Abstract
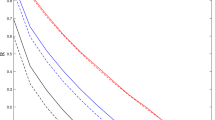
Quantum channel loopholes due to imperfect implementations of practical devices expose quantum key distribution (QKD) systems to potential eavesdropping attacks. Even though QKD systems are implemented with optical devices that are highly selective on spectral characteristics, information theory-based analysis about a pertinent attack strategy built with a reasonable framework exploiting it has never been clarified. This paper proposes a new type of trojan horse attack called hidden pulse attack that can be applied in a plug-and-play QKD system, using general and optimal attack strategies that can extract quantum information from phase-disturbed quantum states of eavesdropper’s hidden pulses. It exploits spectral characteristics of a photodiode used in a plug-and-play QKD system in order to probe modulation states of photon qubits. We analyze the security performance of the decoy-state BB84 QKD system under the optimal hidden pulse attack model that shows enormous performance degradation in terms of both secret key rate and transmission distance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H, Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers System and Signal Processing, pp. 175-179 (1984)
Wootters, W.K., Zurek, W.H.: A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 299(5886), 802–803 (1982)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(2), 441 (2000)
Renner, R.: Security of quantum key distribution. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 6(01), 1–127 (2008)
Lim, K., Ko, H., Kim, K., Suh, C., Rhee, J.K.: The Error Tolerance Bound for Secure Multi-Qubit QKD Against Incoherent Attack. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 21(3), 1–9 (2015)
Lydersen, L., Wiechers, C., Wittmann, C., Elser, D., Skaar, J., Makarov, V.: Hacking commercial quantum cryptography systems by tailored bright illumination. Nature Photon. 4(10), 686–689 (2010)
Li, H.W., Wang, S., Huang, J.Z., Chen, W., Yin, Z.Q., Li, F.Y., Zhou, Z., Liu, D., Zhang, Y., Guo, G.C., Bao, W.S.: Attacking a practical quantum-key-distribution system with wavelength-dependent beam-splitter and multiwavelength sources. Phys. Rev. A 84(6), 062308 (2011)
Xu, F., Qi, B., Lo, H.K.: Experimental demonstration of phase-remapping attack in a practical quantum key distribution system. New J. Phys. 12(11), 113026 (2010)
Sun, S.H., Jiang, M.S., Liang, L.M.: Passive Faraday-mirror attack in a practical two-way quantum-key-distribution system. Phys. Rev. A 83(6), 062331 (2011)
Jiang, M.S., Sun, S.H., Li, C.Y., Liang, L.M.: Wavelength-selected photon-number-splitting attack against plug-and-play quantum key distribution systems with decoy states. Phys. Rev. A 86(3), 032310 (2012)
Sun, S.H., Gao, M., Jiang, M.S., Li, C.Y., Liang, L.M.: Partially random phase attack to the practical two-way quantum-key-distribution system. Phys. Rev. A 85(3), 032304 (2012)
Sajeed, S., Radchenko, I., Kaiser, S., Bourgoin, J.P., Pappa, A., Monat, L., Legré, M., Makarov, V.: Attacks exploiting deviation of mean photon number in quantum key distribution and coin tossing. Phys. Rev. A 91(3), 032326 (2015)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(13), 130503 (2012)
Liu, Y., Chen, T.Y., Wang, L.J., Liang, H., Shentu, G.L., Wang, J., Cui, K., Yin, H.L., Liu, N.L., Li, L., Ma, X.: Experimental measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(13), 130502 (2013)
Kim, Y. S., Choi, Y., Kwon, O., Han, S. W., and Moon, S.: Plug-and-Play Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution. arXiv preprint arXiv:1501.03344 (2015)
Muller, A., Herzog, T., Huttner, B., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H., Gisin, N.: Plug and play systems for quantum cryptography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 70(7), 793–795 (1997)
Ma, H.Q., Wei, K.J., Yang, J.H.: Simple quantum key distribution scheme with excellent long-term stability. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30(9), 2560–2562 (2013)
Pappa, A., Jouguet, P., Lawson, T., Chailloux, A., Legré, M., Trinkler, P.,Kerenidis, I., Diamanti, E.: Experimental plug and play quantum coin flipping. Nat. Commun. 5 (2014)
Radchenko, I.V., Kravtsov, K.S., Kulik, S.P., Molotkov, S.N.: Relativistic quantum cryptography. Laser Phys. Lett. 11(6), 065203 (2014)
Gisin, N., Fasel, S., Kraus, B., Zbinden, H., Ribordy, G.: Trojan-horse attacks on quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 73(2), 022320 (2006)
Jain, N., Stiller, B., Khan, I., Makarov, V., Marquardt, C., Leuchs, G.: Risk analysis of Trojan-horse attacks on practical quantum key distribution systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 21(3), 1–10 (2015)
Lo, H.K., Ma, X., Chen, K.: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(23), 230504 (2005)
Ma, X., Qi, B., Zhao, Y., Lo, H.K.: Practical decoy state for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 72(1), 012326 (2005)
Gobby, C., Yuan, Z.L., Shields, A.J.: Quantum key distribution over 122 km of standard telecom fiber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(19), 3762–3764 (2004)
Agrawal, G.P.: Fiber-optic communication systems. Wiley, New Jersey (2012)
Huttner, B., Imoto, N., Gisin, N., Mor, T.: Quantum cryptography with coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 51(3), 1863 (1995)
Ltkenhaus, N.: Security against individual attacks for realistic quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 61(5), 052304 (2000)
Holevo, A.S.: Bounds for the quantity of information transmitted by a quantum communication channel. Problemy Peredachi Informatsii 9(3), 3–11 (1973)
Pearsall, T.P.: Ga 0.47 In 0.53 As: A ternary semiconductor for photodetector applications. IEEE J. of. Quantum Electron. 16(7), 709–720 (1980)
http://www.idquantique.com/images/stories/PDF/clavis2-quantum-key-distribution/clavis2-specs
Aleksic, S., Winkler, D., Franzl, G., Poppe, A., Schrenk, B., and Hipp, F.: Quantum key distribution over optical access networks. In Network and Optical Communications (NOC), 2013 18th European Conference on and Optical Cabling and Infrastructure (OC&i), 2013 8th Conference on (pp. 11–18). IEEE. (2013, July)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the ICT R&D program of MSIP/IITP. [R-20150903-002203, Standardization for Quantum Key Distribution]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, H., Lim, K., Oh, J. et al. Informatic analysis for hidden pulse attack exploiting spectral characteristics of optics in plug-and-play quantum key distribution system. Quantum Inf Process 15, 4265–4282 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1400-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1400-2