Abstract
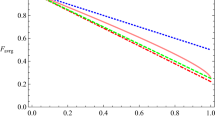
Quantum secret sharing is a way to share secret messages among the clients in a group with complete security. For the first time, Hillery et al. (Phys Rev A 59:1829, 1999) proposed the quantum version of classical secret sharing protocol using GHZ states. Here, we implement the above quantum secret sharing protocol in ‘IBM Q 5 Tenerife’ quantum processor and compare the experimentally obtained results with the theoretically predicted ones. Further, a new quantum binary voting protocol is proposed and implemented in the 14-qubit ‘IBM Q 14 Melbourne’ quantum processor. The results are analyzed through the technique of quantum state tomography, and the fidelity of states is calculated for different number of executions made in the device.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shamir, A.: How to share a secret. Commun. ACM 22, 612 (1979)
Blakley, G.R.: Safeguarding cryptographic keys. In: International Workshop on Managing Requirements Knowledge, pp. 313–317. IEEE Computer Society, New York (1979)
Gottesman, D.: Theory of quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 61, 042311 (2000)
Singh, S.K., Srikanth, R.: Generalized quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 71, 012328 (2005)
Schneier, B.: Applied Cryptography, p. 70. Wiley, New York (1996)
Gruska, J.: Foundations of Computing, p. 504. Thomson Computer Press, London (1997)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 124–134. Santa Fe, New Mexico (1994)
Grover, L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual ACM Symposium Theory of Computing, pp. 212–219. ACM Press, New York (1996)
Gangopadhyay, S., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Generalization and demonstration of an entanglement-based Deutsch–Jozsa-like algorithm using a 5-qubit quantum computer. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 160 (2018)
Wang, J., Li, L., Peng, H., Yang, Y.: Quantum-secret-sharing scheme based on local distinguishability of orthogonal multiqudit entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 95, 022320 (2017)
Hillery, M., Bužek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829 (1999)
Wiesner, S.: Conjugate coding. ACM SIGACT News 15, 78 (1983)
Wang, Z.Y., Yuan, H., Shi, S.H., Zhang, Z.J.: Three-party qutrit-state sharing. Eur. Phys. J. D 41, 371 (2007)
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K.: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648 (1999)
Matsumoto, R.: Unitary reconstruction of secret for stabilizer-based quantum secret sharing. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 202 (2017)
Lu, H., et al.: Secret sharing of a quantum state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 030501 (2016)
Sarvepalli, P.: Nonthreshold quantum secret-sharing schemes in the graph-state formalism. Phys. Rev. A 86, 042303 (2012)
Gravier, S., Javelle, J., Mhalla, M., Perdrix, S.: On weak odd domination and graph-based quantum secret sharing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 598, 129 (2015)
Diep, D.N., Giang, D.H., Phu, P.H.: Application of quantum Gauss–Jordan elimination code to quantum secret sharing code. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 841 (2018)
Gao, G., Wang, Y., Wang, D., Ye, L.: Comment on ’Authenticated quantum secret sharing with quantum dialogue based on Bell states’. Phys. Scr. 93, 027002 (2018)
Abulkasim, H., Hamad, S., Elhadad, A.: Reply to Comment on ’Authenticated quantum secret sharing with quantum dialogue based on Bell states’. Phys. Scr. 93, 027001 (2018)
Liu, F., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y.: A quantum secret-sharing protocol with fairness. Phys. Scr. 89, 075104 (2014)
Lai, H., Xiao, J., Orgun, M.A., Xue, L., Pieprzyk, J.: Quantum direct secret sharing with efficient eavesdropping-check and authentication based on distributed fountain codes. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 895 (2014)
Xie, C., Li, L., Qiu, D.: A novel semi-quantum secret sharing scheme of specific bits. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54, 3819 (2015)
Li, L., Qiu, D., Mateus, P.: Quantum secret sharing with classical Bobs. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 46, 045304 (2013)
Tsai, C., Hwang, T.: Multi-party quantum secret sharing based on two special entangled states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 55, 460 (2012)
Helwig, W., Cui, W., Latorre, J.I., Riera, A., Lo, H.K.: Absolute maximal entanglement and quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 86, 052335 (2012)
Liao, C.H., Yang, C.W., Hwang, T.: Dynamic quantum secret sharing protocol based on GHZ state. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 1907 (2014)
Gao, G.: Improvement of efficient multiparty quantum secret sharing based on bell states and continuous variable operations. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53, 2231 (2014)
Zhang, L., Guo, Y., Huang, D.: High-efficient quantum secret sharing with arrangements of lines on two-dimensional planes. Int. J. Internet Protoc. Technol. 8, 116 (2014)
Zhang, Z.J., Man, Z.X.: Multiparty quantum secret sharing of classical messages based on entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. A 72, 022303 (2005)
Massoud, H.D., Elham, F.: A novel and efficient multiparty quantum secret sharing scheme using entangled states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 55, 1828 (2012)
Guo, G.P., Guo, G.C.: Quantum secret sharing without entanglement. Phys. Lett. A 310, 247 (2003)
Hsu, L.Y., Li, C.M.: Quantum secret sharing using product states. Phys. Rev. A 71, 022321 (2005)
Yan, F., Gao, T.: Quantum secret sharing between multiparty and multiparty without entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 72, 012304 (2005)
Han, L.F., Liu, Y.M., Liu, J., Zhang, Z.J.: Multiparty quantum secret sharing of secure direct communication using single photons. Opt. Commun. 281, 2690 (2008)
Zhang, Z.J., Li, Y., Man, Z.X.: Multiparty quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 71, 044301 (2005)
Chen, X.B., Niu, X.X., Zhou, X.J., Yang, Y.X.: Multi-party quantum secret sharing with the single-particle quantum state to encode the information. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 365 (2013)
Wang, H., Huang, Y., Fang, X., Gu, B., Fu, D.: High-capacity three-party quantum secret sharing with single photons in both the polarization and the spatial-mode degrees of freedom. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 1043 (2013)
Wang, T.Y., Wen, Q.Y., Chen, X.B., Guo, F.Z., Zhu, F.C.: An efficient and secure multiparty quantum secret sharing scheme based on single photons. Opt. Commun. 281, 6130 (2008)
Hao, S.B., Yu, B.: Multiparty quantum secret information sharing in enterprise management based on single qubit with random rotation angle. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 1674 (2012)
Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Perfect teleportation, quantum-state sharing, and superdense coding through a genuinely entangled five-qubit state. Phys. Rev. A 77, 032321 (2008)
Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Quantum-information splitting using multipartite cluster states. Phys. Rev. A 78, 062333 (2008)
Choudhury, S., Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Quantum teleportation and state sharing using a genuinely entangled six-qubit state. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 42, 115303 (2009)
Hou, K., Li, Y.B., Shi, S.H.: Quantum state sharing with a genuinely entangled five-qubit state and Bell-state measurements. Opt. Commun. 283, 1961 (2010)
Li, Y.H., Liu, J.C., Nie, Y.Y.: Quantum teleportation and quantum information splitting by using a genuinely entangled six-qubit state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 49, 2592 (2010)
Nie, Y.Y., Li, Y.H., Liu, J.C., Sang, M.H.: Quantum information splitting of an arbitrary three-qubit state by using two four-qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 10, 297 (2011)
Nie, Y.Y., Li, Y.H., Liu, J.C., Sang, M.H.: Quantum state sharing of an arbitrary three-qubit state by using four sets of W-class states. Opt. Commun. 284, 1457 (2011)
Muralidharan, S., Karumanchi, S., Narayanaswamy, S., Srikanth, R., Panigrahi, P.K.: In How Many Ways Can Quantum Information Be Split? arXiv:0907.3532
Tittel, W., Zbinden, H., Gisin, N.: Experimental demonstration of quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 63, 042301 (2011)
Schmid, C., Trojek, P., Bourennane, M., Kurtsiefer, C., Zukowski, M., Weinfurter, H.: Experimental single qubit quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 230505 (2005)
Gaertner, S., Kurtsiefer, C., Bourennane, M., Weinfurter, H.: Experimental demonstration of four-party quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 020503 (2007)
Wei, K.J., Ma, H.Q., Yang, J.H.: Experimental circular quantum secret sharing over telecom fiber network. Opt. Express 21, 16663 (2013)
IBM—Quantum Network. https://www.research.ibm.com/ibm-q/network/overview/. Accessed 18 July 2019
Boixo, S., et al.: Characterizing quantum supremacy in near-term devices. Nat. Phys. 14, 595–600 (2018)
Connover, E.: Google moves toward quantum supremacy with 72-qubit computer. Sci. News 193, 6 (2018)
Gibney, E.: Inside Microsoft’s quest for a topological quantum computer. Nat. News (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2016.20774
Microsoft Quantum Development Kit. https://microsoft.com/quantum (2017). Accessed 18 July 2019
The Future of Quantum Computing is Counted in Qubits. https://newsroom.intel.com/news/future-quantum-computing-counted-qubits/ (2018). Accessed 18 July 2019
Rigetti, C.: The Rigetti 128-qubit chip and what it means for quantum, Medium https://medium.com/rigetti/the-rigetti-128-qubit-chip-and-what-it-means-for-quantum-df757d1b71ea (2018). Accessed 18 July 2019
D-Wave Announces D-Wave 2000Q Quantum Computer and First System Order, press release. https://www.dwavesys.com/press-releases/d-wave%C2%A0announces%C2%A0d-wave-2000q-quantum-computer-and-first-system-order (2017). Accessed 18 July 2019
Neukart, F., Compostella, G., Seidel, C., Von Dollen, D., Yarkoni, S., Parney, B.: Traffic flow optimization using a quantum annealer. Front. ICT 4, 29 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3389/fict.2017.00029
Boyda, E., Basu, S., Ganguly, S., Michaelis, A., Mukhopadhyay, S., Nemani, R.R.: Deploying a quantum annealing processor to detect tree cover in aerial imagery of California. PLoS ONE 12(2), e0172505 (2017)
O’Malley, D., Vesselinov, V.V., Alexandrov, B.S., Alexandrov, L.B.: Nonnegative/binary matrix factorization with a D-Wave quantum annealer. PLoS ONE 13(12), e0206653 (2018)
Srivastava, R., Choi, I., Cook, T.: The Commercial Prospects of Quantum Computing. Technical report, Networked Quantum Information Technologies (2016)
Gabriel, P.: Quest for qubits. Science 354(6316), 1090–1093 (2016)
Cusumano, M.A.: The business of quantum computing. Commun. ACM 61(10), 20–22 (2018)
Fedortchenko, S.: A Quantum Teleportation Experiment for Undergraduate Students (2016). arXiv:1607.02398
Sisodia, M., Shukla, A., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Design and experimental realization of an optimal scheme for teleportation of an n-qubit quantum state. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 292 (2017)
Alsina, D., Latorre, J.I.: Experimental test of Mermin inequalities on a five-qubit quantum computer. Phys. Rev. A 94, 012314 (2016)
Berta, M., Wehner, S., Wilde, M.M.: Entropic uncertainty and measurement reversibility. New J. Phys. 18, 073004 (2016)
Devitt, S.J.: Performing quantum computing experiments in the cloud. Phys. Rev. A 94, 032329 (2016)
Takita, M., Corcoles, A.D., Magesan, E., Abdo, B., Brink, M., Cross, A., Chow, J.M., Gambetta, J.M.: Demonstration of weight-four parity measurements in the surface code architecture. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 210505 (2016)
Wootton, J.R., Loss, D.: Repetition code of 15 qubits. Phys. Rev. A 97, 052313 (2018)
Ghosh, D., Agarwal, P., Pandey, P., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Automated error correction in IBM quantum computer and explicit generalization. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 153 (2018)
Behera, B.K., Banerjee, A., Panigrahi, P.K.: Experimental realization of quantum cheque using a five-qubit quantum computer. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 312 (2017)
Sisodia, M., Shukla, A., Pathak, A.: Experimental realization of nondestructive discrimination of Bell states using a five-qubit quantum computer. Phys. Lett. A 381, 3860 (2017)
Vuillot, C.: Is Error Detection Helpful on IBM 5Q Chips? (2018). arXiv:1705.08957v1
Huang, H.L., Zhao, Y.W., Li, T., Li, F.G., Du, Y.T., Fu, X.Q., Zhang, S., Wang, X., Bao, W.S.: Homomorphic encryption experiments on IBM’s cloud quantum computing platform. Front. Phys. 12, 120305 (2017)
Wooton, J.R.: Demonstrating non-Abelian braiding of surface code defects in a five qubit experiment. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2, 015006 (2017)
Li, R., Alvarez-Rodriguez, U., Lamata, L., Solano, E.: Approximate quantum adders with genetic algorithms: an IBM quantum experience. Quantum Meas. Quantum Metrol. 4, 1 (2017)
Deffner, S.: Demonstration of entanglement assisted invariance on IBM’s quantum experience. Heliyon 3, e00444 (2017)
Hebenstreit, M., Alsina, D., Latorre, J.I., Kraus, B.: Compressed quantum computation using a remote five-qubit quantum computer. Phys. Rev. A 95, 052339 (2017)
Linke, N.M., Maslov, D., Roetteler, M., Debnath, S., Figgatt, C., Landsman, K.A., Wright, K., Monroe, C.: Experimental comparison of two quantum computing architectures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, 3305 (2017)
Hillery, M., Ziman, M., Bužek, V., Bieliková, M.: Towards quantum-based privacy and voting. Phys. Lett. A 349, 75–81 (2006)
Sharma, R.D., De, A.: Quantum voting using single qubits. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 9(42), 032329 (2016)
Ghose, S., Kumar, A., Madhok, V., Hamel, A.M.: Multiparty quantum communication using multiqubit entanglement and teleportation. Phys. Res. Int. 2014, 948750 (2014)
Tian, J.H., Zhang, J.Z., Li, Y.P.: A voting protocol based on the controlled quantum operation teleportation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55, 2303 (2016)
Thapliyal, K., Sharma, R.D., Pathak, A.: Protocols for quantum binary voting. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 15(1), 1750007 (2017)
Lou, X.: Quantum distributed ballot scheme based on entanglement swapping. In: 10th International Conference on Trust. Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications, IEEE (2011)
Cao, H.J., Ding, L.Y., Jiang, X.L., Li, P.F.: A new proxy electronic voting scheme achieved by six-particle entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 674 (2017)
Borras, A., Plastino, A.R., Batle, J., Zander, C., Casas, M., Plastino, A.: Multiqubit systems: highly entangled states and entanglement distribution. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 40, 13407 (2007)
Zhang, J.L., Xie, S.C., Zhang, J.Z.: An elaborate secure quantum voting scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 3019 (2018)
Xue, P., Zhang, X.: A simple quantum voting scheme with multi-qubit entanglement. Sci. Rep. 7, 7586 (2017)
Karlsson, A., Bourennane, M.: Quantum teleportation using three-particle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 58, 4394 (1998)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Wootters, W.K., Zurek, W.H.: A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 299, 802–803 (1982)
Benenti, G., Casati, G., Strini, G.: Principles of Quantum Computation and Information-Volume I: Basic Concepts, p. 118. World scientific, Singapore (2004)
Pathak, A.: Experimental Quantum Mechanics in the Class Room: Testing Basic Ideas of Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Computing Using IBM Quantum Computer (2018). arXiv:1805.06275v1
Altepeter, J.B., James, D.F.V., Kwiat, P.G.: Quantum state tomography. In: Paris, M., Rehácek, J. (eds.) Quantum State Estimation. Lecture Notes in Physics, vol. 649. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information, p. 409. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Zhang, J.L., Zhan, J.Z., Xie, S.C.: A choreographed distributed electronic voting scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 2676 (2018)
Vaccaro, J.A., Spring, J., Chefles, A.: Quantum protocols for anonymous voting and surveying. Phys. Rev. A 75, 012333 (2007)
Sun, X., Wang, Q., Kulicki, P.: A simple voting protocol on quantum blockchain. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58, 275 (2018)
Zhou, N., Zeng, G., Zeng, W., Zhu, F.: Cross-center quantum identification scheme based on teleportation and entanglement swapping. Opt. Commun. 254, 380 (2005)
Cabello, A.: Quantum key distribution in the Holevo limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 5635 (2000)
Banerjee, A., Pathak, A.: Maximally efficient protocols for direct secure quantum communication. Phys. Lett. A 376, 2944–2950 (2012)
Acknowledgements
D.J. thanks U.G.C., New Delhi, for providing the financial support through BSR fellowship and Athul R.T. for the technical support. B.K.B. acknowledges the financial support of IISER Kolkata. The authors are extremely grateful to IBM team and IBM QE project. The discussions and opinions developed in this paper are only those of the authors and do not reflect the opinions of IBM or IBM Quantum Experience team.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joy, D., Sabir, M., Behera, B.K. et al. Implementation of quantum secret sharing and quantum binary voting protocol in the IBM quantum computer. Quantum Inf Process 19, 33 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2531-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2531-z