Abstract
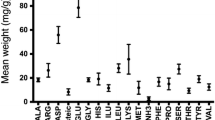
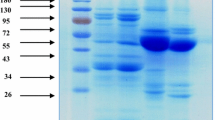
Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) is a good source of protein, vitamins, minerals and complex carbohydrates. The objective was to compare protein profile, including anti-nutrient proteins, and potential bioactive peptides of improved common bean cultivars grown in Mexico and Brazil. Bean protein isolates (BPI) were prepared from 15 common bean cultivars and hydrolyzed using pepsin/pancreatin. Thirteen proteins were identified by SDS-PAGE and protein in-gel tryptic-digestion-LC/MS. Protein profile was similar among common bean cultivars with high concentrations of defense-related proteins. Major identified proteins were phaseolin, lectin, protease and α-amylase inhibitors. Lectin (159.2 to 357.9 mg lectin/g BPI), Kunitz trypsin inhibitor (inh) (4.3 to 75.5 mg trypsin inh/g BPI), Bowman-Birk inhibitor (5.4 to 14.3 μg trypsin-chymotrypsin inh/g BPI) and α-amylase inhibitor activity (2.5 to 14.9 % inhibition relative to acarbose/mg BPI) were higher in Mexican beans compared to Brazilian beans. Abundant peptides were identified by HPLC-MS/MS with molecular masses ranging from 300 to 1500 Da and significant sequences were SGAM, DSSG, LLAH, YVAT, EPTE and KPKL. Potential bioactivities of sequenced peptides were angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE), dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor (DPP-IV) and antioxidant capacity. Peptides from common bean proteins presented potential biological activities related to control of hypertension and type-2 diabetes.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Acarbose
- BBI:
-
Bowman-Birk inhibitor
- BPI:
-
Bean protein isolate
- BRS:
-
Brazilian
- FJ:
-
Flor de Junio
- FM:
-
Flor de Mayo
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- inh:
-
Inhibitor
- KTI:
-
Kunitz trypsin inhibitor
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
References
Sathe SK, Deshpande SS (2003) Beans. In: Encyclopedia of Food Science Technology, Academic Press, London, UK, pp 403–412
Campos-Vega R, Reynoso-Camacho R, Pedraza-Aboytes G, Acosta-Gallegos JA, Guzman-Maldonado SH, Paredes-López O, Oomah BD, Loarca-Pina G (2009) Chemical composition and in vitro polysaccharide fermentation of different beans. J Food Sci 74(7):59–65
Paredes-López O, Guevara-Lara F, Bello-Pérez LA (2006) Los Alimentos Mágicos de las Culturas Indígenas Mesoamericanas. Fondo de Cultura Económica 3:59–81
Celleno L, Tolaini MV, D’Amore A, Perricone NV, Preuss HG (2007) A dietary supplement containing standardized Phaseolus vulgaris extract influences body composition of overweight men and women. Int J Med Sci 4:45–52
Oseguera-Toledo M, Gonzalez de Mejia E, Dia VP, Amaya-Llano S (2011) Common bean hydrolysates inhibit inflammation in LPS-induced macrophages through suppression of NF- ΚB pathways. Food Chem 127:1175–1185
Hernández-Saavedra D, Mendoza-Sánchez M, Hernández-Montiel HL, Guzmán-Maldonado HS, Loarca-Piña G, Salgado LM, Reynoso-Camacho R (2013) Cooked common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) protect against β-cell damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 68:207–212
Feregrino-Perez AA, Piñol-Felis C, Gomez-Arbones X, Guevara-González RG, Campos-Vega R, Acosta-Gallegos J, Loarca-Piña G (2014) A non-digestible fraction of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis during early carcinogénesis. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 69:248–254
Pereira MP, Tavano (2014) Use of different spices as potential natural antioxidant additives on cooked beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). Increase of DPPH radical scavenging activity and total phenolic content. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 69:337–343
Mojica L, Chen K, Gonzalez de Mejia E (2014) Impact of commercial precooking of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) on the generation of peptides, after pepsin–pancreatin hydrolysis, capable to inhibit dipeptidyl peptidase-IV. J Food Sci 80:H188–H198
López-Barrios JA, Gutiérrez-Uribe S, Serna-Saldívar S (2014) Bioactive peptides and hydrolysates from pulses and their potential use as functional ingredients. J Food Sci 79:273–283
Luna-Vital DA, Mojica L, Gonzalez de Mejia E, Mendoza S, Loarca-Pina G (2015) Biological potential of protein hydrolysates and peptides from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): a review. Food Res Int. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2014.11.024
Sarmadi A, Ismail A (2010) Antioxidative peptides from food proteins: a review. Peptides 31:1949–1956
Alves M, Chavez I, Carrilho D, Veloso M, Pinto CR (2010) Detection of novel trypsin inhibitors in the cotyledons of Phaseolus vulgaris seeds. J Plant Physiol 167:848–854
Chan SY, Zhang Y, Ng TB (2013) Brown kidney bean Bowman-Birk trypsin inhibitor is heat and pH stable and exhibits anti-proliferative activity. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169:1306–1314
Mittal A, Kansal R, Kalia V, Tripathi M, Gupta VK (2014) A kidney bean trypsin inhibitor with an insecticidal potential against Helicoverpa armigera and Spodoptera litura. Acta Physiol Plant 36:525–539
Zaugg I, Magni C, Panzeri D, Maminati MG, Bollini R, Benrey B, Bacher S, Sparvoli F (2013) QUES, a new Phaseolus vulgaris genotype resistant to common bean weevils, contains the arcelin-8 allele coding for new lectin-related variants. Theor Appl Genet 126:647–661
Marsolais F, Pajak A, Yin F et al (2010) Proteomic analysis of common bean seed with storage protein deficiency reveals up-regulation of sulfur-rich proteins and starch and raffinose metabolic enzymes, and down-regulation of the secretory pathway. J Proteomics 73:1587–1600
Silva-Sanchez C, de la Rosa AP B, Leon-Galvan MF, De Lumen BO, De Leon-Rodrıguez A, Gonzalez de Mejıa E (2008) Bioactive peptides in amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) seed. J Agric Food Chem 56:1233–1240
Dia VP, Gomez T, Vernaza G, Berhow M, Chang YK, Gonzalez de Mejia E (2012) Bowman-Birk and Kunitz protease inhibitors among antinutrients and bioactives modified by germination and hydrolysis in Brazilian soybean cultivar BRS 133. J Agric Food Chem 60:7886–7894
Megías C, Yust M, Pedroche J, Lquari H, Giron-Calle J, Alaiz M (2009) Purification of an ACE inhibitory peptide after hydrolysis of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) protein isolates. J Agric Food Chem 52:1928–1932
de Souza-Rocha T, Real LMH, Chang YK, González de Mejía E (2014) Impact of germination and enzymatic hydrolysis of cowpea bean (Vigna unguiculata) on the generation of peptides capable of inhibiting dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Food Res Int 64:799–809
Rui X, Boye J, Ribereau S, Simpson B, Prasher S (2011) Comparative study of the composition and thermal properties of protein isolates prepared from nine Phaseolus vulgaris legume varieties. Food Res Int 44:2497–2504
Montoya C, Lalles J, Beebe S, Leterme P (2010) Phaseolin diversity as a possible strategy to improve the nutritional value of common beans. Food Res Int 43:443–449
Carrasco-Castilla J, Hernandez-Alvarez A, Jimenez-Martinez C, Jacinto-Hernandez C, Alaiz M, Giron-Calle J, Vioque J, Davila-Ortiz G (2012) Antioxidant and metal chelating activities of Phaseolus vulgaris L. var. Jamapa protein isolates, phaseolin and lectin hydrolysates. Food Chem 131:1157–1164
Tang C, Chen L, Ma C (2009) Thermal aggregation, amino acid composition and in vitro digestibility of vicilin-rich protein isolates from three Phaseolus legumes: a comparative study. Food Chem 113:957–963
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Ing. José Ángel Cid Ríos, Dr. Jorge Acosta-Gallegos and Dr. Hercia Stampini Duarte Marino for providing bean samples from Mexico and Brazil.
Funding sources
LM was supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia CONACyT—Mexico. Funds provided by a research partnership National University, México / University of Illinois.
Conflict of Interest
Luis Mojica does not have a Conflict of Interest.
Elvira Gonzalez de Mejia does not have a Conflict of Interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 35 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mojica, L., de Mejía, E.G. Characterization and Comparison of Protein and Peptide Profiles and their Biological Activities of Improved Common Bean Cultivars (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) from Mexico and Brazil. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 70, 105–112 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-015-0477-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-015-0477-6