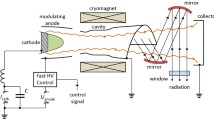
We present the results of experimental studies of submillimeter-wave gyrotrons, which were obtained in the Research Center for Development of Far-Infrared Region of Fukui University (Japan). Distinctive features of the systems forming helical electron beams in submillimeter-wave gyrotrons are described. The results of the theoretical studies, which were aimed at excitation of higher harmonics in submillimeter-wave gyrotrons, reducing the operating voltage, and creating devices with smooth wideband tuning of the generation frequency, are presented. It is shown that modern gyrotrons are capable of ensuring continuous-wave generation at the frequencies from 200 to 400 GHz at a power level of up to hundreds of watts, and up to tens of kilowatts in the pulse-generation regime.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Griffin, in: Joint 33rd Int. Conf. on Infrared and Millimeter Waves and 16th Int. Conf. on Terahertz Electronics, Pasadena, USA, 2008, p. F1P2.
V.E. Zapevalov, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 49, No. 10, 779 (2006).
P. Krivosheev, V. Lygin, V.Manuilov, and Sh. Tsimring Sh., Int. J. Infrared Millimeter Waves, 22, No. 8, 1119 (2001).
V. E. Zapevalov, A. N.Kuftin, and V.K. Lygin, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 50, No. 9, 702 (2007).
T. Idehara, T. Saito, and I.Ogawa, Appl. Magnetic Resonance, 34, Nos. 3–4, 265 (2009).
T. Idehara, I.Ogawa, S.Kobayashi, et al., in: 35th Int. Conf. Plasma Sci. (ICOPS 2008), Karlsruhe, Germany, 2008, p. 253.
V.Manuilov, T. Idehara, T. Saito, et al., Int. J. Infrared Millimeter Waves, 29, No. 12, 1103 (2008).
T. Notake, T. Saito, Y.Tatematsu, et al., Plasma Fusion Res., 4, 011 (2009).
T.B. Pankratova and G. S.Nusinovich, Zh. Tekh. Fiz., 59, No. 8, 110 (1989).
T. Idehara, I.Ogawa, S. Mitsudo, et al., IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 27, No. 2, 340 (1999).
M. Hornstein, V. Bajaj, R. Griffin, et al., IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, 52, 798 (2005).
V. Bratman, M. Glyavin, T. Idehara, et al., IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 37, No. 1, 36 (2009).
D.B.McDermott, N. C. Luhmann, A. Kupiszewski, Jr., and H.R. Jory, Phys. Fluids, 26, No. 7, 1936 (1983).
V. Bratman, Yu.Kalynov, and V. Manuilov, Phys. Rev. Lett., 102, 245101 (2009).
S. A. Malygin, Elektron. Tekh. Ser. Electron. SVCh, 31, 106 (1986).
M. Glyavin, A. Luchinin, V.Manuilov, and G.Nusinovich, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 36, No. 3, 591 (2008).
V.E. Zapevalov and O. V. Malygin, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Radiofiz., 26, No. 7, 903 (1983).
B.Danly and R.Temkin, Phys. Fluids, 29, 561 (1986).
L. Becerra, G.Gerfen, R.Temkin, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 71, 3561 (1993).
K.Hong, G.Brand, and T. Idehara, J. Appl. Phys., 74, 5250 (1993).
S. N. Vlasov, G.M. Zhislin, I.M.Orlova, et al., Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 12, No. 8, 1236 (1977).
S. T.Han, I.Mastovsky, M.A. Shapiro, et al., in: Int. PPPS Conf., Albuquerque, New Mexico, 2007, p. 7B6.
A. L. Gol’denberg, M.Yu. Glyavin, N. A. Zavolsky, and V. N.Manuilov, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 48, No. 10–11, 741 (2005).
La Agusu, T. Idehara, T. Saito, et al., in: Joint 33rd Int. Conf. on Infrared and Millimeter Waves and 16th Int. Conf. on Terahertz Electronics, Pasadena, USA, 2008, p. 5D26.1308.
M.Thumm, Laboratory Report FZKA 7467, Karlsruhe (2009), bibliothek.fzk.de/zb/berichte/FZKA7467.pdf.
I. I.Antakov, S. N. Vlasov, V.A.Gintsburg, et al., Elektron. Tekh. Ser. Electron. SVCh, 27, No. 8, 20 (1975).
E. Zasypkin, I.Antakov, I.Gachev, et al., in: Proc. 23rd Int. Conf. Infrared and Millimeter Waves, Colchester, 1998, p. 323.
S. Sabchevski and T. Idehara, Int. J. Infrared Millimeter Waves, 29, 1 (2008).
O.Dumbrajs and A.Möbius, Int. J. Electron., 84, No. 4, 411 (1998).
M.Yu.Glyavin, A.G. Luchinin, M.V.Morozkin, and V. I. Khiznyak, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 51, No. 1, 57 (2008).
M. Glyavin, V.Khizhnyak, A. Luchinin, et al., Int. J. Infrared Millimeter Waves, 29, No. 7, 641 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Radiofizika, Vol. 52, No. 7, pp. 557–568, July 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glyavin, M.Y., Idehara, T., Manuilov, V.N. et al. Studies of continuous-wave submillimeter-wave gyrotrons for spectroscopy and diagnostics of various media. Radiophys Quantum El 52, 500–510 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-009-9153-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-009-9153-8