng CH, Yang TCK, Wu HE et al (2009) Catalysis of oxidation of carbon monoxide on supported gold nanoparticle. J Hazard Mater 166:686–694
Kucerová G, Strunk J, Muhler M et al (2017) Effect of titania surface modification of mesoporous silica SBA-15 supported Au catalysts: activity and stability in the CO oxidation reaction. J Catal 356:214–228
Qi CX, Su HJ, Guan RG et al (2012) An investigation into phosphate-doped Au/alumina for low temperature CO oxidation. J Phys Chem C 116:17492–17500
Christian S, Christian H (2017) CO oxidation on ceria supported gold catalysts studied by combined operando Raman/UV-Vis and IR spectroscopy. Top Catal 60:131–140
Li L, Wang AQ, Qiao BT et al (2013) Origin of the high activity of Au/FeOx for low-temperature CO oxidation: direct evidence for a redox mechanism. J Catal 299:90–100
Krämer M, Schmidt T, Stöwe K et al (2006) Structural and catalytic aspects of sol-gel derived copper manganese oxides as low-temperature CO oxidation catalyst. Appl Catal A 302:257–263
Jones C, Taylor SH, Burrows A et al (2008) Cobalt promoted copper manganese oxide catalysts for ambient temperature carbon monoxide oxidation. Chem Commun 14:1707–1709
Song W, Poyraz AS, Meng Y et al (2014) Mesoporous Co3O4 with controlled porosity: inverse micelle synthesis and high-performance catalytic CO oxidation at -60°C. Chem Mater 26:4629–4639
Xie XW, Li Y, Liu ZQ et al (2009) Low-temperature oxidation of CO catalysed by Co3O4 nanorods. Nature 458:746–749
Wang X, Zhong W, Li YW (2015) Nanoscale Co-based catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal Sci Technol 5:1014–1020
Wang YZ, Zhao YX, Gao CG et al (2007) Preparation and catalytic performance of Co3O4 catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal Lett 116:136–142
Wang YZ, Zhao YX, Gao CG et al (2008) Origin of the high activity and stability of Co3O4 in low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal Lett 125:134–138
Hou XD, Wang YZ, Zhao YX (2008) Effect of CeO2 doping on structure and catalytic performance of Co3O4 catalyst for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal Lett 123:321–326
Koh DJ, Song JH, Ha SW et al (1997) Low temperature oxidation of CO over supported PdCl2-CuCl2 catalysts. Korean J Chem Eng 14:486–490
Wang L, Zhou YB, Liu QF et al (2010) Effect of surface properties of activated carbon on CO oxidation over supported Wacker-type catalysts. Catal Today 153:184–188
Park ED, Lee JS (1998) Effects of copper phase on CO oxidation over supported wacker-type catalysts. J Catal 180:123–131
Wang SP, Li W, Dong YY et al (2015) Effects of potassium promoter on the performance of PdCl2-CuCl2/AC catalysts for the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from CO and methyl nitrite. Chin Chem Lett 26:1359–1363
Wang FG, Zhang HJ, He DN (2014) Catalytic oxidation of low-concentration CO at ambient temperature over supported Pd-Cu catalysts. Environ Technol 35:347–354
Shen YX, Lu GZ, Guo Y et al (2010) A synthesis of high-eficiency Pd-Cu-Clx/Al2O3 catalyst for low temperature CO oxidation. Chem Commun 46:8433–8435
Shen YX, Guo Y, Wang L et al (2011) The stability and deactivation of Pd-Cu-Clx/Al2O3 catalyst for low temperature CO oxidation: an effect of moisture. Catal Sci Technol 1:1202–1207
Feng YF, Li W, Zhang YH et al (2013) Deactivation mechanism of PdCl2-CuCl2/Al2O3 catalysts for CO oxidation at low temperatures. Chin J Catal 34:923–931
Shen YX, Lu GZ, Guo Y et al (2011) Study on the catalytic reaction mechanism of low temperature oxidation of CO over Pd-Cu-Clx/Al2O3 catalyst. Catal Today 175:558–567
Du XX, Li HY, Yu J et al (2015) Realization of a highly effective Pd-Cu-Clx/Al2O3 catalyst for low temperature CO oxidation by pre-synthesizing the active copper phase of Cu2Cl(OH)3. Catal Sci Technol 5:3970–3979
Zhou FY, Du XX, Yu J et al (2016) Highly water-resistant carbon nanotube supported PdCl2-CuCl2 catalysts for low temperature CO oxidation. Rsc Adv 6:66553–66563
Wang YZ, Fan LY, Shi J et al (2015) Effect of preparation method on the catalytic activities of Pd-Cu/apt catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal Lett 145:1429–1435
Yuan ZY, Ren TZ, Vantomme AA et al (2004) Facile and generalized preparation of hierarchically mesoporous-macroporous binary metal oxide materials. Chem Mater 16:5096–5106
You J, Chen F, Zhao XB et al (2010) Preparation, characterization and catalytic oxidation property of CeO2/Cu2+-attapulgite (ATP) nanocomposites. J Rare Earth 28:347–352
Cao JL, Shao GS, Wang Y et al (2008) CuO catalysts supported on attapulgite clay for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal Commun 9:2555–2559
Han WL, Zhang P, Pan X et al (2013) Influence of promoter on the catalytic activity of high performance Pd/PATP catalysts. J Hazard Mater 263:299–306
Yang HM, Tang AD, Ouyang J et al (2010) From natural attapulgite to mesoporous materials: methodology, characterization and structural evolution. J Phys Chem B 114:2390–2398
Wei W, Gao P, Xie JM et al (2013) Uniform Cu2Cl(OH)3 hierarchical microspheres: a novel adsorbent for methylene blue adsorptive removal from aqueous solution. J Solid State Chem 204:305–313
Zhu CL, Chen CN, Hao LY et al (2004) Template-free synthesis of Cu2Cl(OH)3 nanoribbons and use as sacrificial template for CuO nanoribbon. J Cryst Growth 263:473–479
Elzey S, Baltrusaitis J, Bian S et al (2011) Formation of paratacamite nanomaterials via the conversion of aged and oxidized copper nanoparticles in hydrochloric acidic media. J Mater Chem 21:3162–3169
Wang FG, Zhao KF, Zhang HJ (2014) Low temperature CO catalytic oxidation over supported Pd-Cu catalysts calcined at different temperatures. Chem Eng J 242:10–18
Veprek S, Cocke DL, Kehl S et al (1986) Mechanism of the deactivation of hopcalite catalysts studied by XPS, ISS, and other techniques. J Catal 100:250–263
Mirzaei AA, Shaterian HR, Joyner RW et al (2003) Ambient temperature carbon monoxide oxidation using copper manganese oxide catalysts: effect of residual Na+ acting as catalyst poison. Catal Commun 4:17–20
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from Shanxi provincial key research and development plan project (201603D121018-1); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21673132); and the Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry (Shaanxi Normal University).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Li, X., Lv, T. et al. Effect of precipitants on the catalytic performance of Pd–Cu/attapulgite clay catalyst for CO oxidation at room temperature and in humid circumstances. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 124, 203–216 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-018-1355-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-018-1355-7