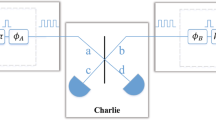
Abstract
Bell experiments require post-selection of data to define coincident detections. In the case of stations of observation placed far away from each other, this implies a heavy and time consuming numerical task of convolution of time series, and may lead to poor results. The core of the problem is to synchronize independent clocks during long observation runs. A pulsed source gets rid of clocks’ drift, but there is still the problem of identifying the same pulse in each remote station. We test using a “frequency modulated” pulsed source to achieve it. This method is found to immediately and optimally define the set of entangled pairs. Besides, it is robust against a hostile adversary in comparison with GPS-synchronization. The tested method is of interest in both pure and applied experiments with entangled states observed in remote stations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekert, A.: “Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661 (1991)
Clauser, J., Shimony, A.: Bell’s theorem: experimental tests and implications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 41, 1881 (1978)
Hnilo, A., et al.: Low dimension dynamics in the EPRB experiment with random variable analyzers. Found. Phys. 37, 80 (2007)
Hadi Madjid, F., Myers, J.M.: Clocks without ‘Time’ in entangled-state experiments. Entropy 22, 434 (2020)
Agüero, M., et al.: Measuring the entanglement of photons produced by a nanosecond pulsed source. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 31, 3088 (2014)
Agüero, M., et al.: Testing a hypothetical transient deviation from quantum mechanics: preliminary results. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 40(4), C28–C34 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This work received support from the grants N62909-18-1-2021 Office of Naval Research Global (USA), PIP 202200484CO and PUE 229-2018-0100018CO CONICET (Argentina).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Agüero, M., Hnilo, A., Kovalsky, M. et al. Frequency-modulated pulsed Bell setup avoids post-selection. Quantum Inf Process 22, 450 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-04202-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-04202-y