Abstract
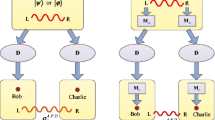
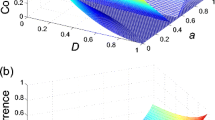
The restoration of three-qubit entanglement is investigated under the amplitude damping (AD) decoherence with environment-assisted measurement (EAM) and reversal weak measurement (RWM). The results show that there exists a critical strength of RWM dependent of the initial three-qubit entangled state under a given damping rate of the AD channel, i.e., if the selected RWM strength is higher than the critical strength, the entanglement will be reduced compared to one without RWM. Some three-qubit entangled states cannot be restored. We calculated the restorable condition of the initial entanglement and illustrated the valid area for three-qubit GHZ state and W state. Fortunately, an optimal strength of RWM corresponding to a certain damping rate of AD channels can be found within the valid area for a restorable initial state, by which a noise-infected entanglement can be restored to its maximum value. Particularly, when three qubits of W state are subjected to their respective AD channels, due to the symmetry of three qubits, the W state cannot be decohered provided the EAM is successful, and no RWM is required. This is beneficial to quantum communication over the noisy channel. Applying this protection regime to tripartite QSS and taking appropriate initial entangled state as the quantum channel, the fidelity of the shared state can be improved to the maximum 1 probabilistically. Thus, the decoherence effect of the noisy channels can be significantly suppressed or even avoided.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crepeaue, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Bouwmeester, D., Pan, J.W., Mattle, K., Eibl, M., Weinfurter, H., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 390, 575 (1997)
Riebe, M., Häffner, H., Roos, C.F., Hänsel, W., Benhelm, J., Lancaster, G.P.T., Körber, T.W., Becher, C., Schmidt-Kaler, F., James, D.F.V., Blatt, R.: Deterministic quantum teleportation with atoms. Nature 429, 734 (2004)
Bennett, C.H., Wiesner, S.J.: Communication via one- and two-particle operators on Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2881 (1992)
Hillery, M., Buzek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829–1834 (1999)
Boströem, K., Felbinger, T.: Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 187902 (2002)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042317 (2003)
Zhu, A.D., Xia, Y., Fan, Q.B., Zhang, S.: Secure direct communication based on secret transmitting order of particles. Phys. Rev. A 73, 022338 (2006)
Zhang, Y.J., Man, Z.X., Zou, X.B., Xia, Y.J., Guo, G.C.: Dynamics of multipartite entanglement in the non-Markovian environments. J. Phys. B 43, 045502 (2010)
Zhang, Y.J., Xia, Y.J., Fan, H.: Role of initial system-bath correlation on coherence trapping. Sci. Rep. 5, 13359 (2015)
Zhang, Y.J., Han, W., Xia, Y.J., Yu, Y.M., Fan, H.: Control of quantum dynamics: non-Markovianity and the speedup of the open system. Europhys. Lett. 116, 30001 (2016)
Bennett, C.H., Bernstein, H.J., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B.: Concentrating partial entanglement by local operations. Phys. Rev. A 53, 2046–2052 (1996)
Pan, J.W., Simon, C., Brukner, C., Zelliinger, A.: Entanglement purification for quantum communication. Nature (London) 410, 1067 (2001)
Pan, J.W., Gasparoni, S., Ursin, R., Weihs, G., Zeillinger, A.: Experimental entanglement purification of arbitrary unknown states. Nature (London) 423, 417 (2003)
Paunković, N., Omar, Y., Bose, S., Vedral, V.: Entanglement concentration using quantum statistics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 187903 (2002)
Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Concentration and purification scheme for two partially entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 64, 012304 (2001)
Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Ozdemir, S.K., Imoto, N.: Experimental extraction of an entangled photon pair from two identically decohered pairs. Nature 421, 343 (2003)
Shor, P.W.: Scheme for reducing decoherence in quantum computer memory. Phys. Rev. A 52, R2493 (1995)
Calderbank, A.R., Shor, P.W.: Good quantum error-correcting codes exist. Phys. Rev. A 54, 1098 (1996)
Zhang, Y.J., Zou, X.B., Xia, Y.J., Guo, G.C.: Different entanglement dynamical behaviors due to initial system-environment correlations. Phys. Rev. A 82, 022108 (2010)
Zhang, Y.J., Han, W., Xia, Y.J., Tian, J.X., Fan, H.: Speedup of quantum evolution of multiqubit entanglement states. Sci. Rep. 6, 27349 (2016)
Korotkov, A.N., Keane, K.: Decoherence suppression by quantum measurement reversal. Phys. Rev. A 81, 040103(R) (2010)
Kim, Y.S., Lee, J.-C., Kwon, O., Kim, Y.-H.: Protecting entanglement from decoherence using weak measurement and quantum measurement reversal. Nat. Phys. 8, 117 (2012)
Wang, S.C., Yu, Z.W., Zou, W.J., Wang, X.B.: Protecting quantum states from decoherence of finite temperature using weak measurement. Phys. Rev. A 89, 022318 (2014)
Xu, X.M., Cheng, L.Y., Liu, A.P., Su, S.L., Wang, H.F., Zhang, S.: Environment-assisted entanglement restoration and improvement of the fidelity for quantum teleportation. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 4147 (2015)
Wang, X.W., Yu, S., Zhang, D.Y., Oh, C.H.: Effect of weak measurement on entanglement distribution over noisy channels. Sci. Rep. 6, 22408 (2016)
Zhang, Y.J., Han, W., Fan, H., Xia, Y.J.: Enhancing entanglement trapping by weak measurement and quantum measurement reversal. Ann. Phys. New York 354, 202 (2015)
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K.: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648 (1999)
Murao, M., Jonathan, D., Plenio, M.B., Vedral, V.: Quantum telecloning and multiparticle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 59, 156 (1999)
Zheng, S.B.: Splitting quantum information via W states. Phys. Rev. A 74, 054303 (2006)
Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Perfect teleportation, quantum-state sharing, and superdense coding through a genuinely entangled five-qubit state. Phys. Rev. A 77, 032321 (2008)
Wang, H.F., Ji, X., Zhang, S.: Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret splitting and quantum state sharing. Phys. Lett. A 358, 11–14 (2006)
Zhang, Z.J., Man, Z.X.: Multiparty quantum secret sharing of classical messages based on entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. A 72, 022303 (2005)
Zhang, Z.J., Li, Y., Man, Z.X.: Multiparty quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 71, 044301 (2005)
Nielson, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information, pp. 380–381. Higher Education Press, Cambridge (2003)
Sabín, C., García-Alcaine, G.: A classification of entanglement in three-qubit systems. Eur. Phys. J. D 48, 435–442 (2008)
Miranowicz, A., Grudka, A.: A comparative study of relative entropy of entanglement, concurrence and negativity. J. Opt. B Quantum Semiclassical Opt. 6, 542 (2004)
Vidal, G., Werner, R.F.: Computable measure of entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032314 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China under Grant Nos. 11564041, 11165015, 11264042, 11465020 and 61465013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, SY., Jin, Z., Wu, HJ. et al. Restoration of three-qubit entanglements and protection of tripartite quantum state sharing over noisy channels via environment-assisted measurement and reversal weak measurement. Quantum Inf Process 16, 137 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1584-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1584-0