Abstract
Purpose
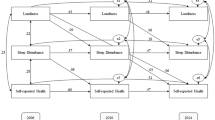
There is evidence for negative associations between social isolation and loneliness and sleep quality in older adults. However, it is unclear to what extent these two factors independently affect sleep quality. This study examined the simultaneous associations of social isolation and loneliness with sleep quality in a longitudinal study of older adults.
Methods
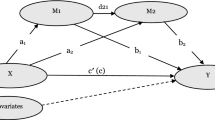
Data were analyzed from the Social Environment and Biomarkers of Aging Study in Taiwan collected in 2000 and 2006, involving a cohort of 639 participants (mean age = 66.14, SD 7.26). Poisson regression models were conducted to examine the association of social isolation and/or loneliness with sleep quality at follow-up after adjusting for multiple confounding variables.
Results
Univariate analysis showed that sleep quality was inversely associated with both social isolation and loneliness. After demographic, health, cognitive factors, and depressive symptoms were controlled in multivariable analysis, social isolation at the baseline still predicted poor sleep quality 6 years later (incident rate ratio, IRR 1.14; 95% CI 1.04–1.24; p < 0.01), while the association between loneliness and sleep quality was no longer significant (IRR 1.08; 95% CI 0.94–1.23; p = 0.27). The results were unchanged when participants who had poor sleep quality at the baseline were excluded from the analysis.
Conclusions
These findings confirm an adverse effect of social isolation on the sleep quality of older adults, but indicate that this effect is independent of loneliness. Social isolation and loneliness seem to have distinct pathways in affecting the sleep quality of older adults.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ancoli-Israel, S., & Ayalon, L. (2006). Diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders in older adults. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 14(2), 95–103.
Crowley, K. (2011). Sleep and sleep disorders in older adults. Neuropsychology Review, 21(1), 41–53.
Roth, T. (2007). Insomnia: Definition, prevalence, etiology, and consequences. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 3(5 Suppl), S7–S10.
Leng, Y., Cappuccio, F. P., Wainwright, N. W., Surtees, P. G., Luben, R., Brayne, C., & Khaw, K. T. (2015). Sleep duration and risk of fatal and nonfatal stroke: A prospective study and meta-analysis. Neurology, 84(11), 1072–1079.
Cappuccio, F. P., Cooper, D., D’Elia, L., Strazzullo, P., & Miller, M. A. (2011). Sleep duration predicts cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. European Heart Journal, 32(12), 1484–1492.
Chen, J. H., Waite, L. J., & Lauderdale, D. S. (2015). Marriage, relationship quality, and sleep among U.S. older adults. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 56(3), 356–377.
Chen, J. H., Lauderdale, D. S., & Waite, L. J. (2016). Social participation and older adults’ sleep. Social Science & Medicine, 149, 164–173.
Gu, D., Sautter, J., Pipkin, R., & Zeng, Y. (2010). Sociodemographic and health correlates of sleep quality and duration among very old Chinese. Sleep, 33(5), 601–610.
Cacioppo, J. T., & Patrick, W. (2008). Loneliness : Human nature and the need for social connection 1. New York: Norton.
Jacobs, J. M., Cohen, A., Hammerman-Rozenberg, R., & Stessman, J. (2006). Global sleep satisfaction of older people: The Jerusalem Cohort Study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 54(2), 325–329.
McHugh, J. E., & Lawlor, B. A. (2013). Perceived stress mediates the relationship between emotional loneliness and sleep quality over time in older adults. British Journal of Health Psychology, 18(3), 546–555.
Hawkley, L. C., Preacher, K. J., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2010). Loneliness impairs daytime functioning but not sleep duration. Health Psychology, 29(2), 124–129.
Shankar, A., Hamer, M., McMunn, A., & Steptoe, A. (2013). Social isolation and loneliness: Relationships with cognitive function during 4 years of follow-up in the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Psychosomatic Medicine, 75(2), 161–170.
Holwerda, T. J., Deeg, D. J., Beekman, A. T., van Tilburg, T. G., Stek, M. L., Jonker, C., & Schoevers, R. A. (2014). Feelings of loneliness, but not social isolation, predict dementia onset: Results from the Amsterdam Study of the Elderly (AMSTEL). Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 85(2), 135–142.
Steptoe, A., Shankar, A., Demakakos, P., & Wardle, J. (2013). Social isolation, loneliness, and all-cause mortality in older men and women. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(15), 5797–5801.
Cornman, J. C., Glei, D. A., Goldman, N., Chang, M. C., Lin, H. S., Chuang, Y. L., Hurng, B. S., Lin, Y. H., Lin, S. H., Liu, I. W., Liu, H. Y., & Weinstein, M. (2014). Cohort profile: The Social Environment and Biomarkers of Aging Study (SEBAS) in Taiwan. International Journal of Epidemiology. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyu1179.
Vasunilashorn, S., Glei, D. A., Lin, Y.-H., & Goldman, N. (2013). Apolipoprotein E and measured physical and pulmonary function in older Taiwanese adults. Biodemography and Social Biology, 59(1), 57–67.
Carney, C. E., & Edinger, J. D. (2010). Insomnia and anxiety. New York: Springer.
Smith, M. T., & Wegener, S. T. (2003). Measures of sleep. Rheumatoid Arthritis, 49(5S), S184–S196.
Buysse, D. J., Reynolds, C. F., Monk, T. H., Berman, S. R., & Kupfer, D. J. (1989). The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research, 28(2), 193–213.
Lin, C.-L., Su, T.-P., & Chang, M. (2003). Quality of sleep and its associated factors in the institutionalized elderly. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association, 7(2), 174–184.
Wu, C.-Y., Su, T.-P., Fang, C.-L., & Chang, M. Y. (2012). Sleep quality among community-dwelling elderly people and its demographic, mental, and physical correlates. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association, 75(2), 75–80.
Dowd, J. B., Goldman, N., & Weinstein, M. (2011). Sleep duration, sleep quality, and biomarkers of inflammation in a Taiwanese population. Ann Epidemiol, 21(11), 799–806.
Cornwell, E. Y., & Waite, L. J. (2009). Social disconnectedness, perceived isolation, and health among older adults. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 50(1), 31–48.
Gersten, O. (2008). Neuroendocrine biomarkers, social relations, and the cumulative costs of stress in Taiwan. Social Science & Medicine, 66(3), 507–519.
Glei, D. A., Goldman, N., Ryff, C. D., Lin, Y. H., & Weinstein, M. (2012). Social relationships and inflammatory markers: An analysis of Taiwan and the U.S. Social Science & Medicine, 74(12), 1891–1899.
Luo, Y., & Waite, L. J. (2014). Loneliness and mortality among older adults in China. Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 69(4), 633–645.
Nummela, O., Seppanen, M., & Uutela, A. (2011). The effect of loneliness and change in loneliness on self-rated health (SRH): A longitudinal study among aging people. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, 53(2), 163–167.
Tilvis, R. S., Pitkala, K. H., Jolkkonen, J., & Strandberg, T. E. (2000). Social networks and dementia. Lancet, 356(9223), 77–78.
Hu, W., & Lu, J. (2015). Associations of chronic conditions, APOE4 allele, stress factors, and health behaviors with self-rated health. BMC Geriatrics, 15, 137. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-12015-10132-y.
Department of Health. (2003). Identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults in Taiwan. Taiwan: Department of Health.
Chien, K. L., Chen, P. C., Hsu, H. C., Su, T. C., Sung, F. C., Chen, M. F., & Lee, Y. T. (2010). Habitual sleep duration and insomnia and the risk of cardiovascular events and all-cause death: Report from a community-based cohort. Sleep, 33(2), 177–184.
Grandner, M. A., Patel, N. P., Perlis, M. L., Gehrman, P. R., Xie, D., Sha, D., Pigeon, W. R., Teff, K., Weaver, T., & Gooneratne, N. S. (2011). Obesity, diabetes, and exercise associated with sleep-related complaints in the American population. Z Gesundh Wiss, 19(5), 463–474.
Leng, Y., Wainwright, N. W., Cappuccio, F. P., Surtees, P. G., Hayat, S., Luben, R., Brayne, C., & Khaw, K. T. (2016). Daytime napping and increased risk of incident respiratory diseases: Symptom, marker, or risk factor? Sleep Med, 23, 12–15.
Katz, S., & Akpom, C. A. (1976). A measure of primary sociobiological functions. International Journal of Health Services, 6(3), 493–508.
Spector, W. D., & Fleishman, J. A. (1998). Combining activities of daily living with instrumental activities of daily living to measure functional disability. Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 53(1), S46–S57.
Ku, P. W., Fox, K. R., Gardiner, P. A., & Chen, L. J. (2016). Late-life exercise and difficulty with activities of daily living: An 8-year nationwide follow-up study in Taiwan. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 50(2), 237–246.
Chu, D.-C., Fox, K. R., Chen, L.-J., & Ku, P.-W. (2015). Components of late-life exercise and cognitive function: An 8-year longitudinal study. Prevention Science, 16(4), 568–577.
Boey, K. W. (1999). Cross-validation of a short form of the CES-D in Chinese elderly. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 14(8), 608–617.
Chen, L.-J., Stevinson, C., Ku, P. W., Chang, Y.-K., & Chu, D.-C. (2012). Relationships of leisure-time and non-leisure-time physical activity with depressive symptoms: A population-based study of Taiwanese older adults. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 9, 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-1189-1128.
Chou, K. L. (2010). Moderating effect of apolipoprotein genotype on loneliness leading to depressive symptoms in Chinese older adults. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 18(4), 313–322.
Hosmer, D. W., & Lemeshow, S. (2000). Applied logistic regression (2). New York: Wiley.
Locher, J. L., Ritchie, C. S., Roth, D. L., Baker, P. S., Bodner, E. V., & Allman, R. M. (2005). Social isolation, support, and capital and nutritional risk in an older sample: Ethnic and gender differences. Social Science & Medicine, 60(4), 747–761.
Vandervoort, D. (2000). Social isolation and gender. Current Psychology, 19(3), 229–236.
Tanskanen, J., & Anttila, T. (2016). A prospective study of social isolation, loneliness, and mortality in Finland. American Journal of Public Health, 106, e1–e7.
Kent, R. G., Uchino, B. N., Cribbet, M. R., Bowen, K., & Smith, T. W. (2015). Social relationships and sleep quality. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 49(6), 912–917.
Worthman, C. M., & Melby, M. K. (2002). Toward a comparative developmental ecology of human sleep. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Kurina, L. M., Knutson, K. L., Hawkley, L. C., Cacioppo, J. T., Lauderdale, D. S., & Ober, C. (2011). Loneliness is associated with sleep fragmentation in a communal society. Sleep, 34(11), 1519–1526.
Petersen, J., Kaye, J., Jacobs, P. G., Quinones, A., Dodge, H., Arnold, A., & Thielke, S. (2016). Longitudinal relationship between loneliness and social isolation in older adults: Results from the cardiovascular health study. Journal of Aging and Health, 28(5), 775–795.
Victor, C., Grenade, L., & Boldy, D. (2005). Measuring loneliness in later life: A comparison of differing measures. Reviews in Clinical Gerontology, 15(01), 63–70.
Dickens, A. P., Richards, S. H., Greaves, C. J., & Campbell, J. L. (2011). Interventions targeting social isolation in older people: A systematic review. BMC Public Health, 11, 647.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the SEBAS research group for collecting the data and making it available to researchers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures, including the informed consent process, were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, B., Steptoe, A., Niu, K. et al. Prospective associations of social isolation and loneliness with poor sleep quality in older adults. Qual Life Res 27, 683–691 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-017-1752-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-017-1752-9