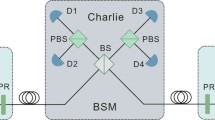
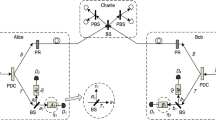
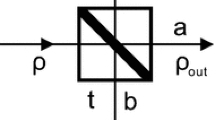
Abstract
By employing pulses involving three-intensity, we propose a scheme for the measurement device-independent quantum key distribution with heralded single-photon sources. We make a comparative study of this scheme with the standard three-intensity decoy-state scheme using weak coherent sources or heralded single-photon sources. The advantage of this scheme is illustrated through numerical simulations: It can approach very closely the asymptotic case of using an infinite number of decoy-states and exhibits excellent behavior in both the secure transmission distance and the final key generation rate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing. IEEE, New York, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145195 (2002)
Gisin, N., Thew, R.: Quantum communication. Nat. Photonics 1, 165 (2007)
Dusek, M., Lütkenhaus, N., Hendrych, M.: Quantum cryptography. In: Wolf, E. (ed.) Progress in Optics VVVX. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2006)
Scarani, V., et al.: The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1301 (2009)
Huttner, B., Imoto, N., Gisin, N., Mor, T.: Quantum cryptography with coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 51, 1863 (1995)
Yuen, H.P.: Quantum amplifiers, quantum duplicators and quantum cryptography. Quantum Semiclass. Opt. 8, 939 (1996)
Brassard, G., Lütkenhaus, N., Mor, T., Sanders, B.C.: Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1330 (2000)
Lütkenhaus, N., Jahma, M.: Quantum key distribution with realistic states: photon-number statistics in the photon-number splitting attack. New J. Phys. 4, 44 (2002)
Lütkenhaus, N.: Security against individual attacks for realistic quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 61, 052304 (2000)
Fung, C.H.F., Qi, B., Tamaki, K., Lo, H.K.: Phase-remapping attack in practical quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 75, 032314 (2007)
Qi, B., Fung, C.H.F., Lo, H.K., Ma, X.: Time-shift attack in practical quantum cryptosystems. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7, 73 (2007)
Zhao, Y., et al.: Quantum hacking: experimental demonstration of time-shift attack against practical quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 78, 042333 (2008)
Lydersen, L., et al.: Hacking commercial quantum cryptography systems by tailored bright illumination. Nat. Photonics 4, 686 (2010)
Jain, N., et al.: Device calibration impacts security of quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 110501 (2011)
Inamori, H., Lütkenhaus, N., Mayers, D.: Unconditional security of practical quantum key distribution. Eur. Phys. J. D 41, 599 (2007)
Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K., Lütkenhaus, N., Preskill, J.: Security of quantum key distribution with imperfect devices. Quantum Inf. Comput. 4, 325 (2004)
Hwang, W.Y.: Quantum key distribution with high loss: toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 057901 (2003)
Wang, X.B.: Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230503 (2005)
Lo, H.K., Ma, X., Chen, K.: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230504 (2005)
Wang, Q., et al.: Experimental decoy-state quantum key distribution with a sub-poissionian heralded single-photon source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 090501 (2008)
Mayers, D., Yao, A.C.: Quantum cryptography with imperfect apparatus. In: Proceedings of the 39th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, p. 503 (1998)
Acín, A., Gisin, N., Masanes, L.: From Bells theorem to secure quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 120405 (2006)
Acín, A., et al.: Device-independent security of quantum cryptography against collective attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 230501 (2007)
Gisin, N., Pironio, S., Sangouard, N.: Proposal for implementing device-independent quantum key distribution based on a heralded qubit amplifier. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 070501 (2010)
Curty, M., Moroder, T.: Heralded-qubit amplifiers for practical device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 84, 010304(R) (2011)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Braunstein, S.L., Pirandola, S.: Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130502 (2012)
Wang, X.B.: Three-intensity decoy-state method for device-independent quantum key distribution with basis-dependent errors. Phys. Rev. A 87, 012320 (2013)
Wang, Q., Wang, X.B.: Efficient implementation of the decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with heralded single-photon sources. Phys. Rev. A 88, 052332 (2013)
Yu, Z.W., Zhou, Y.H., Wang, X.B.: Three-intensity decoy-state method for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 88, 062339 (2013)
Ma, X., Fung, C.-H.F., Razavi, M.: Statistical fluctuation analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 86, 052305 (2012)
Curty, M., Xu, F., Cui, W., Lim, C.C.W., Tamaki, K., Lo, H.K.: Finite-key analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 5, 3732 (2014)
Shan, Y.Z., et al.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with a passive decoy-state method. Phys. Rev. A 90, 042334 (2014)
Zhou, Y.H., Yu, Z.W., Wang, X.B.: Tightened estimation can improve the key rate of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution by more than 100%. Phys. Rev. A 89, 052325 (2014)
Yurke, B., Potasek, M.: Obtainment of thermal noise from a pure quantum state. Phys. Rev. A 36, 3464 (1987)
Wang, Q., Wang, X.B., Guo, G.C.: Practical decoy-state method in quantum key distribution with a heralded single-photon source. Phys. Rev. A 75, 012312 (2007)
Wang, Q., Karlsson, A.: Performance enhancement of a decoy-state quantum key distribution using a conditionally prepared down-conversion source in the Poisson distribution. Phys. Rev. A 76, 014309 (2007)
Ribordy, G., Brendel, J., Gautier, J.D., Gisin, N., Zbinden, H.: Long-distance entanglement-based quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 63, 012309 (2000)
Adachi, Y., Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Simple and efficient quantum key distribution with parametric down-conversion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 180503 (2007)
Ma, X., Lo, H.K.: Quantum key distribution with triggering parametric down-conversion sources. New J. Phys. 10, 073018 (2008)
Wang, Q., Wang, X.B., Björk, G., Karlsson, A.: Improved practical decoy state method in quantum key distribution with parametric downconversion source. Europhys. Lett. 79, 40001 (2007)
Wang, Q., Wang, X.B.: Simulating of the measurement-device independent quantum key distribution with phase randomized general sources. Sci. Rep. 4, 4612 (2014)
Zhang, C.H., Luo, S.L., Guo, G.C., Wang, Q.: Approaching the ideal quantum key distribution with two-intensity decoy states. Phys. Rev. A 92, 022332 (2015)
Xu, F., Xu, He, Lo, H.K.: Protocol choice and parameter optimization in decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 89, 052333 (2014)
Zhou, Y.H., Yu, Z.W., Wang, X.B.: Making the decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution practically useful. Phys. Rev. A 93, 042324 (2016)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Prof. X. B. Wang for useful discussion during this work. We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China through Grant Nos. 11274178, 61475197 and 61590932, the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions through Grant No. 15KJA120002, the Outstanding Youth Project of Jiangsu Province through Grant No. BK20150039 and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions through Grant No. YX002001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Zhang, CH., Luo, S. et al. An enhanced proposal on decoy-state measurement device-independent quantum key distribution. Quantum Inf Process 15, 3785–3797 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1359-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1359-z