Abstract
Background
No quick and easy assessment tool is presently available to measure asthma control and outcome in Chinese children.
Methods
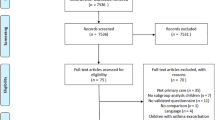
We translated an established seven-item questionnaire into the Chinese Childhood Asthma Control Test (C-CACT) to measure asthma symptoms and their effect on daily function in 247 children aged 4–11 years enrolled from specialty clinics around Tainan. Subjects were classed as having either intermittent or persistent asthma and were evaluated at two outpatient visits 4–8 weeks apart (baseline and follow-up).
Results
C-CACT at baseline correlated significantly with physician evaluation scores (PES) except in predicted peak expiratory flow rate. There were significant differences for mean C-CACT score and mean PES between the intermittent group and persistent group. Internal consistency reliability of the survey was 0.741 at baseline and 0.759 at the follow-up visit. Test–retest reliability among 209 patients with the same specialist rating of asthma control at baseline and follow-up was r = 0.546 (P < 0.001). C-CACT scores of patients whose therapy needed to be stepped up was significantly lower than in those with unchanged or stepped-down therapy (F = 39.61, P < 0.001).
Conclusions
C-CACT provides a reliable, valid, and responsive measure of asthma control in Chinese children.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trends in Asthma Morbidity and Mortality. (2005). American Lung Association Epidemiology and Statistics Unit Research and Program Services. May 2005.
Centers for Disease Control, Prevention. (2004). Asthma prevalence and control characteristics by race/ethnicity—United States, 2002. MMWR Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 53, 145–148.
Sullivan, S. D. (2003). Asthma in the United States: Recent trends and current status. Journal of Managed Care Pharmacy, 9(suppl), 3–7.
Weiss, K. B., & Sullivan, S. D. (2001). The health economics of asthma and rhinitis. I. Assessing the economic impact. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 107, 3–8.
Jan, I. S., Chou, W. H., Wang, J. D., & Kuo, S. H. (2004). Prevalence of and major risk factors for adult bronchial asthma in Taipei city. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association, 103, 259–263.
Kao, C. C., Huang, J. L., Ou, L. S., & See, L. C. (2005). The prevalence, severity and seasonal variations of asthma, rhinitis and eczema in Taiwanese schoolchildren. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology, 16, 408–415.
Lee, Y. L., Hwang, B. F., Lin, Y. C., Guo, Y. L., & Taiwan ISAAC Study Group. (2007). Time trend of asthma prevalence among school children in Taiwan: ISAAC phase I and III surveys. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology, 18, 188–195.
Yan, D. C., Ou, L. S., Tsai, T. L., Wu, W. F., & Huang, J. L. (2005). Prevalence and severity of symptoms of asthma, rhinitis, and eczema in 13- to 14-year-old children in Taipei, Taiwan. Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, 95, 579–585.
Lai, C. K. W., De Guia, T. S., Kim, Y. Y., et al. (2003). Asthma control in the Asia-Pacific region: The Asthma Insights and Reality in Asia-Pacific (AIRIAP) Study. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 111, 263–268.
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). (2006). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. http://www.ginasthma.org. Accessed 30 July 2007.
Li, J. T., Oppenheimer, J., Bernstein, I. L., & Nicklas, R. A. (2005). Attaining optimal asthma control: A practice parameter. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 116, S3–S11.
Bateman, E. D. (2001). Measuring asthma control. Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 1, 211–216.
Bateman, E. D., Boushey, H. A., Bousquet, J., et al. (2004). Can guideline defined asthma control be achieved? The Gaining Optimal Asthma controL study. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 170, 836–844.
Magnan, A. (2004). Tools to assess (and achieve?) long-term asthma control. Respiratory Medicine, 98(Suppl. 2), S16–S21.
Nathan, R. A., Sorkness, C. A., Kosinski, M., et al. (2004). Development of the asthma control test: A survey for assessing asthma control. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 113, 59–65.
Schatz, M., Sorkness, C. A., Li, J. T., Marcus, P., Murray, J. J., Nathan, R. A., Kosinski, M., Pendergraft, T. B., & Jhingran, P. (2006). Asthma Control Test: Reliability, validity, and responsiveness in patients not previously followed by asthma specialists. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 117, 549–556.
Juniper, E. F., Guyatt, G. H., Feeny, D. H., et al. (1996). Measuring quality of life in children with asthma. Quality of Life Research, 5, 35–46.
Chong, L. Y., Chay, O. M., & Shu-Chuen, L. (2006). Is the childhood asthma questionnaire a good measure of health-related quality of life of asthmatic children in Asia?: Validation among paediatric patients with asthma in Singapore. Pharmacoeconomics, 24, 609–621.
Guyatt, G. H., Jenifer, E. F., Feeny, D. H., et al. (1997). Children and adult perception of childhood asthma. Pediatrics, 99, 165–168.
Liu, A. H., Zeiger, R. S, Welch, M., et al. (2007). Development and cross-sectional validation of the Childhood Asthma Control Test. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 119, 817–825.
Niu, C. K, Chen, W. Y., Huang, J. L, Lue, K. H., & Wang, J. Y. (2006). Efficacy and safety of sublingual immunotherapy with high dose house dust mites extract in asthmatic children: A multi-center, double blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled study in Taiwan. Respiratory Medicine, 100, 1374–1383.
The NAEPP Expert Panel Report. (2003). Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma—update on selected topics (EPR—Update 2002). NIH Publication No. 02-5075. Besthesda, MD: National Institutes of Health.
Wang, J. Y., & Chen, W. Y. (1992). Inhalant allergens in asthmatic children in Taiwan: Comparison evaluation of skin testing, radioallergosorbent test and multiple allergosorbent chemiluminescent assay for specific IgE. Journal of Formosan Medical Association, 91, 1127–1132.
Carlton, B. G., Lucas, D. O., Ellis, E. F., Conboy-Ellis, K., Shoheiber, O., & Stempel, D. A. (2005). The status of asthma control and asthma prescribing practices in the United States: Results of a large prospective asthma control survey of primary care practices. Journal of Asthma, 42, 529–535.
Townsend, M., Feeny, D. H, Guyatt, G. H., Furlong, W. I., Seip, A. E., & Dolovich, J. (1991). Evaluation of the burden of illness for pediatric asthmatic patients and their parents. Annals of Allergy, 67, 403–408.
Lara, M., Duan, N., Sherbourne, C., Lewis, M., Landon, C., Halfon, N., & Brook, R. H. (1998). Differences between child and parent reports of symptoms among latino children with asthma. Pediatrics, 102, 68.
Guyatt, G. H., Juniper, E. F., Griffith, L. E., Feeny, D. H., & Ferrie, P. J. (1997). Children and adult perceptions of childhood asthma. Pediatrics, 99, 165–168.
Nathan, R. A., Sorkness, C. A., Kosinski, M., Schatz, M., Li, J. T., Marcus, P., Murray, J. J., & Pendergraft, T. B. (2004). Development of the asthma control test: A survey for assessing asthma control. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 113, 59–65.
Juniper, E. F., O’Byrne, P. M., Guyatt, G. H., Ferrie, P. J., & King, D. R. (1999). Development and validation of a questionnaire to measure asthma control. European Respiratory Journal, 14, 902–907.
Santanello, N. C. (2001). Pediatric asthma assessment: Validation of 2 symptom diaries. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 107, S465–S472.
Skinner, E. A., Diette, G. B., Algatt-Bergstrom, P. J., Nguyen, T. H., Clark, R. D., Markson, L. E., & Wu, A. W. (2004). The asthma therapy assessment questionnaire (ATAQ) for children and adolescents. Disease Management, 7, 305–313.
Sly, P. D. (1997). Relationship between change in PEF and symptoms: Questions to ask in paediatric clinics. European Respiratory Journal Supplement, 24, 80S–83S.
Lara, M., Sherbourne, C., Duan, N., Morales, L., Gergen, P., & Brook, R. H. (2000). An English and Spanish pediatric asthma symptom scale. Medical Care, 38, 342–350.
van Dellena, Q. M., Stronksb, K., Bindelsc, P. J. E., Bruild, F. G. O, van Aalderena, W. M. C., & the PEACE Study Group. (2007). Predictors of asthma control in children from different ethnic origins living in Amsterdam. Respiratory Medicine, 101, 779–785.
Yang, K. S., Ng, T. P., Kwang, Y. P., Thilagaratnam, S., Wong, C. S., & Chia, F. (2007). Prevalence of childhood asthma and control in children assessed in a pilot school-based intervention program in Singapore. Journal of Pediatrics Child Health, 43, 353–358.
Brand, P. L., & Roorda, R. J. (2003). Usefulness of monitoring lung function in asthma. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 88, 1021–1025.
Yoos, H. L., Kitzman, H., McMullen, A., et al. (2002). Symptom monitoring in childhood asthma: A randomized clinical trial comparing peak expiratory flow rate with symptom monitoring. Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, 88, 283–291.
Juniper, E. F., O’Byrne, P. M., & Roberts, J. N. (2001). Measuring asthma control in group studies: Do we need airway caliber and rescue b2-agonist use? Respiratory Medicine, 95, 319–323.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Chin-Li Lu, Department of Medical Information, Chi-Mei Medical Center, for statistical consultation, Mr. Chih-Cheng Wang and Ms. Yu-Chin Lai for administering the questionnaire, and the families of asthmatic children for their willingness to participate in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HH., Wang, JY., Jan, RL. et al. Reliability and validity of childhood asthma control test in a population of Chinese asthmatic children. Qual Life Res 17, 585–593 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-008-9335-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-008-9335-4