Abstract
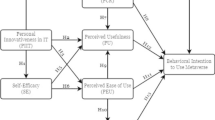
To understand the factors influencing medical robot use, this study developed a conceptual model and hypothesized that personal innovativeness in IT, perceived usefulness of IT and perceived ease of use of IT positively affect attitude toward medical robots, which in turn facilitates medical robot intention and medical robot use. By analyzing data from 276 surveys from Taiwan’s respondents who have employed medical robots, we demonstrate a positive effect of personal innovativeness in IT, perceived usefulness of IT and perceived ease of use of IT on attitude toward medical robots. In addition, attitude toward medical robots has a positive effect on medical robot intention and medical robot use. The main implications of study for medical robots firms are to conduct business activities to stress perceived usefulness of IT and perceived ease of use of IT, they can use Ads to describe the functions and advantages to draw user’ attitude toward medical robots.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, R., Prasad, J.: A conceptual and operational definition of personal innovativeness in the domain of information technology. Inf. Syst. Res. 9(2), 204–215 (1998)
Armstrong, G., Kotler, P.: Marketing, Paper presented at the 5th ed., Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, pp. 153–154 (2000)
Brown, S.A., Venkatesh, V.: Model of adoption of technology in household: a baseline model test and extension incorporating household life cycle. MIS Q. 29(3), 399–426 (2005)
Davis, F.D.: Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 13(3), 319–340 (1989)
DeLone, W.H., Mclean, E.R.: Information system success: the quest for the dependent variable. Inf. Syst. Res. 3, 60–95 (1992)
Fornell, C., Larcker, D.F.: Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 19(1), 39–50 (1981)
Grandom, E., Mykytyn, P.: Theory-based instrumentation to measure the intention to use electronic commerce in small and medium sized businesses. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 44, 44–57 (2004)
Haque, A., Sadeghzadeh, J., Khatibi, A.: Identifying potentiality online sales in Malaysia: a study on customer relationships online shopping. J. Appl. Bus. Res. 22, 119–130 (2006)
Hopkins, N., Sylvester, A., Tate, M.: Motivations for BYOD: An Investigation of the Contents of a 21st Century School Bag, ECIS 2013 Completed Research (2013)
Ida, R., Saud, M., Mustain, M.: Persistence of social media on political activism and engagement among Indonesian and Pakistani Youths. J. Web-based Commun. Inderscience Publ. (2020)
Ida, R., Saud, M., Mashud, M.: An empirical analysis of social media usage, political learning and participation among youth: a comparative study of Indonesia and Pakistan. Qual. Quantity: Int. J. Methodol. 1, 1–13 (2020)
Lewis, W., Agarwal, R., Sambamurthy, V.: Sources of influence on beliefs about information technology use: an empirical study of knowledge workers. MIS Q. 27(4), 657–678 (2003)
Nüesch, R., Alt, R., Puschmann, T.: Hybrid customer interaction. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 57(1), 73–82 (2015)
Nunnally, J.C.: Psychometric Theory. McGraw-Hill, New York (1978)
Nunnally, J.C., Bernstein, I.H.: Psychometric Theory, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York (1994)
Schiffman, L.G., Kanuk, L.L.: Consumer Behavior. Prentice Hall, Wisconsin (2000)
Taylor, S., Todd, P.A.: Decomposition of cross effects in the theory of planned behavior: a study of consumer adoption intentions. Int. J. Res. Mark. 12, 137–155 (1995)
Udell, J.G.: Can attitude measurement predict consumer behaviour. J. Mark. 29, 46–50 (1965)
Vantomme, D., Geuens, M., De Houwer, J., De Pelsmacker, P.: Implicit attitudes toward green consumer behaviour. Psychol. Belgica 45, 217–239 (2005)
Weeger, A., Gewald, H.: Factors influencing future employees decision-making to participate in a BYOD program: does risk matter? In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS), Tel-Aviv, Israel (2014)
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hung, CL. The research of factors influencing advanced medical robot use. Qual Quant 55, 385–393 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-020-01007-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-020-01007-4