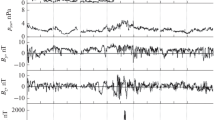
We present the results of comparing the total electron content measurements based on GLONASS satellite signals and the EISCAT UHF incoherent scatter radar (Tromsø, Norway) during modification of the high-latitude ionosphere in the magnetic zenith direction by high-frequency radio waves of the EISCAT/Heating facility (Tromsø, Norway). The measurements were performed during two experiment campaigns in October 2013 and in October 2018. In general, the total electron content variations obtained from the radar data in the altitude range 100–400 km were consistent with the total electron content variations from the GLONASS satellites. The efficiency of using GLONASS satellites for observations of high-latitude phenomena was shown. The anomalous increase in the total electron content by 4 TECU obtained from the incoherent scatter radar when the ionosphere was heated in the region close to the magnetic zenith is considered. The GLONASS satellite data show the total electron content reduction in the same region. To explain the disagreement between measurements by these two methods, the effect of smallscale electron-density irregularities arising in the region modified by high-power HF radio waves is considered. It is shown that when the electron density in artificial irregularities exceeds the background density of the medium by 2 ・ 10−3 times in relative units, scattering by irregularities with spatial scales of the order of 16 cm becomes predominant in the reflected signal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Forte, N. D. Smith, C. N. Mitchell, et al., Ann. Geophys., 31, 745 (2013).
N. Jakowski, E. Sardon, E. Engler, et al., Ann. Geophys., 14, 1429 (1996).
J. Lilensten and Lj.R.Cander, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys., 65, 833 (2003).
J. Lilensten, Lj.R.Cander, M.T. Rietveld, et al., Ann. Geophys., 23, 183 (2005).
M.T. Rietveld, H. Kohl, H. Kopka, et al., J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 55, 577 (1993).
M.T.Rietveld, M. J. Kosch, N. F. Blagoveshchenskaya, et al., J. Geophys. Res., 108, No. A4, 1141 (2003).
E.D.Tereshchenko, B. Z. Khudukon, M.T.Rietveld, et al., Ann. Geophys., 16, No. 7, 812 (1998).
E.D.Tereshchenko, B. Z. Khudukon, A.V.Gurevich, et al., Phys. Lett. A, 325, Nos. 5–6, 381 (2004).
E. D. Tereshchenko, A.N.Milichenko, V. L. Frolov, et al., Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 51, No. 11, 842 (2008).
V. E. Kunitsyn, A.M. Padokhin, E. S. Andreeva, et al., in: Proc. of the XXXth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium, 13–20 August 2011, Istanbul, Turkey, Art. No. 6051133.
N. F. Blagoveshchenskaya, T. D. Borisova, T.K.Yeoman, et al., Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 53, Nos. 9–10, 512 (2010).
M. Lockwood, K. Suvanto, J.-P. Maurice, et al., J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 50, Nos. 4–5, 467 (1988).
J. Wu, J.Wu, M.T. Rietveld, et al., J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys., 122, 1277 (2017).
V. L. Frolov, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 55, 110 (2012).
V.E.Kunitsyn, E. S. Andreeva, V. L. Frolov, et al., Radio Sci ., 47, RS0L15 (2012).
M. S. Lehtinen and A. Huuskonen, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 58, 435 (1996).
M. S. Lehtinen, A. Huuskonen, and J. Pirttila, Ann. Geophys. Atmos. Hydrospheres Space Sci ., 14, No. 12, 1487 (1996).
T. Rexer, B. Gustavsson, T. Leyser, et al., SGO Report No. 68, 94 (2019).
M.T.Rietveld and A. Senior, SGO Report No. 68, 95 (2019).
F.G.Bass, S.Ya. Braude, E. A. Kaner, and A.V.Men’, Sov. Phys. Usp., 4, No. 1, 51 (1961).
L.D. Landau and E. M. Lifshitz, Course of Theoretical Physics, Vol. 8, Electrodynamics of Continuous Media, Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK (1960).
V. E. Kunitsyn, E.D.Tereshchenko, and E. S. Andreeva, Radio Tomography of the Ionosphere [in Russian], Fizmatlit, Moscow (2007).
The Collected Papers of Albert Einstein, Volume 3 [Russian translation], Nauka, Moscow (1966), p. 216.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Radiofizika, Vol. 62, No. 10, pp. 747–758, October 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tereshchenko, E.D., Cherniakov, S.M., Yurik, R.Y. et al. Total Electron Content Measurements in the Ionosphere Disturbed by High-Power High-Frequency Waves by the Methods of Incoherent Scattering of Radio Waves and Radio Sounding by Glonass Satellite Signal. Radiophys Quantum El 62, 667–676 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-020-10012-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-020-10012-4