Abstract
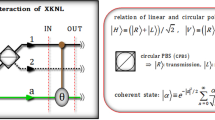
Nondestructive entangled-state analyzers could save the physical entanglement resource and boost the efficiency of quantum information processing (QIP). However, up to now, there is no much progress in the nondestructive analysis of Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger (GHZ) states. In this paper, a nondestructive photonic polarization GHZ-state analyzer, based on the interaction between circularly polarized light and quantum-dot cavity systems, is proposed. We can distinguish the GHZ states deterministically in theory, and the states are not destroyed because no single-photon detectors are required. Our scheme can be extended to \(n\)-photon GHZ states analysis directly and can be used to achieve QIP with less resource.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., et al.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70(13), 1895–1899 (1993)
Bennett, C.H., Wiesner, S.J.: Communication via one- and two-particle operators on Enstein–Podolsky–Rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69(20), 2881–2884 (1992)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042317 (2003)
Zheng, C., Long, G.F.: Quantum secure direct dialogue using Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pairs. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57(7), 1238–1243 (2014)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bells theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67(6), 661–663 (1991)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65(3), 032302 (2002)
Hou, K., Liu, G.H., Zhang, X.Y., et al.: An efficient scheme for five-party quantum state sharing of an arbitrary m-qubit state using multi-qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 10(4), 463–473 (2011)
Shi, R.H., Huang, L.S., Yang, W., et al.: Multi-party quantum state sharing of an arbitrary two-qubit state with Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 10(2), 231–239 (2011)
ukowski, M., Zeilinger, A., Horne, M.A., et al.: Event-ready-detectors’ Bell experiment via entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. Lett 71(26), 4287–4290 (1993)
Calsamiglia, J.: Generalized measurements by linear elements. Phys. Rev. A 65(3), 030301 (2002)
Pan, J.W., Zeilinger, A.: Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger-state analyzer. Phys. Rev. A 57(3), 2208–2211 (1998)
Van Houwelingen, J.A.W., Brunner, N., Beveratos, A., et al.: Quantum teleportation with a three-Bell-state analyzer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(13), 130502 (2006)
Walborn, S.P., Pádua, S., Monken, C.H.: Hyperentanglement-assisted Bell-state analysis. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042313 (2003)
Song, S.Y., Cao, Y., Sheng, Y.B., et al.: Complete Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger state analyzer using hyperentanglement. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(1), 381–393 (2013)
Guo, Q., Bai, J., Cheng, L.Y., et al.: Simplified optical quantum-information processing via weak cross-Kerr nonlinearities. Phys. Rev. A 83(5), 054303 (2011)
Qian, J., Feng, X.L., Gong, S.Q.: Universal Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger-state analyzer based on two-photon polarization parity detection. Phys. Rev. A 72(5), 052308 (2005)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Complete hyperentangled-Bell-state analysis for quantum communication. Phys. Rev. A 82(3), 032318 (2010)
Xia, Y., Chen, Q.Q., Song, J., et al.: Efficient hyperentangled Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger states analysis with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29(5), 1029–1037 (2012)
Duan, L.M., Kimble, H.J.: Scalable photonic quantum computation through cavity-assisted interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(12), 127902 (2004)
Mei, F., Feng, M., Yu, Y.F., et al.: Scalable quantum information processing with atomic ensembles and flying photons. Phys. Rev. A 80(4), 042319 (2009)
Lin, X.M., Chen, Z.H., Lin, G.W., et al.: Optical Bell state and Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger-state analyzers through the cavity input-output process. Opt. Commun. 282(16), 3371–3374 (2009)
Nowack, K.C., Koppens, F.H.L., Nazarov, Y.V., et al.: Coherent control of a single electron spin with electric fields. Science 318(5855), 1430–1433 (2007)
Mikkelsen, M.H., Berezovsky, J., Coldren, L.A., et al.: Optically detected coherent spin dynamics of a single electron in a quantum dot. Nat. Phys. 3(10), 770–773 (2007)
Xu, X., Sun, B., Berman, P.R., et al.: Coherent optical spectroscopy of a strongly driven quantum dot. Science 317(5840), 929–932 (2007)
Hu, C.Y., Young, A., OBrien, J.L., et al.: Giant optical Faraday rotation induced by a single-electron spin in a quantum dot: applications to entangling remote spins via a single photon. Phys. Rev. B 78(8), 085307 (2008)
Hu, C.Y., Rarity, J.G.: Loss-resistant state teleportation and entanglement swapping using a quantum-dot spin in an optical microcavity. Phys. Rev. B 83(11), 115303 (2011)
Bonato, C., Haupt, F., Oemrawsingh, S.S.R., et al.: CNOT and Bell-state analysis in the weak-coupling cavity QED regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104(16), 160503 (2010)
Ren, B.C., Wei, H.R., Hua, M., et al.: Complete hyperentangled-Bell-state analysis for photon systems assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Opt. Express 20(22), 24664–24677 (2012)
Liu, Q., Zhang, M.: Complete and deterministic analysis for spatial-polarization hyperentangled Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger states with quantum-dot cavity systems. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30(8), 2263–2270 (2013)
Wang, T.J., Song, S.Y., Long, G.L.: Quantum repeater based on spatial entanglement of photons and quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 85(6), 062311 (2012)
Wei, H.R., Deng, F.G.: Universal quantum gates for hybrid systems assisted by quantum dots inside double-sided optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 87(2), 022305 (2013)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Wang, L.: Efficient entanglement concentration for quantum dot and optical microcavities systems. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(5), 1885–1895 (2013)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L.: Efficient W-state entanglement concentration using quantum-dot and optical microcavities. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30(3), 678–686 (2013)
Wang, C., He, L.Y., Zhang, Y., et al.: Complete entanglement analysis on electron spins using quantum dot and microcavity coupled system. Scie. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56(11), 2054–2058 (2013)
Ren, B.C., Deng, F.G.: Hyper-parallel photonic quantum computation with coupled quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 4, 4623 (2014)
Walls, D.F., Milburn, G.J.: Quantum Optics. Springer, Berlin (1994)
Reithmaier, J.P., Sek, G., Löffler, A., et al.: Strong coupling in a single quantum dot semiconductor microcavity system. Nature 432(7014), 197–200 (2004)
Yoshie, T., Scherer, A., Hendrickson, J., et al.: Vacuum Rabi splitting with a single quantum dot in a photonic crystal nanocavity. Nature 432(7014), 200–203 (2004)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 61275059 and No. 61307062) and the Scientific Research Foundation of Graduate School of South China Normal University
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, RT., Liang, RS. & Wang, FQ. Nondestructive photonic polarization Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger states analyzer assisted by quantum-dot cavity systems. Quantum Inf Process 13, 2719–2729 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0823-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0823-x