Abstract
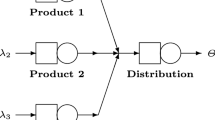
We study the dynamic admission control for a finite shared buffer with support of multiclass traffic under Markovian assumptions. The problem is often referred to as buffer sharing in the literature. From the linear programming (LP) formulation of the continuous-time Markov decision process (MDP), we construct a hierarchy of increasingly stronger LP relaxations where the hierarchy levels equal the number of job classes. Each relaxation in the hierarchy is obtained by projecting the original achievable performance region onto a polytope of simpler structure. We propose a heuristic policy for admission control, which is based on the theory of Marginal Productivity Index (MPI) and the Lagrangian decomposition of the first order LP relaxation. The dual of the relaxed buffer space constraint in the first order LP relaxation is used as a proxy to the cost of buffer space. Given that each of the decomposed queueing admission control problems satisfies the indexability condition, the proposed heuristic accepts a new arrival if there is enough buffer space left and the MPI of the current job class is greater than the incurred cost of buffer usage. Our numerical examples for the cases of two and eight job classes show the near-optimal performance of the proposed MPI heuristic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aein, J.M.: A multi-user-class, blocked-calls-cleared, demand access model. IEEE Trans. Commun. COM-26(3), 378–385 (1978)
Ahlfors, U., Fyhn, A., Tufvesson, P.: Method and arrangement for managing packet queues in switches. US Patent 6977940 (Dec. 2005)
Aweya, J., Montuno, D.Y., Ouellette, M.: Method and apparatus for active queue management based on desired queue occupancy. US Patent 6690645 (Feb. 2004)
Bertsekas, D.P.: Dynamic Programming and Optimal Control, 3rd edn. Athena Scientific, Nashua (2005)
Bertsimas, D., Niño-Mora, J.: Restless bandits, linear programming relaxations and primal-dual index heuristic. Oper. Res. 48(1), 80–90 (2000)
Choudhury, A.K., Hahne, E.L.: Dynamic queue length thresholds in a shared memory ATM switch. US Patent 5541912 (July 1996)
Cidon, I., Georgiadis, L., Guerin, R., Khamisy, A.: Optimal buffer sharing. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 13(7), 1229–1240 (1995)
Eng, K.Y., Gitlin, R.D., Karol, M.J.: Channel sharing and memory sharing in a packet switching system. US Patent 5457679 (Oct. 1995)
Freedman, D., Diaconis, P.: On the histogram as a density estimator: L 2 theory. Z. Wahrsch. Verw. Geb. 57(4), 453–476 (1981)
Foschini, G.J., Gopinath, B.: Sharing memory optimally. IEEE Trans. Commun. COM-31(3), 352–360 (1983)
Foschini, G.J., Gopinath, B., Hayes, J.F.: Optimal allocation of servers to two types of competing customers. IEEE Trans. Commun. COM-29(7), 1051–1055 (1981)
Han, M., Kwon, Y., Nam, H., Rhee, W.: Adaptive buffer partitioning method for shared buffer switch and switch therefor. US Patent 7009988 (Mar. 2006)
Janoska, M.W., Heller, A.D., Pezeshki-Esfahani, H.: Method and apparatus for data buffer management in a communications switch. US Patent 6539024 (Mar. 2003)
Jordan, S., Varaiya, P.P.: Control of multiple service, multiple resource communication networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 42(11), 2979–2988 (1994)
Lovász, L., Schrijver, A.: Cones of matrices and set functions and 0-1 optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 166–190 (1991)
Mitra, D.: Method for shared memory management in network nodes. US Patent 5909547 (June 1999)
Niño-Mora, J.: Restless bandits, partial conservation laws and indexability. Adv. Appl. Probab. 33, 76–98 (2001)
Niño-Mora, J.: Dynamic allocation indices for restless projects and queueing admission control: a polyhedral approach. Math. Program. Ser. A 93(3), 361–413 (2002)
Niño-Mora, J.: A (2/3)n 3 fast-pivoting algorithm for the Gittins index and optimal stopping for a Markov chain. INFORMS J. Comput. 19(4), 596–606 (2006)
Niño-Mora, J.: Marginal productivity index policies for scheduling a multiclass delay-/loss-sensitive queue. Queueing Syst. 54(4), 281–312 (2006)
Niño-Mora, J.: Restless bandit marginal productivity indices, diminishing returns and optimal control of make-to-order/make-to-stock M/G/1 queues. Math. Oper. Res. 31(1), 50–84 (2006)
Niño-Mora, J.: Dynamic priority allocation via restless bandit marginal productivity indices. Top 15(2), 161–198 (2007)
Ren, J.-F., Landry, R.J.: Static and dynamic flow control using virtual input queueing for shared memory Ethernet switches. US Patent 6456590 (Sep. 2002)
Ross, K.W.: Multiservice Loss Models for Broadband Telecommunication Networks. Springer, New York (1995)
Varma, S., Daniel, T.: Shared memory fabric architecture for very high speed ATM switches. US Patent 5831980 (Nov. 1998)
Whittle, P.: Restless bandits: activity allocation in a changing world. J. Appl. Probab. 25A, 287–298 (1988)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Nyberg, C. Linear programming relaxations and marginal productivity index policies for the buffer sharing problem. Queueing Syst 60, 247–269 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11134-008-9096-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11134-008-9096-3
Keywords
- Buffer sharing problem
- Multi-class queueing system
- Linear programming relaxation
- Marginal productivity index policy
- Markov decision process