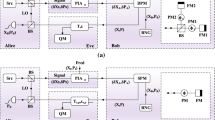
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a scheme that integrates quantum key distribution and private classical communication via continuous variables. The integrated scheme employs both quadratures of a weak coherent state, with encrypted bits encoded on the signs and Gaussian random numbers encoded on the values of the quadratures. The integration enables quantum and classical data to share the same physical and logical channel. Simulation results based on practical system parameters demonstrate that both classical communication and quantum communication can be implemented over distance of tens of kilometers, thus providing a potential solution for simultaneous transmission of quantum communication and classical communication.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scarani, V., Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H., Cerf, N.J., Dus̆ek, M., Lütkenhaus, N., Peev, M.: The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1301–1350 (2009)
Weedbrook, C., Pirandola, S., García-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.J., Ralph, T.C., Shapiro, J.H., Lloyd, S.: Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 621–669 (2012)
Grosshans, F., Cerf, N.J., Wenger, J., Tualle-Brouri, R., Grangier, P.: Virtual entanglement and reconciliation protocols for quantum cryptography with continuous variables. Quantum Inf. Comput. 3, 535–553 (2003)
García-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.J.: Unconditional optimality of Gaussian attacks against continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190503 (2006)
Navascués, M., Grosshans, F., Acín, A.: Optimality of Gaussian attacks in continuous-variable quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190502 (2006)
Leverrier, A., Grangier, P.: Simple proof that Gaussian attacks are optimal among collective attacks against continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a Gaussian modulation. Phys. Rev. A 81, 062314 (2010)
Grosshans, F., Assche, G., Wenger, J., Brouri, R., Cerf, N.J., Grangier, P.: Quantum key distribution using Gaussian-modulated coherent states. Nature 421, 238–241 (2003)
Lodewyck, J., Bloch, M., García-Patrón, R., Fossier, S., Karpov, E., Diamanti, E., Debuisschert, T., Cerf, N.J., Tualle-Brouri, R., McLaughlin, S.W., Grangier, P.: Quantum key distribution over 25 km with an all-fiber continuous-variable system. Phys. Rev. A 76, 042305 (2007)
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Leverrier, A., Grangier, P., Diamanti, E.: Experimental demonstration of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photon. 7, 378–381 (2013)
Huang, D., Huang, P., Lin, D., Zeng, G.: Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution by controlling excess noise. Sci. Rep. 6, 19201 (2016)
Shannon, C.: Communication theory of secrecy systems. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 28, 656–715 (1949)
Peters, N.A., Toliver, P., Chapuran, T.E., Runser, R.J., McNown, S.R., Peterson, C.G., Rosenberg, D., Dallmann, N., Hughes, R.J., McCabe, K.P., Nordholt, J.E., Tyagi, K.T.: Dense wavelength multiplexing of 1550 nm QKD with strong classical channels in reconfigurable networking environments. New J. Phys. 11, 045012 (2009)
Qi, B., Zhu, W., Qian, L., Lo, H.-K.: Feasibility of quantum key distribution through a dense wavelength division multiplexing network. New J. Phys. 12, 103042 (2010)
Kumar, R., Qin, H., Alleaume, R.: Coexistence of continuous variable QKD with intense DWDM classical channels. New J. Phys. 17, 043027 (2015)
Qi, B.: Simultaneous classical communication and quantum key distribution using continuous variable. Phys. Rev. A 94, 042340 (2016)
Wilde, M.M., Hsieh, M.-H.: Public and private resource trade-offs for a quantum channel. Quantum Inf. Process. 11, 1465–1501 (2012)
Wilde, M.M., Hsieh, M.-H.: The quantum dynamic capacity formula of a quantum channel. Quantum Inf. Process. 11, 1431–1463 (2012)
Renner, R.: Symmetry of large physical systems implies independence of subsystems. Nat. Phys. 3, 645–649 (2007)
Renner, R., Cirac, J.I.: de Finetti representation theorem for infinite-dimensional quantum systems and applications to quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 110504 (2009)
Kikuchi, K.: Fundamentals of coherent optical fiber communications. J. Lightwave Technol. 34, 157–179 (2016)
Shannon, C.: A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27, 623–656 (1948)
Holevo, A.S.: Bounds for the quantity of information transmitted by a quantum communication channel. Probl. Inf. Transm. 9, 177–183 (1973)
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Leverrier, A.: Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a Gaussian modulation. Phys. Rev. A 84, 062317 (2011)
Chang, F., Onohara, K., Mizuochi, T.: Forward error correction for 100 G transport networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 48, S48–S55 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The work is supported in part by the Special Project of International Cooperation and Exchange of Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No. 2014DFA00670), the National Science & Technology Support Program (No. 2015BAK28B02), in part by the Major Project of Guizhou Province (No. [2016]3022), in part by the Science & Technology Cooperation Project of Guizhou Province (No. [2014]7002, No. [2016]7431), in part by the Science Foundation of Guizhou Province (No. [2017]1047), and in part by the Scientific Research Foundation for Talent Introduced in Guizhou University (No. [2015]45).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Gong, F., Lu, A. et al. Integration of quantum key distribution and private classical communication through continuous variable. Quantum Inf Process 16, 289 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1740-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1740-6