Abstract
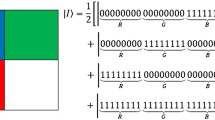
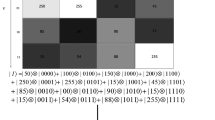
The arithmetic of finite fields with characteristic 2 is central in many cryptographic algorithms. Based on the normal basis representation for elements of the finite field \(\mathbb {F}_{2^n}\), quantum circuits for addition and multiplication have complexities O(n) and \(O(n^3)\), respectively. However, the complexity of the quantum circuit performing multiplication in \(\mathbb {F}_{2^n}\) can be reduced to \(O(n^2)\) provided that \(\mathbb {F}_{2^n}\) contains an optimal normal basis. In this paper, a lossless quantum circuit for the affine transforms on \(\mathbb {F}_{2^n}\) is designed with the quadratic time complexity for some values of n. Moreover, each constituent of the affine transforms on \(\mathbb {F}_{2^n}\) is a unitary operation, and accordingly, the domain of these transforms can be extended to the \(2^n\)-dimensional Hilbert space \(\mathbb {H}^{\otimes n}\). In addition, these transforms are one–one mappings from the set of computational basis states, of \(\mathbb {H}^{\otimes n}\), to itself. This property of affine transforms confirms that these transforms can be used in the encryption algorithms for quantum images because a quantum image uses the computational basis states for storing the color and positional information of pixels. Accordingly, a fast quantum image encryption algorithm combining affine transforms with fractional-order Lorenz-like system is presented for the novel quantum representation of color digital images. A selected pair of affine transforms is used to scramble the position information of the quantum image, while the color information of red, blue, and green layers of the scrambled quantum image is encrypted through controlled right translations determined by the fractional-order Lorenz-like system. Analyses of the time complexity reveal that the proposed quantum image scrambling scheme is exponentially faster than some state-of-the-art schemes. Simulation results confirm that the newly suggested encryption algorithm is fast, robust, and reliable.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (2002)
Feynman, R.P.: Simulating physics with computers. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 21(6), 467–488 (1982)
Deutsch, D., Jozsa, R.: Rapid solution of problems by quantum computation. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 439(1907), 553–558 (1992)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings of 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 124–134. IEEE (1994)
Grover, L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 212–219. ACM (1996)
Ashikhmin, A., Litsyn, S., Tsfasman, M.A.: Asymptotically good quantum codes. Phys. Rev. A 63(3), 032311 (2001)
Ashikhmin, A., Knill, E.: Nonbinary quantum stabilizer codes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 47(7), 3065–3072 (2001)
Trugenberger, C.A.: Probabilistic quantum memories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(6), 067901 (2001)
Trugenberger, C.A.: Phase transitions in quantum pattern recognition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89(27), 277903 (2002)
Venegas-Andraca, S.E., Bose, S.: Storing, processing, and retrieving an image using quantum mechanics. In: Quantum Information and Computation, vol. 5105, pp. 137–148. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2003)
Klappenecker, A., Rotteler, M.: Discrete cosine transforms on quantum computers. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis. ISPA 2001, pp. 464–468. IEEE (2001)
Fijany, A., Williams, C.P.: Quantum wavelet transforms: fast algorithms and complete circuits. In: Quantum Computing and Quantum Communications, pp. 10–33. Springer (1999)
Beach, G., Lomont, C., Cohen, C.: Quantum image processing (quip). In: Proceedings of 32nd Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop, pp. 39–44. IEEE (2003)
Caraiman, S., Manta, V.I.: New applications of quantum algorithms to computer graphics: the quantum random sample consensus algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM Conference on Computing Frontiers, pp. 81–88. ACM (2009)
Caraiman, S., Manta, V.I.: Image segmentation on a quantum computer. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(5), 1693–1715 (2015)
Venegas-Andraca, S.E., Ball, J.L.: Processing images in entangled quantum systems. Quantum Inf. Process. 9(1), 1–11 (2010)
Le, P.Q., Dong, F., Hirota, K.: A flexible representation of quantum images for polynomial preparation, image compression, and processing operations. Quantum Inf. Process. 10(1), 63–84 (2011)
Zhang, Y., Kai, L., Gao, Y., Wang, M.: Neqr: a novel enhanced quantum representation of digital images. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(8), 2833–2860 (2013)
Sun, B., Le, P.Q., Iliyasu, A.M., Yan, F., Garcia, J.A., Dong, F., Hirota, K.: A multi-channel representation for images on quantum computers using the rgb\(\alpha \) color space. In: 2011 IEEE 7th International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing, pp. 1–6. IEEE (2011)
Li, H.-S., Qingxin, Z., Lan, S., Shen, C.-Y., Zhou, R., Mo, J.: Image storage, retrieval, compression and segmentation in a quantum system. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(6), 2269–2290 (2013)
Yuan, S., Mao, X., Xue, Y., Chen, L., Xiong, Q., Compare, A.: Sqr: a simple quantum representation of infrared images. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(6), 1353–1379 (2014)
Zhang, Y., Kai, L., Gao, Y., Kai, X.: A novel quantum representation for log-polar images. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(9), 3103–3126 (2013)
Sun, B., Iliyasu, A., Yan, F., Dong, F., Hirota, K.: An rgb multi-channel representation for images on quantum computers. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inf. 17(3) (2013)
Jiang, N., Wang, L.: Quantum image scaling using nearest neighbor interpolation. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(5), 1559–1571 (2015)
Li, H.-S., Fan, P., Xia, H.-Y., Peng, H., Song, S.: Quantum implementation circuits of quantum signal representation and type conversion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 66(1), 341–354 (2018)
Sang, J., Wang, S., Li, Q.: A novel quantum representation of color digital images. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(2), 42 (2017)
Li, H.-S., Chen, X., Xia, H., Liang, Y., Zhou, Z.: A quantum image representation based on bitplanes. IEEE Access 6, 62396–62404 (2018)
Wang, L., Ran, Q., Ma, J., Siyuan, Yu., Tan, L.: Qrci: a new quantum representation model of color digital images. Opt. Commun. 438, 147–158 (2019)
Liu, K., Zhang, Y., Kai, L., Wang, X., Wang, X.: An optimized quantum representation for color digital images. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(10), 2938–2948 (2018)
Abdolmaleky, M., Naseri, M., Batle, J., Farouk, A., Gong, L.-H.: Red-green-blue multi-channel quantum representation of digital images. Optik 128, 121–132 (2017)
Khan, R.A.: An improved flexible representation of quantum images. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(7), 1–19 (2019)
Jie, S., Guo, X., Liu, C., Shuhan, L., Li, L.: An improved novel quantum image representation and its experimental test on ibm quantum experience. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–13 (2021)
Nasr, N., Younes, A., Elsayed, A.: Efficient representations of digital images on quantum computers. Multim. Tools Appl. 80, 34019–34034 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11355-4
Yang, Y.-G., Jia, X., Sun, S.-J., Pan, Q.-X.: Quantum cryptographic algorithm for color images using quantum fourier transform and double random-phase encoding. Inf. Sci. 277, 445–457 (2014)
Wang, J., Geng, Y.-C., Han, L., Liu, J.-Q.: Quantum image encryption algorithm based on quantum key image. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(1), 308–322 (2019)
Heidari, S., Vafaei, M., Houshmand, M., Tabatabaey-Mashadi, N.: A dual quantum image scrambling method. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(1), 9 (2019)
Li, X.-Z., Chen, W.-W., Wang, Y.-Q.: Quantum image compression-encryption scheme based on quantum discrete cosine transform. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(9), 2904–2919 (2018)
Jiang, N., Dong, X., Hu, H., Ji, Z., Zhang, W.: Quantum image encryption based on henon mapping. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1–13 (2019)
Tan, R.-C., Lei, T., Zhao, Q.-M., Gong, L.-H., Zhou, Z.-H.: Quantum color image encryption algorithm based on a hyper-chaotic system and quantum fourier transform. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(12), 5368–5384 (2016)
Ran, Q., Wang, L., Ma, J., Tan, L., Siyuan, Yu.: A quantum color image encryption scheme based on coupled hyper-chaotic lorenz system with three impulse injections. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(8), 188 (2018)
Lorenz, E.N.: Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 20(2), 130–141 (1963)
Li, P., Zhao, Y.: A simple encryption algorithm for quantum color image. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(6), 1961–1982 (2017)
Ran, Q., Wang, L., Ma, J., Tan, L., Siyuan, Yu.: A quantum color image encryption scheme based on coupled hyper-chaotic lorenz system with three impulse injections. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(8), 1–30 (2018)
Khan, M., Rasheed, A.: Permutation-based special linear transforms with application in quantum image encryption algorithm. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(10), 1–21 (2019)
Vedral, V., Barenco, A., Ekert, A.: Quantum networks for elementary arithmetic operations. Phys. Rev. A 54(1), 147 (1996)
Jiang, N., Wen-Ya, W., Wang, L.: The quantum realization of arnold and fibonacci image scrambling. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(5), 1223–1236 (2014)
Jiang, N., Wang, L.: Analysis and improvement of the quantum arnold image scrambling. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(7), 1545–1551 (2014)
Zhou, N.R., Hua, T.X., Gong, L.H., Pei, D.J., Liao, Q.H.: Quantum image encryption based on generalized arnold transform and double random-phase encoding. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(4):1193–1213 (2015)
Zhou, R.-G., Sun, Y.-J., Fan, P.: Quantum image gray-code and bit-plane scrambling. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(5), 1717–1734 (2015)
Liang, H.-R., Tao, X.-Y., Zhou, N.-R.: Quantum image encryption based on generalized affine transform and logistic map. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(7), 2701–2724 (2016)
Zhou, N., Yiqun, H., Gong, L., Li, G.: Quantum image encryption scheme with iterative generalized arnold transforms and quantum image cycle shift operations. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(6), 164 (2017)
Zhou, N., Yan, X., Liang, H., Tao, X., Li, G.: Multi-image encryption scheme based on quantum 3d arnold transform and scaled zhongtang chaotic system. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(12), 338 (2018)
Omura, J.K., Massey, J.L.: Computational method and apparatus for finite field arithmetic, May 6 1986. US Patent 4587627
Mullin, R.C., Onyszchuk, I.M., Vanstone, S.A., Wilson, R.M.: Optimal normal bases in GF(pn). Disc. Appl. Math. 22(2), 149–161 (1989)
Gao, S., Lenstra, H.W.: Optimal normal bases. Des. Codes Crypt. 2(4), 315–323 (1992)
Ash, D.W., Blake, I.F., Vanstone, S.A.: Low complexity normal bases. Discret. Appl. Math. 25(3), 191–210 (1989)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M., Rasheed, A. A fast quantum image encryption algorithm based on affine transform and fractional-order Lorenz-like chaotic dynamical system. Quantum Inf Process 21, 134 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03474-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03474-0