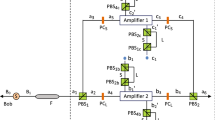
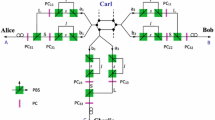
Abstract
Hyperentanglement can enlarge the capacity of quantum channel and has big potential application in long-distance quantum communication. However, the channel noise may cause photon transmission loss, which largely limits the practical application of hyperentanglement. In the paper, we propose a linear-optical heralded amplification protocol for protecting the two-photon spatial-mode-polarization hyperentangled state. Our protocol can effectively increase the fidelity of the hyperentangled state while preserve its encoded spatial and polarization features. Comparing with previous heralded amplification protocol for the spatial-mode-polarization hyperentangled state, our protocol is easier to be implemented under current experimental condition. Moreover, besides amplification, if necessary, our protocol can adjust the entanglement coefficients in both polarization and spatial-mode degrees of freedom of the distilled hyperentangled state and recover the less-entangled hyperentangled state into the maximally entangled state. Based on above features, our protocol gives a possible solution to overcome the photon loss and decoherence problems occurred in practical noisy quantum channel condition.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bells theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661 (1991)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Mermin, N.D.: Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 557 (1992)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042317 (2003)
Zhang, W., Ding, D.S., Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Shi, B.S., Guo, G.C.: Quantum secure direct communication with quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 220501 (2017)
Zhu, F., Zhang, W., Sheng, Y.B., Huang, Y.D.: Experimental long-distance quantum secret direct communication. Sci. Bull. 62, 1519 (2017)
Qin, H.W., Tang, W.K.S., Tso, R.: Establishing rational networking using the DL04 quantum secure direct communication protocol. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 152 (2018)
Zheng, X.Y., Long, Y.X.: Controlled quantum secure direct communication with authentication protocol based on five-particle cluster state and classical XOR operation. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 129 (2019)
Chen, S.S., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Three-step three-party quantum secure direct communication. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 61, 90312 (2018)
Wu, F.Z., Yang, G.J., Wang, H.B., Xiong, J., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Deng, F.G.: High-capacity quantum secure direct communication with two-photon six-qubit hyperentangled states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 60, 120313 (2017)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crepeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Wang, M.Y., Yan, F.L.: Quantum teleportation of a generic two-photon state with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearities. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 3383–3392 (2016)
Li, T.C., Yin, Z.Q.: Quantum superposition, entanglement, and state teleportation of a microorganism on an electromechanical oscillator. Sci. Bull. 61, 163 (2016)
Deng, F.G., Ren, B.C., Li, X.H.: Quantum hyperentanglement and its applications in quantum information processing. Sci. Bull. 62, 46 (2017)
Ding, D., He, Y.Q., Yan, F.L., Gao, T.: On four-photon entanglement from parametric down-conversion process. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 243 (2018)
Chen, N., Zhang, L.X., Pei, C.X.: Faithful qubit transmission in a quantum communication network with heterogeneous channels. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 79 (2018)
Bruss, D., Macchiavello, C.: Optimal eavesdropping in cryptography with three-dimensional quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 127901 (2002)
Cerf, N.J., Bourennane, M., Karlsson, A., Gisin, N.: Security of quantum key distribution using d-level systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 127902 (2002)
Wilde, M.M., Uskov, D.B.: Linear-optical hyperentanglement assisted quantum error-correcting code. Phys. Rev. A 79, 022305 (2009)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal Bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys. Rev. A 81, 032307 (2010)
Ren, B.C., Long, G.L.: General hyperentanglement concentration for photon systems assisted by quantum dot spins inside optical microcavities. Opt. Exp. 22, 6547 (2014)
Du, F.F., Shi, Z.R.: Robust hybrid hyper-controlled-not gates assisted by an input–output process of low-Q cavities. Opt. Exp. 27, 17493 (2019)
Wang, G.Y., Ren, B.C., Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Complete analysis of hyperentangled Bell states assisted with auxiliary hyperentanglement. Opt. Exp. 27, 8994 (2019)
Ren, B.C., Wang, H., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration of nonlocal two-photon six-qubit systems with linear optics. Ann. Phys. 385, 86–94 (2017)
Wang, H., Ren, B.C., Wang, A.H., Alsaedi, A., Hayat, T., Deng, F.G.: General hyperentanglement concentration for polarization-spatial-time-bin multi-photon systems with linear optics. Front. Phys. 13, 130315 (2018)
Zheng, Y.Y., Liang, L.X., Zhang, M.: Error-heralded generation and self-assisted complete analysis of two-photon hyperentangled Bell states through single-sided quantum-dot-cavity systems. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 62, 970312 (2019)
Wang, M.Y., Yan, F.L., Gao, T.: Deterministic state analysis for polarization-spatial-time-bin hyperentanglement with nonlinear optics. Laser Phys. Lett. 15, 125206 (2018)
Wang, M.Y., Xu, J.Z., Yan, F.L., Gao, T.: Entanglement concentration for polarization-spatial-time-bin hyperentangled Bell states. EPL 123, 60002 (2018)
Ralph, T.C., Lund, A.P.: Quantum communication measurement and computing. In: lvovsky, A. (ed.) Proceedings of the 9th International Conference. pp. 155–160. AIP , New York (2009)
Gisin, N., Pironio, S., Sangouard, N.: Proposal for implementing device-independent quantum key distribution based on a heralded qubit amplifier. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 070501 (2010)
Curty, M., Moroder, T.: Heralded-qubit amplifiers for practical device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 84, 010304 (2011)
Pitkanen, D., Ma, X., Wickert, R., van Loock, P., Lütkenhaus, N.: Effcient heralding of photonic qubits with applications to device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 84, 022325 (2011)
Kaushik, P., Seshadreesan, Takeoka M., Sasaki, M.: Progress towards practical device-independent quantum key distribution with spontaneous parametric down-conversion sources, on–off photodetectors, and entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. A 93, 042328 (2016)
Meyer-Scott, E., Bula, M., Bartkiewicz, K., C̆ernoch, A., Soubusta, J., Jennewein, T., Lemr, K.: Entanglement-based linear-optical qubit amplifier. Phys. Rev. A 88, 012327 (2013)
Zapatero, V., Curty, M.: Long-distance device-independent quantum key distribution (2019). arXiv:1905.03591
Osorio, C.I., Bruno, N., Sangouard, N., Zbinden, H., Gisin, N., Thew, R.T.: Heralded photon amplification for quantum communication. Phys. Rev. A 86, 023815 (2012)
Zhang, S.L., Yang, S., Zou, X.B., Shi, B.S., Guo, G.C.: Protecting single-photon entangled state from photon loss with noiseless linear amplification. Phys. Rev. A 86, 034302 (2012)
Minár̆, J., de Riedmatten, H., Sangouard, N.: Quantum repeaters based on heralded qubit amplifiers. Phys. Rev. A 85, 032313 (2012)
Bruno, N., Pini, V., Martin, A., Thew, R.T.: A complete characterization of the heralded noiseless amplification of photons. New J. Phys. 15, 093002 (2013)
Kocsis, S., Xiang, G.Y., Ralph, T.C., Pryde, G.J.: Heralded noiseless amplification of a photon polarization qubit. Nat. Phys. 9, 23–28 (2013)
McMahon, N.A., Lund, A.P., Ralph, T.C.: Optimal architecture for a nondeterministic noiseless linear amplifier. Phys. Rev. A 89, 023846 (2014)
Sheng, Y.B., Ou-Yang, Y., Zhou, L., Wang, L.: Protecting single-photon multi-mode W state from photon loss. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 1595 (2014)
Wang, T.J., Cao, C., Wang, C.: Linear-optical implementation of hyperdistillation from photon loss. Phys. Rev. A 89, 052303 (2014)
Wang, T.J., Liu, L.L., Zhang, R., Cao, C., Wang, C.: One-step hyperentanglement purification and hyperdistillation with linear optics. Opt. Exp. 23, 9284 (2015)
Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B.: Recyclable amplification protocol for the single-photon entangled state. Laser Phys. Lett. 12, 045203 (2015)
Ou-Yang, Y., Feng, Z.F., Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B.: Protecting single-photon entanglement with imperfect single-photon source. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 635 (2015)
Ou-Yang, Y., Feng, Z.F., Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B.: Linear-optical qubit amplification with spontaneous parametric down-conversion source. Laser Phys. 26, 015204 (2016)
Zhou, L., Ou-Yang, Y., Wang, L., Sheng, Y.B.: Protecting single-photon entanglement with practical entanglement source. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 151 (2017)
Bruno, N., Pini, V., Martin, A., Verma, V.B., Nam, S.W., Mirin, R., Lita, A., Marsili, F., Korzh, B., Bussieres, F., Sangouard, N., Zbinden, H., Gisin, N., Thew, R.: Heralded amplification of photonic qubits. Opt. Exp. 24, 125 (2016)
Monteiro, F., Verbanis, E., Vivoli Caprara, V., Martin, A., Gisin, N., Zbinden, H., Thew, R.T.: Heralded amplification of path entangled quantum states. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2, 024008 (2017)
Wang, D.D., Jin, Y.Y., Qin, S.X., Zu, H., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Heralded noiseless amplification for single-photon entangled state with polarization feature. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 56 (2018)
Jin, Y.Y., Qin, S.X., Zu, H., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Heralded amplification of single-photon entanglement with polarization feature. Front. Phys. 13, 130321 (2018)
Chen, L.Q., Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L.: Noiseless linear amplification for the single-photon entanglement of arbitrary polarization–time-bin qudit. Chin. Phys. B 28, 010302 (2019)
Deng, F.G.: Optimal nonlocal multipartite entanglement concentration based on projection measurements. Phys. Rev. A 85, 022311 (2012)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Zhao, S.M., Zheng, B.Y.: Efficient single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration for partially entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 85, 012307 (2012)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Zhao, S.M.: Efficient two step entanglement concentration for arbitrary W states. Phys. Rev. A 85, 042302 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11974189, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant No. 2018M642293, the open research fund of the Key Lab of Broadband Wireless Communication and Sensor Network Technology, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Ministry of Education, under Grant No. JZNY201908, and a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, G., Zhang, YS., Yang, ZR. et al. Linear-optical heralded amplification protocol for two-photon spatial-mode-polarization hyperentangled state. Quantum Inf Process 18, 317 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2432-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2432-1