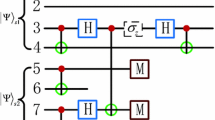
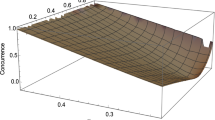
Abstract
In this work, we extensively study the problem of broadcasting of entanglement as state-dependent versus state-independent cloners. We start by re-conceptualizing the idea of state-dependent quantum cloning machine (SD-QCM), and in that process, we introduce different types of SD-QCMs, namely orthogonal and non-orthogonal cloners. We derive the conditions for which the fidelity of these cloners will become independent of the input state. We note that such a construction allows us to maximize the cloning fidelity at the cost of having partial information of the input state. In the discussion on broadcasting of entanglement, we start with a general two-qubit state as our resource and later we consider a specific example of Bell diagonal state. We apply both state-dependent and state-independent cloners (orthogonal and non-orthogonal), locally and non-locally, on input resource state and obtain a range for broadcasting of entanglement in terms of the input state parameters. Our results highlight several instances where the state-dependent cloners outperform their state-independent counterparts in broadcasting entanglement. Our study provides a comparative perspective on the broadcasting of entanglement via cloning in two-qubit scenario, when we have some knowledge of the resource ensemble versus a situation when we have no such information.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heisenberg, W.: Über den anschaulichen Inhalt der quantentheoretischen Kinematik und Mechanik. Z. Phys. 43, 172 (1927)
Einstein, A.: Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete? Phys. Rev. 47, 777 (1935)
Ollivier, H., Zurek, W.H.: Quantum discord: a measure of the quantumness of correlations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 017901 (2001)
Baumgratz, T., Cramer, M., Plenio, M.B.: Quantifying coherence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 140401 (2014)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, 1984 (IEEE, New York, 1984) pp. 175–179
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the bb84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441 (2000)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661 (1991)
Hillery, M., Bužek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829 (1999)
Sazim, S., Chiranjeevi, V., Chakrabarty, I., Srinathan, K.: Retrieving and routing quantum information in a quantum network. Quant. Inf. Proc. 14, 4651 (2015)
Adhikari, S., Chakrabarty, I., Agrawal, P.: Probabilistic secret sharing through noisy quantum channels. arXiv preprint arXiv:1012.5570 (2010)
Ray, M., Chatterjee, S., Chakrabarty, I.: Sequential quantum secret sharing in a noisy environment aided with weak measurements. Eur. Phys. J. D 70, 114 (2016)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Horodecki, R., Horodecki, M., Horodecki, P.: Teleportation, Bell’s inequalities and inseparability. Phys. Lett. A 222, 21 (1996)
Bennett, C.H., Wiesner, S.J.: Communication via one and two-particle operators on Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2881 (1992)
Nepal, R., Prabhu, R., Sen De, A., Sen, U.: Maximally-dense-coding-capable quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 87, 032336 (2013)
Horodecki, R., Horodecki, P., Horodecki, M., Horodecki, K.: Quantum entanglement. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 865 (2009)
Bose, S., Vedral, V., Knight, P.L.: Multiparticle generalization of entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. A 57, 822 (1998)
Zukowski, M., Zeilinger, A., Horne, M.A., Ekert, A.K.: “Event-ready-detectors” Bell experiment via entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 4287 (1993)
Sazim, S., Chakrabarty, I.: A study of teleportation and super dense coding capacity in remote entanglement distribution. Eur. Phys. J. D 67, 174 (2013)
Deutsch, D., Ekert, A., Jozsa, R., Macchiavello, C., Popescu, S., Sanpera, A.: Quantum privacy amplification and the security of quantum cryptography over noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2818 (1996)
Wootters, W.K., Zurek, W.H.: A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 299, 802 (1982)
Pati, A.K., Braunstein, S.L.: Impossibility of deleting an unknown quantum state. Nature 404, 164 (2000)
Pati, A.K., Sanders, B.C.: No-partial erasure of quantum information. Phys. Lett. A 359, 31 (2006)
Chattopadhyay, I., Choudhary, S.K., Kar, G., Kunkri, S., Sarkar, D.: No-flipping as a consequence of no-signalling and non-increase of entanglement under LOCC. Phys. Lett. A 351, 384 (2006)
Chakrabarty, I.: Impossibility of partial swapping of quantum information. Int. J. Quant. Inf. 5, 605 (2007)
Zhou, D.L., Zeng, B., You, L.: Quantum information cannot be split into complementary parts. Phys. Lett. A 352, 41 (2006)
Oszmaniec, M., Grudka, A., Horodecki, M., Wójcik, A.: Creating a superposition of unknown quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 110403 (2016)
Bužek, V., Hillery, M.: Quantum copying: beyond the no cloning theorem. Phys. Rev. A 54, 1844 (1996)
Gisin, N., Massar, S.: Optimal quantum cloning machines. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 2153 (1997)
Bužek, V., Hillery, M.: Universal optimal cloning of arbitrary quantum states: from qubits to quantum registers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 5003 (1998)
Bruß, D., DiVincenzo, D.P., Ekert, A., Fuchs, C.A., Macchiavello, C., Smolin, J.A.: Optimal universal and state dependent quantum cloning. Phys. Rev. A 57, 2368 (1998)
Cerf, N.J.: Pauli cloning of a quantum bit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 4497 (2000)
Cerf, N.J.: Asymmetric quantum cloning machines in any dimension. J. Mod. Opt. 47, 187 (2000)
Scarani, V., Iblisdir, S., Gisin, N., Acin, A.: Quantum cloning. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 1225 (2005)
Adhikari, S., Choudhury, B.S., Chakrabarty, I.: Broadcasting of inseparability. J. Phys. A 39, 8439 (2006)
Wang, M.-H., Cai, Q.-Y.: High-fidelity quantum cloning of two non orthogonal quantum states via weak measurements. Phys. Rev. A 99, 012324 (2019)
Cerf, N.J., Bourennane, M., Karlsson, A., Gisin, N.: Security of quantum key distribution using d-level systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 127902 (2002)
Ghiu, I.: Asymmetric quantum telecloning of d-level systems and broadcasting of entanglement to different locations using the “many-to-many” communication protocol. Phys. Rev. A 67, 012323 (2003)
Gruska, J.: Quantum entanglement as a new information processing resource. New Gener. Comput. 21, 279 (2003)
Werner, R.F.: Quantum states with Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen correlations admitting a hidden-variable model. Phys. Rev. A 40, 4277 (1989)
White, A.G., James, D.F., Eberhard, P.H., Kwiat, P.G.: Non maximally entangled states: production, characterization, and utilization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3103 (1999)
Bennett, C.H., Bernstein, H.J., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B.: Concentrating partial entanglement by local operations. Phys. Rev. A 53, 2046 (1996)
Murao, M., Plenio, M.B., Popescu, S., Vedral, V., Knight, P.L.: Multiparticle entanglement purification protocols. Phys. Rev. A 57, R4075 (1998)
Jain, A., Chakrabarty, I., Chatterjee, S.: Asymmetric broadcasting of entanglement and correlations. Phys. Rev. A 99, 022315 (2019)
Bužek, V., Vedral, V., Plenio, M.B., Knight, P.L., Hillery, M.: Broadcasting of entanglement via local copying. Phys. Rev. A 55, 3327 (1997)
Bandyopadhyay, S., Kar, G.: Broadcasting of entanglement and universal quantum cloners. Phys. Rev. A 60, 3296 (1999)
Henderson, L., Vedral, V.: Classical, quantum and total correlations. J. Phys. A Math. General 34, 6899 (2001)
Chatterjee, S., Sazim, S., Chakrabarty, I.: Broadcasting of quantum correlations: possibilities and impossibilities. Phys. Rev. A 93, 042309 (2016)
Lang, M.D., Caves, C.M.: Quantum discord and the geometry of Bell-diagonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 150501 (2010)
Bužek, V., Hillery, M.: Universal optimal cloning of qubits and quantum registers. In: Quantum Computing and Quantum Communications. Springer, pp. 235–246 (1999)
Sharma, U.K., Chakrabarty, I., Shukla, M.K.: Broadcasting quantum coherence via cloning. Phys. Rev. A 96, 052319 (2017)
Peres, A.: Separability criterion for density matrices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 1413 (1996)
Horodecki, M.: Separability of mixed states: necessary and sufficient conditions. Phys. Lett. A 223, 1 (1996)
Chitambar, E., Leung, D., Mancinska, L., Ozols, M., Winter, A.: Everything you always wanted to know about LOCC (but were afraid to ask). Commun. Math. Phys. 328, 303 (2014)
Acknowledgements
S.C. thanks Prof. Mark M. Wilde for his insightful suggestions. S.C. acknowledges the internship grant from Erlangen Graduate School in Advanced Optical Technologies (SAOT) for supporting the research work as an intern at IIIT, Hyderabad and HRI, Allahabad, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, M.K., Chakrabarty, I. & Chatterjee, S. Broadcasting of entanglement via orthogonal and non-orthogonal state-dependent cloners. Quantum Inf Process 19, 15 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2500-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2500-6