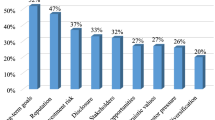
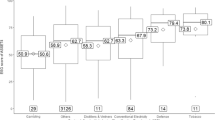
Abstract
In recent years, environmental problems have occurred frequently in China, and the relationship between environmental performance (EP) and financial performance (FP) plays an indispensable role in exploring the internalization of corporate environmental responsibility. Using a sample of Chinese listed firms in heavily polluting industries and collected data of the Unit Sewage Fee, we empirically examine the impact of EP on FP. Our empirical results show a concave-down quadratic relationship between EP and FP. After heavily polluting industries became subject to stricter environmental disclosure regulations, however, we found that the quadratic relationship between EP and FP became weaker. Moreover, we revealed that for state-owned firms, the quadratic relationship between EP and FP is not as obvious as it is for non-state-owned firms. Our paper contributes to the growing literature on EP management. It also offers evidence of experience in perfecting the design of enterprise environmental information disclosure systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Based on the industry classification of China Securities Regulatory Commission(CSRC).
Some firms do not disclose the sewage fee every year.
References
Aragoncorrea, J.: Strategic proactivity and firm approach to the natural environment. Acad. Manag. J. 41(5), 556–567 (1998)
Aschehoug, S.H., Boks, C., Støren, S.: Environmental information from stakeholders supporting product development. J. Clean. Prod. 31(12), 1–13 (2012)
Bruton, G.D., Peng, M.W., Ahlstrom, D., Stan, C.V., Xu, K.: State-owned enterprises around the world as hybrid organizations. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 29(1), 92–114 (2015)
Chang, L., Li, W., Lu, X.: Government engagement, environmental policy, and environmental performance: evidence from the most polluting Chinese listed firms. Bus. Strategy Environ. 24(1), 1–19 (2015)
Chen, F., Xu, Y.: Democratization in the host country and institutional risk of cross-border M&A: an empirical study on Chinese listed enterprises. Qual. Quant. 48(2), 1013–1025 (2014)
Cohen, M.A., Fenn, S., Naimon, J.S.: Environmental and Financial Performance: Are They Related?. Investor Responsibility Research Center, Environmental Information Service, New York City (1995)
Coleman, L.: Losses from failure of stakeholder sensitive processes: financial consequences for large US companies from breakdowns in product, environmental, and accounting standards. J. Bus. Ethics 98(2), 247–258 (2011)
Connors, E., Johnston, H.H., Gao, L.S.: The informational value of Toxics Release Inventory performance. Sustain. Acc. Manag. Policy J. 4(1), 32–55 (2013)
Dögl, C., Holtbrügge, D.: Corporate environmental responsibility, employer reputation and employee commitment: an empirical study in developed and emerging economies. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 25(12), 1739–1762 (2014)
Gerde, V.W., Logsdon, J.M.: Measuring environmental performance: use of the toxics release inventory (tri) and other us environmental databases. Bus. Strategy Environ. 10(5), 269–285 (2010)
Gilley, K.M., Worrell, D.L., Iii, W.N.D., Abuzar, E.-J.: Corporate environmental initiatives and anticipated firm performance: the differential effects of process-driven versus product-driven greening initiatives. J. Manag. 26(6), 1199–1216 (2000)
Gonenc, H., Scholtens, B.: Environmental and financial performance of fossil fuel firms: a closer inspection of their interaction. Ecol. Econ. 132, 307–328 (2017)
Hart, S.L.: A natural-resource-based view of the firm. Acad. Manag. Rev. 20(4), 986–1014 (1995)
Hart, S.L., Ahuja, G.: Does it pay to be green? an empirical examination of the relationship between emission reduction and firm performance. Bus. Strategy Environ. 5(1), 30–37 (1996)
He, Y., Chiu, Y., Zhang, B.: The impact of corporate governance on state-owned and non-state-owned firms efficiency in China. N. Am. J. Econ. Finance 33, 252–277 (2015)
Horváthová, E.: Does environmental performance affect financial performance? A meta-analysis. Ecol. Econ. 70(1), 52–59 (2010)
Horváthová, E.: The impact of environmental performance on firm performance: short-term costs and long-term benefits? Ecol. Econ. 84(2), 91–97 (2012)
Iwata, H., Okada, K.: How does environmental performance affect financial performance? Evidence from Japanese manufacturing firms. Ecol. Econ. 70(9), 1691–1700 (2011)
Jaggi, B., Freedman, M.: An examination of the impact of pollution performance on economic and market performance: pulp and paper firms. J. Bus. Finance Acc. 19(5), 697–713 (2006)
Khanna, T., Nohria, G.N.: The dynamics of learning alliances: competition, cooperation, and relative scope. Strateg. Manag. J. 19(3), 193–210 (1998)
Kubas, A., Inan, I.H., Unakitan, G., Erbay, E.R.: The estimation of the relationships between water-natural gas usage and discharge-emission permission by using binary logistic model for the industrial establishments. Qual. Quant. 42(1), 35–44 (2008)
Latan, H., Chiappetta Jabbour, C.J., Beatriz, L.D.S.J.A., Renwick, D.W.S., Wamba, S.F., Shahbaz, M.: ‘Too-much-of-a-good-thing’? The role of advanced eco-learning and contingency factors on the relationship between corporate environmental and financial performance. J. Environ. Manag. 220, 163–172 (2018)
Li, Q., Luo, W., Wang, Y., Wu, L.: Firm performance, corporate ownership, and corporate social, responsibility disclosure in China. Bus. Ethics A Eur. Rev. 22(2), 159–173 (2013)
Lucato, W.C., Costa, E.M., Cardoso, D.O.N.G.: The environmental performance of SMEs in the Brazilian textile industry and the relationship with their financial performance. J. Environ. Manag. 203, 550–556 (2017)
Montabon, F., Sroufe, R., Narasimhan, R.: An examination of corporate reporting, environmental management practices and firm performance. J. Oper. Manag. 25(5), 998–1014 (2007)
Muhammad, N., Scrimgeour, F., Reddy, K., Abidin, S.: The impact of corporate environmental performance on market risk: the Australian industry case. J. Bus. Ethics 132(2), 347–362 (2015)
Muhammad, N., Scrimgeour, F., Reddy, K., Abidin, S.: Emission indices for hazardous substances: an alternative measure of corporate environmental performance. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 23(1), 15–26 (2016)
Nasrin, S., Rasiah, R., Baskaran, A., Masud, M.M.: What determines the financial performance of microfinance institutions in Bangladesh? a panel data analysis. Qual. Quant. 52(3), 1409–1422 (2018)
Nishitani, K., Jannah, N., Kaneko, S.: Does corporate environmental performance enhance financial performance? An empirical study of indonesian firms. Environ. Dev. 23, 10–21 (2017)
Porter, M.E., Linde, C.V.D.: Toward a new conception of the environment–competitiveness relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 9(4), 97–118 (1995)
Qi, G.Y., Zeng, S.X., Shi, J.J., Meng, X.H., Lin, H., Yang, Q.X.: Revisiting the relationship between environmental and financial performance in Chinese industry. J. Environ. Manag. 145, 349–356 (2014)
Qiu, R., Xu, J., Zeng, Z.: Carbon emission allowance allocation with a mixed mechanism in air passenger transport. J. Environ. Manag. 200, 204–216 (2017)
Rassier, D.G., Earnhart, D.: Does the porter hypothesis explain expected future financial performance? The effect of clean water regulation on chemical manufacturing firms. Environ. Resour. Econ. 45(3), 353–377 (2010)
Sarkis, J., Cordeiro, J.J.: An empirical evaluation of environmental efficiencies and firm performance: pollution prevention versus end-of-pipe practice. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 135(1), 102–113 (2001)
Sen, P., Roy, M., Pal, P.: Exploring role of environmental proactivity in financial performance of manufacturing enterprises: a structural modelling approach. J. Clean. Prod. 108, 583–594 (2015)
Song, H., Zhao, C., Zeng, J.: Can environmental management improve financial performance: an empirical study of A-shares listed companies in China. J. Clean. Prod. 141, 1051–1056 (2017)
Tan, S.H., Habibullah, M.S., Tan, S.K., Choon, S.W.: The impact of the dimensions of environmental performance on firm performance in travel and tourism industry. J. Environ. Manag. 203, 603–611 (2017)
Wagner, M.: The role of corporate sustainability performance for economic performance: a firm-level analysis of moderation effects. Ecol. Econ. 69(7), 1553–1560 (2010)
Wagner, M., Schaltegger, S., Wehrmeyer, W.: The relationship between the environmental and economic performance of firms: what does theory propose and what does empirical evidence tell us? Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 9(3), 133–146 (2012)
Wang, L.: The changes of China’s environmental policies in the latest 30 years. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2, 1026–1212 (2010)
Xie, C., Luo, C., Yu, X.: Financial distress prediction based on SVM and MDA methods: the case of Chinese listed companies. Qual. Quant. 45(3), 671–686 (2011)
Xu, X., Zeng, Z., Xu, J., Zhang, M.: Fuzzy dynamical system scenario simulation-based cross-border financial contagion analysis: a perspective from international capital flows. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 25(2), 439–459 (2017)
Zeng, Z., Zhu, W., Ke, R., Ash, J., Wang, Y., Xu, J., Xu, X.: A generalized nonlinear model-based mixed multinomial logit approach for crash data analysis. Accid. Anal. Prev. 99, 51–65 (2017)
Zhu, Q., Liu, J., Lai, K.H.: Corporate social responsibility practices and performance improvement among Chinese national state-owned enterprises. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 171, 417–426 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Humanities and Social Sciences Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (Grant Nos. 17YJC630119, 16YJC630089). It was also supported by Soft Science Program of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2019JDR0155), by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. JBK1801009) and the Research Center for System Sciences and Enterprise Development (Grant No. Xq18B07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, F., Ma, Y., Wang, R. et al. Does environmental performance affect financial performance? Evidence from Chinese listed companies in heavily polluting industries. Qual Quant 53, 1941–1958 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-019-00849-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-019-00849-x