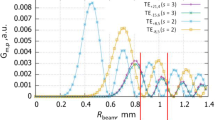
We have developed a method for optimization of a planar magnetron-injection gun (MIG) with allowance for the three-dimensional configuration of the electron-optical system and the electron drift in crossed fields, which is transverse to the direction of the translational beam propagation direction. Recommendations are given on how to minimize the spread of transverse velocities with retaining the pitch factor, which is acceptable for efficient electron-wave interaction. The influence of roughness of the emission surface on the parameters and the operation regime of the planar MIG is studied. The optimal electrode configurations of a planar MIG have been found for a gyrotron with an operating frequency of 140 GHz at the first cyclotron-frequency harmonic with an accelerating voltage of 50 kV, a current of 30 A, and a magnetic-field compression of 36. These confirm good electric strength of the gun and manufacturability of the design of the planar electron-optical system. The obtained calculated distribution of the transverse velocities in a ribbon helical electron beam ensures the possibility of selective excitation of the high-order working mode TE11, 1 of a planar electrodynamic system and an output radiation power of several hundreds of kilowatts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. A. Flyagin, ed., Gyrotrons [in Russian], Inst. Appl. Phys., Gorky (1980).
A. V. Gaponov-Grekhov, ed., Gyrotron [in Russian], Inst. Appl. Phys., Gorky (1981).
A. V. Gaponov, M. I. Petelin, and V.K.Yulpatov, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 10, Nos. 9–10, 794–813 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01031607
N. S. Ginzburg, N. A. Zavol’skii, G. S. Nusinovich and A. S. Sergeev, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 29, No. 1, 89–97 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01034008
T. Idehara, H. Tsuchiya, O. Watanabe, et al., Int. J. Infrared Millim. Waves, 27, 319–331 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-006-9084-9
M.Yu.Glyavin, A.G. Luchinin, and G.Yu. Golubiatnikov, Phys. Rev. Lett., No. 1, 100, 015101 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.015101
M.Yu.Glyavin and A.G. Luchinin, Terahertz Sci. Technol., 2, No. 4, 150–155 (2009). https://doi.org/10.11906/TST.150-155.2009.12.16
M.Yu.Glyavin, A.G. Luchinin, V. N. Manuilov, et al., Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 54, No. 8, 600–608 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-012-9319-7
N. S. Ginzburg, I.V. Zotova, V.Yu. Zaslavskii, et al., Tech. Phys. Lett., 37, No. 1, 79–82 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785011010196
N. S. Ginzburg, I.V. Zotova, A. S. Sergeev, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 108, No. 10, 105101 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.105101
V.Yu. Zaslavsky, N. S. Ginzburg, M.Yu.Glyavin, et al., Phys. Plasmas, 20, No. 4, 043103 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4799819
V.Yu. Zaslavsky, I.V. Zheleznov, N. S. Ginzburg, et al., IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, 68, No. 3, 1267–1270 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2020.3049108
V. N. Manuilov, V.Yu. Zaslavsky, N. S. Ginzburg, et al., Phys. Plasmas, 21, No. 2, 023106 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4864630
P. V. Krivosheev, V.K. Lygin, V.N.Manuilov, and Sh. E. Tsimring, Int. J. Infrared Millim. Waves, 22, 1119–1145 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015006230396
Sh. E. Tsimring, in: Lectures on Microwave Electronics (3rd Winter Workshop School for Engineers), Pt. 4 [in Russian], Saratov State Univ., Saratov (1974), pp. 3–94.
Sh. E. Tsimring, Electron Beams and Microwave Vacuum Electronics, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ (2007).
Sh. E. Tsimring, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 15, No. 8, 952–961 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01030951
K. A. Leshcheva and V. N. Manuilov, Usp. Prikl. Fiz., 7, No. 3, 298–308 (2019).
V. K. Lygin, Int. J. Infrared Millim. Waves, 16, No. 2, 363–376 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02096323
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Radiofizika, Vol. 64, No. 4, pp. 253–264, April 2021. Russian DOI: 10.52452/00213462_2021_64_04_253
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manuilov, V.N., Zaslavsky, V.Y., Kuftin, A.N. et al. Optimization of the Magnetron-Injection Gun for a High-Power Planar Millimeter-Wave Gyrotron. Radiophys Quantum El 64, 229–239 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-021-10126-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-021-10126-3