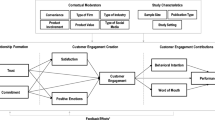
Abstract
Partial Least Squares (PLS) path modeling is suitable for predictive research and can also handle both reflective and formative measurement models. On the other hand, when the data derive from a common factor model population, PLS-SEM’s parameter estimates differ from the prespecified values. This trait is PLS-Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) bias, which is a controversial issue among many researchers. Bearing that in mind, the study's ultimate aim is to evaluate PLS-SEM bias at a relatively large sample size through regular and consistent PLS-SEM in the mobile shopping context. The subsidiary goal is to assess word-of-mouth concept, which is rarely used in the mobile context, within Technology Acceptance Model by employing PLS path modeling. Data were collected from 560 consumers via questionnaires and analyzed via SmartPLS 3. Findings show that regular PLS-SEM bias does not seem to diminish at a relatively large sample size when estimating data from common factor population. This study, also, offers to prefer PLSc in reflectively structured models in marketing, and also put forward that word-of-mouth is a substantial determinant in the acceptance of mobile shopping.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrebi, S., Jallais, J.: Explain the intention to use smartphones for mobile shopping. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 22, 16–23 (2015)
Ali, M., Kan, K.A.S., Sarstedt, M.: Direct and configurational paths of absorptive capacity and organizational innovation to successful organizational performance. J. Bus. Res. 69(11), 5317–5323 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.04.131
Bansal, H., Voyer, P.A.: Word-of-mouth processes within a services purchase decision context. J. Serv. Res. 3(2), 166–177 (2000)
Barclay, D., Higgins, C., Thompson, R.: The partial least squares (PLS) approach to causal modeling: personal computer adoption and use as an illustration. Technol. Stud. 2(2), 285–309 (1995)
Bilgihan, A., Kandampully, J., Zhang, T.: Towards a unified customer experience in online shopping environments: antecedents and outcomes. Int. J. Qual. Serv. Sci. 8(1), 102–119 (2016)
Cheah, J.-H., Memon, M.A., Chuah, F., Ting, H., Ramayah, T.: Assessing reflective models in marketing research: a comparison between Pls And Plsc. Estim. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 19(1), 139–160 (2018)
Chen, L.Y.: Antecedents of customer satisfaction and purchase intention with mobile shopping system use. Int. J. Serv. Operat. Manag. 15(3), 259–274 (2013)
Cheung, C.M., Lee, M.K., Rabjohn, N.: The impact of electronic word of mouth. Inter. Res. 18(3), 229–247 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1108/10662240810883290
Chiem, R., Arriola, J., Browers, D., Gross, J., Limman, E., Nguyen, P.V., Seal, K.C.: The critical success factors for marketing with downloadable applications: lessons learned from selected european countries. Int. J. Mobile Market 5(2), 43–56 (2010)
Chin, W.W., Marcolin, B.L., Newsted, P.R.: A partial least squares latent variable modeling approach for measuring interaction effects: results from a Monte Carlo simulation study and an electronic-mail emotion/adoption study. Inf. Syst. Res. 14(2), 189–217 (2003)
Chin, W.W.: The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling, In: Marcoulides, G.A. (Ed.): Modern Methods for Business Research, pp.295–358, Erlbaum, Mahwah (1998)
Chin, W. W.: How to write up and report PLS analyses, In: V. Esposito Vinzi, W. W. Chin, J. Henseler, H. Wang (Ed). Handbook of partial least squares: Concepts, methods, and applications, pp.665–690 Heidelberg/Dordrecht/London/New York: Springer. (2010)
Davis, F.D.: Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 13(3), 319–340 (1989)
Davis, F.D., Bagozzi, R.P., Warshaw, P.R.: User Acceptance of computer technology: a comparison of two theoretical models. Inst. Manag. Sci. 35(8), 982–1002 (1989)
Dijkstra, T.K., Henseler, J.: Consistent and asymptotically normal PLS estimators for linear structural equations. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 81, 10–23 (2015a)
Dijkstra, T.K., Henseler, J.: Consistent partial least squares path modeling. MIS Q. 39(2), 297–316 (2015b)
Duarte, P.A.O., Raposo, M.L.B.: A PLS Model to Study Brand Preference: An Application to the Mobile Phone Market, in: V. Esposito Vinzi, W. W. Chin, J. Henseler, H. Wang (Ed.). Handbook of partial least squares: Concepts, methods, and applications pp. 449–485 Heidelberg/Dordrecht/London/New York: Springer, (2010)
Edwards, J.R., Bagozzi, R.P.: On the nature and direction of relationships between constructs and measures. Psychol. Methods 5(2), 155–174 (2000)
Fard, M.H., Marvi, R.: Viral marketing and purchase intentions of mobile applications users. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 15(2), 287–301 (2019)
Fishbein, M., Ajzen, I.: Belief, Attitude, Intention, and Behavior: An Introduction to Theory and Research. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA (1975)
Forster J.J.: sample surveys: nonprobability sampling, In: N. J. Smelser, P. B. Baltes (Ed.). International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, pp 13453–13458 United States: Elsevier/Permagon. (2001)
Gaskin, J.: Common Method Bias (CMB) in PLS (partial least squares), askination's Statistics. (2017) http://youtube.com/Gaskination
Goodhue, D.L., Lewis, W., Thompson, R.: Comparing PLS to regression and LISREL: A response to Marcoulides Chin, and Saunders. MIS Q. 36(3), 703–716 (2012a)
Goodhue, D.L., Lewis, W., Thompson, R.: Does PLS have advantages for small sample size or non-normal data? MIS Q. 36(3), 981–1001 (2012b)
Goyette, I., Ricard, L., Bergeron, J., Marticotte, F.: E-WOM scale: word-of-mouth measurement scale for e-services context. Can. J. Adm. Sci. 27(1), 5–23 (2010)
Groß, M.: Exploring the acceptance of technology for mobile shopping: an empirical investigation among Smartphone users. Int. Rev. Retail, Distrib. Consum. Res. 25(3), 215–235 (2014)
Hair, J.F., Ringle, C., Sarstedt, M.: PLS-SEM: Indeed a silver bullet. J Market Theor Pract 19(2), 139–152 (2011)
Hair, J.F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C.M., Mena, J.A.: An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 40(3), 414–433 (2012)
Hair, J.F., Hult, G.T.M., Ringle, C.M., Sarstedt, M.: A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd edn. Sage, Thousand Oaks (2017)
Henseler, J., Ringle, C.M., Sinkovics, R.R.: The use of partial least squares path modeling, in international marketing. New Chall. Int. Market. Adv. Int. Market. 20, 277–319 (2009)
Henseler, J., Dijkstra, T.K., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C.M., Diamantopoulos, A., Straub, D.W., Calantone, R.J.: Common beliefs and reality about PLS comments on Rönkkö and Evermann (2013). Organ. Res. Methods 17(2), 182–209 (2014)
Henseler, J., Ringle, C.M., Sarstedt, M.: A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 43(1), 115–135 (2015)
ICTA Market Data, (2020). Information and Communication Technologies Authority. Electronic Communications Market In Turkey Market Data (2020 Q3). Retrieved from https://www.btk.gov.tr/uploads/pages/pazar-verileri/uc-aylik-pazar-verileri-2020-3-kurumdisi.pdf
Iyzico, (2018). Türkiye’nin Online Ödeme Alışkanlıkları (2017). Retrieved from https://www.iyzico.com/blog/turkiyenin-online-odeme-aliskanliklari-2017-infografik/
Jalilvand, M.R., Samiei, N., Dini, B., Yaghoubi Manzari, P.: Examining the structural relationships of electronic word of mouth, destination image, tourist attitude toward destination and travel intention: an integrated approach. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 1, 134–143 (2012)
Jarvis, C.B., MacKenzie, S.B., Podsakoff, P.M.: A critical review of construct indicators and measurement model misspecification in marketing and consumer research. J. Consum. Res. 30(2), 199–218 (2003)
Kim, B.: The diffusion of mobile data services and applications: exploring the role of habit and its antecedents”. Telecommun. Policy 36, 69–84 (2012)
Kim, S., Baek, T.H., Kim, Y.K., Yoo, K.: Factors affecting stickiness and word of mouth in mobile applications. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 10(3), 177–192 (2016)
Kock, N.: Common method bias in PLS-SEM: A full collinearity assessment approach. Int. J. e-Collaborat. 11(4), 1–10 (2015)
Koller, M., Salzberger, T.: Cognitive dissonance as a relevant construct throughout the decision-making and consumption process – an empirical investigation related to a package tour. J. Cust. Behav. 6(3), 217–227 (2007)
Lee, L., Petter, S., Fayard, D., Robinson, S.: On the use of partial least squares path modeling in accounting research. Int. J. Acc. Inf. Syst. 12(4), 305–328 (2011)
Lin, C.H., Sher, P.J., Shih, H.Y.: Past progress and future directions in conceptualizing customer perceived value. Int. J. Serv. Ind. Manag. 16(3–4), 318–336 (2005)
Moon, E., Domina, T.: Willingness to use fashion mobile applications to purchase fashion products: a comparison between the United States and South Korea. J. Textile Apparel, Technol. Manag. 3, 1–15 (2015)
Nikookar, G., Rahrovy, E., Razi, S., Ghassemi, R.A.: Investigating influential factors on word of mouth in service industries: the case of Iran Airline company. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 177, 217–222 (2015)
Nunnally, J. C., Bernstein, I. H.: The assessment of reliability. Psychom. Theor. 3(1), 248–292 (1994)
Nysveen, H., Pedersen, P.E., Thorbjørnsen, H.: Intentions to use mobile services: antecedents and cross-service comparisons. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 33(3), 330–347 (2005)
Peng, D.X., Lai, F.: Using partial least squares in operations management research: A practical guideline and summary of past research. J. Op. Manag. 30(6) 467–480 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2012.06.002
PwC – Total Retail Survey, (2016) They say they want a revolution, Accessed: 21 April 2019 https://www.pwc.com.tr/en/publications/industrial/retail-consumer/pdf/pwc-total-retail-consumer-survey-2016.pdf
Racherla, P., Furner, C., Babb, J., (2012), Conceptualizing the implications of mobile app usage and stickiness: a research agenda, Accessed: 25 Feb 2019, https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2187056
Rasoolimanesh, S.M., Ringle, C.M., Jaafar, M. and Ramayah, T.: Urban vs. rural destinations: Residents’ perceptions community participation and support for tourism development. Tour. Manag. 60, 147–158 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.11.019
Ringle, C.M., Sarstedt, M., Straub, D.W.: Editor’s comments: a critical look at the use of PLS-SEM in MIS quarterly. MIS Q. 36(1), iii–xiv (2012)
Ringle, C., Wende, S., Becker, J.: SmartPLS 3 (Version 3.2.3). Boenningstedt, Germany: SmartPLS GmbH. (2015)
San-Martín, S., Prodanova, J.: What makes services customers say buy it with a mobile phone?”. J. Serv. Mark. 30(6), 601–614 (2016)
Saprikis, V., Markos, A., Zarmpou, T., Maro, V.: Mobile shopping consumers’ behavior: an exploratory study and review. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 13(1), 71–90 (2018)
Sarstedt, M., Hair, J.F., Ringle, C.M., Thiele, K.O., Gudergan, S.P.: Estimation issues with PLS and CBSEM: where the bias lies!”. J. Bus. Res. 69(10), 3998–4010 (2016)
Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C.M., Hair, J.F.: Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling. In: Christian Homburg, Martin Klarmann, Arnd Vomberg (Ed.) Handbook of Market Research, (Chp. 15, pp.2–40). Publisher: Springer, 2017
SmartPLS, (2018) PLS-SEM Compared With CB-SEM, Accessed: 25 Dec 2018 https://www.smartpls.com/documentation/learn-pls-sem-and-smartpls/pls-sem-compared-with-cbsem
SmartPLS, (2019) Model Fit, Accessed: 25 March 2019 https://www.smartpls.com/documentation/algorithms-and-techniques/model-fit
Tak, P., Panwar, S.: Using UTAUT 2 model to predict mobile app based shopping: evidences from India. J. Indian Bus. Res. 9(3), 248–264 (2017)
Taylor, S., Todd, P.A.: Understanding information technology usage: a test of competing models. Inf. Syst. Res. 6(2), 144–176 (1995)
Turel, O., Serenko, A., Bontis, N.: User acceptance of hedonic digital artifacts: a theory of consumption values perspective. Inform. Manag. 47(1), 53–59 (2010)
Tüsiad, (2017). DİJİTALLEŞEN DÜNYADA EKONOMİNİN İTİCİ GÜCÜ: E-TİCARET, Accessed: 25 March 2019 https://www.eticaretraporu.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/TUSIAD_E-Ticaret_Raporu_2017.pdf
Velázquez, B.M., Blasco, M.F., Saura, I.G.: ICT adoption in hotels and electronic word-of-mouth. Acad. Revista Latinoamericana De Administración 28(2), 227–250 (2015)
Venkatesh, V., Bala, H.: Technology acceptance model 3 and a research agenda on interventions. Decis. Sci 39(2), 273–315 (2008)
Venkatesh, V., Davis, F.D.: A Theoretical extension of technology acceptance model: four longitudinal field studies. Manag. Sci. Inform. 46(2), 186–204 (2000)
Wang, N., Shen, X., Sun, Y.: Transition of electronic word-of-mouth services from web to mobile context: a trust transfer perspective. Decis. Support Syst. 54, 1394–1403 (2013)
Wu, Y.L., Tao, Y.H., Yang, P.C.: The use of unified theory of acceptance and use of technology to confer the behavioral model of 3G mobile telecommunication users. J. Stat. Manag. Syst. 11(5), 919–949 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/09720510.2008.10701351
Yang, H.C.: Bon appetit for apps: young american consumers’ acceptance of mobile applications. J. Comput. Inform. Syst. 53(3), 85–95 (2013)
Yang, H., Zhou, L.: Extending TPB and TAM to mobile viral marketing: An exploratory study on American young consumers' mobile viral marketing attitude intent and behavior. J. Target. Meas. Anal. Market. 19(2), 85–98 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1057/jt.2011.11
Yıldız, O.: A PLS-SEM approach to the consumer adoption of shopping via mobile apps. Int. J. Mobile Communications. 19(5), 589–614 (2021).
Yıldız, O., Kitapci, H.: Exploring factors affecting consumers’ adoption of shopping via mobile applications in Turkey. Int. J. Market. Stud. 10(2), 60–75 (2018)
Funding
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yıldız, O. PLS-SEM bias: traditional vs consistent. Qual Quant 57 (Suppl 4), 537–552 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-021-01289-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-021-01289-2