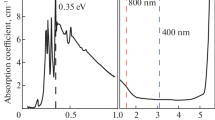
We propose a novel design of the barrier window for the output of microwave radiation at high peak and average power levels. A window based on a plate of polycrystalline CVD diamond with thin (nanometer-thick) boron-doped layers with increased conductivity is considered. Such a window, which retains the low radiation loss due to the small total thickness of the conductive layers and the high thermal conductivity inherent in diamond, prevents accumulation of a static charge on its surface, on the one hand, and allows one to produce a static electric field on the surface of the doped layer, which impedes the development of a multipactor discharge, on the other hand. In this case, a high level of the power of the transmitted radiation and a large passband width are ensured by choosing the configuration of the field in the form of a traveling wave inside the window.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.M.Garin, V.V.Parshin, S. E.Myasnikova, and V.G. Ralchenko, Diamond Rel. Mater., 12, 1755 (2003).
A. Ibarra, M. Gonzfilez, R. Vila, and J. Mollfi, Diam. Rel. Mater., 6, 856 (1997).
V. V. Parshin, A. L. Vikharev, R. Heidinger, et al., Proc. 35th IEEE Int. Conf. on Plasma Science, Karlsruhe, Germany, June 15–19, 2008, doi: 10.1109/PLASMA.2008.4590796.
Status and Applications of Diamond and Diamond-Like Materials: An Emerging Technology. Report of the Committee on Superhard Materials, NMAB-445, National Academy Press, Washington (1990).
A. G. Litvak, G.G. Denisov, V.E.Myasnikov, et al., J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves, 32, 337 (2011).
M. Thumm, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 39, 971 (2011).
A. Neuber, J.Dickens, D.Hemmert, et al., IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 26, 296 (1998).
R. A.Kishek and Y.Y. Lau, Phys. Rev. Lett., 80, 193 (1998).
O. A. Ivanov, M.A. Lobaev, V. A. Isaev, et al., Plasma Phys. Reports, 36, No. 4, 336 (2010).
A. L. Vikharev, A. M. Gorbachev, O. A. Ivanov, et al., Phys. Rev. ST-Accel. Beams, 12, Art. no. 062003 (2009).
U.Klein and D. Pronch, in: Proc. Conf. on Future Possibilities of Electron Accelerators, Univ. of Virginia, Charlottesville (1979), p. 1.
H.Padamsee, D. Pronch, P.Kneisel, et al., IEEE Trans. Magn., 17, 947 (1981).
C.Chang, H. J. Huang, G. Z. Liu, et al., J. Appl. Phys., 105, Art. no. 123305 (2009).
A. R. Nayaiesh, E. L.Garwin, F.K.King, et al., J. Vac. Sci. Technol., 4, No. 5, 2356 (1986).
S. Michizono, A.Kinbara, Y. Saito, et al., J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A, 10, No. 4, 1180 (1992).
L. L. Hatfield, E. R. Boerwinkle, G.R. Leiker, et al., IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul., 24, No. 6, 985 (1989).
J.Tuckmantel, Technical Report 94-26, CERN LEP-2 Notes, Geneva (1994).
O. A. Ivanov, M.A. Lobaev, V. A. Isaev, and A. L. Vikharev, Phys. Rev. ST-Accel. Beams, 13, 022004 (2010).
P. Yla-Oijala and M. Ukkola, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., A474, 197 (2001).
A.Valfells, L.K.Ang, Y.Y. Lau, et al., Phys. Plasmas, 7, No. 2, 750 (2000).
X. Zhang, Y.Wang, and J. Fan, Phys. Plasmas, 22, 022110 (2015).
W.D.Moller, Q. S. Shu, J. T. Susta, et al., in: 12th Int. Workshop on RF Superconductivity, 441, Nos. 1–2, 239 (2005).
S. Bogdanov, A. Vikharev, A. Gorbachev, et al., Chem. Vap. Deposition, 20, 32 (2014).
A. Fiori, F. Jomard, T.Teraji, et al., Thin Solid Films, 557, 222 (2014).
A. L. Vikharev, A. M. Gorbachev, M. A. Lobaev, et al., Phys. Status Solidi RRL, 10, 324 (2016).
R.Edgington, S. Sato, Y. Ishiyama, et al., J. Appl. Phys., 111, 033710 (2012).
C. Mer-Calfati, N.Tranchant, P. N.Volpe, et al., Mater. Lett., 115, 283 (2014).
S. Michizono, A.Kinbara, Y. Saito, et al., J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A10, No. 4, 1180 (1992).
J. Barjon, N.Habka, C.Mer, et al., Phys. Status Solidi RRL, 3, No. 6, 202 (2009).
Y.Otake, S.Tokumoto, S.Yu.Kazakov, et al., in: Proc. Third Workshop on Pulsed RF Sources Linear Colliders, Kanagawa, Japan, April 1996, p. 315.
S.Tokumoto, Y.H.Chin, H. Mizuno, et al., arXiv:hep-ex/0008039 (2000).
S.Kazakov, High-power RF Sources and Components for Linear Colliders, Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, Chicago (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Radiofizika, Vol. 60, No. 5, pp. 449–457, May 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanov, O., Kuzikov, S.V., Vikharev, A.A. et al. The Diamond Window with Boron-Doped Layers for the Output of Microwave Radiation at High Peak and Average Power Levels. Radiophys Quantum El 60, 401–408 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-017-9809-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-017-9809-8