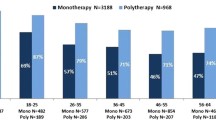
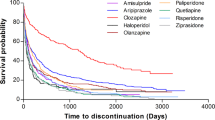
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to determine if Second-Generation Antipsychotics (SGAs), relative to First-Generation Antipsychotics (FGAs), reduced either the length of stay (LOS) or number of re-hospitalizations of schizophrenic patients receiving treatment in a state psychiatric hospital. Medical records were compared for the periods 1991–1994 and 2001–2004 for three inpatient groups: those receiving FGAs, those receiving SGAs, and those switched from FGAs to SGAs. During both time periods, patients on FGAs had significantly shorter LOS than either those receiving SGAs or those switched from FGAs to SGAs. Therefore, inpatients receiving SGAs were hospitalized longer than those receiving FGAs. Conversely, once discharged, patients receiving SGAs were significantly less likely to be re-admitted than patients discharged on FGAs. The data suggest that some patients do benefit from SGAs and it may be cost-effective in the long-term, to determine when to utilize FGAs first and when to switch from the older to the newer agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Advokat C, Comaty JE: Pharmacoeconomics of the second-generation antipsychotics. Contemporary Psychiatry 3:1–10, 2004
Rosenheck RA, Leslie DL, Sindelar J, et al.: Cost-effectiveness of second-generation antipsychotics and perphenazine in a randomized trial of treatment for chronic schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 163:2080–2089, 2006
Gardner DM, Baldessarini RJ, Waraich P: Modern antipsychotic drugs: a critical review. Canadian Medical Association Journal 172:1703–1711, 2005
Leucht S, Wahlbeck K, Hamann J, et al.: New generation antipsychotics versus low-potency conventional antipsychotics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 361:1581–1589, 2003
Rosenheck RA: Open forum: effectiveness versus efficacy of second-generation antipsychotics: haloperidol without anticholinergics as a comparator. Psychiatric Services 56:85–92, 2005
Centorrino F, Goren JL, Hennen J, et al.: Multiple versus single antipsychotic agents for hospitalized psychiatric patients: case–control study of risks versus benefits. American Journal of Psychiatry 161:700–706, 2004
Stahl SM, Grady MM: High-cost use of second-generation antipsychotics under California’s medicaid program. Psychiatric Services 57:127–129, 2006
Awad AG: Antipsychotic medications: compliance and attitudes towards treatment. Current Opinion in Psychiatry 17:75–80, 2004
Dolder CR, Lacro JP, Dunn LB, et al.: Antipsychotic medication adherence: is there a difference between typical and atypical agents? American Journal of Psychiatry 159:103–108, 2002
Nakonezny PA, Byerly MJ: Electronically monitored adherence in outpatients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder: a comparison of first- vs. second-generation antipsychotics. Schizophrenia Research 82:107–114, 2006
Freudenreich O, Cather C, Evins AE, et al.: Attitudes of schizophrenia outpatients toward psychiatric medications: relationship to clinical variables and insight. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 65:1372–1376, 2004
Hertling I, Philipp M, Dvorak A, et al.: Flupenthixol versus risperidone: subjective quality of life as an important factor for compliance in chronic schizophrenic patients. Neuropsychobiology 47(1):37–46, 2003
Jones PB, Barnes TRE, Davies L, et al.: Randomized controlled trial of the effect on quality of life of second- vs. first-generation antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 63:1079–1087, 2006
Kilian R, Dietrich S, Toumi M, et al.: Quality of life in persons with schizophrenia in out-patient treatment with first- or second-generation antipsychotics. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavia 110:108–118, 2004
Leslie DL, Rosenheck RA: From conventional to atypical antipsychotics and back: dynamic processes in the diffusion of new medications. American Journal of Psychiatry 159:1534–1540, 2002
Basu A: Cost-effectiveness analysis of pharmacologic treatments in schizophrenia: critical review of results and methodology issues. Schizophrenia Research 71:445–462, 2004
Polsky D, Doshi JA, Bauer MS, et al.: Clinical trial-based cost-effectiveness analyses of antipsychotic use. American Journal of Psychiatry 163:2047–2056, 2006
Salkever D, Slade E, Karakus M: Differential effects of atypical versus typical antipsychotic medication on earnings of schizophrenia patients—estimates from a prospective naturalistic study. Pharmacoeconomics 24:123–139, 2006
Advokat CD, Bertman LJ, Comaty Jr JE: Clinical outcome to clozapine treatment in chronic psychiatric inpatients. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 23:1–14, 1999
Advokat CD, Dixon D, Schneider J, et al.: Comparison of risperidone and olanzapine as used under “real-world” conditions in a state psychiatric hospital. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 28:487–495, 2004
Comaty JE, Advokat C: “Real world” study of antipsychotic effectiveness for chronic inpatients with schizophrenia in a state psychiatric hospital: preliminary results and commentary. Journal of Mental Health 15:57–62, 2006
Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, et al.: Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 353:1209–1232, 2005
Mauri MC, Regispani F, Beraldo S, et al.: Patterns of clinical use of antipsychotics in hospitalized psychiatric patients. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 29:957–963, 2005
Albright PS, Livingstone S, Keegan DL, et al.: Reduction of healthcare resource utilization and costs following the use of risperidone for patients with schizophrenia previously treated with standard antipsychotic therapy. Clinical Drug Investigation 11:289–299, 1996
Sajatovic M, Ramirez LF, Belton J, et al.: Health resource utilization and clinical outcomes with risperidone therapy in patients with serious mental illness. Comprehensive Psychiatry 40:198–202, 1999
Anderson SW, Crist AJ, Payne N: Predicting inpatient length of stay with the expanded version of the brief psychiatric rating scale (version 4.0). Psychiatric Services 55:77–79, 2004
Barbui C, Nosè M, Mazzi MA, et al.: Determinants of first- and second-generation antipsychotic drug use in clinically unstable patients with schizophrenia treated in four European countries. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 21:73–79, 2005
Jakubaschk J, Waldvogel D, Wűrmle O: Differences between long-stay and short-stay inpatients and estimation of length of stay. Social Psychiatry & Psychiatric Epidemiology 28:84–90, 1993
Taylor D, Mir S, Mace S, Whiskey E: Co-prescribing of atypical and typical antipsychotics-prescribing sequence and documented outcome. Psychiatric Bulletin 26:170–172, 2002
Kreyenbuhl JA, Valenstein M, McCarthy JF, Ganoczy D, Blow FC: Long-term antipsychotic polypharmacy in the VA health system: patient characteristics and treatment patterns. Psychiatric Services 58:489–495, 2007
Tapp A, Kennedy A, Kilzieh N, Rosengren K, Wood A: Combination antipsychotic therapy for the treatment of schizophrenia. Essential Psychopharmacology 6:1–11, 2004
Correll c, Frederickson AM, Kane JM, Manu P: Does antipsychotic polypharmacy increase the risk for metabolic syndrome? Schizophrenia Research 89:91–100, 2007
Chan J, Sweeting M: Combination therapy with non-clozapine atypical antipsychotic medication: a review of current evidence. Journal of Psychopharmacology 21:657–664, 2007
Stroup TS, Alves WM, Hamer RM: Clinical trials for antipsychotic drugs: design conventions, dilemmas and interventions. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 5:133–146, 2006
Acknowledgements
We thank Terri Cochran, in the Louisiana Office of Mental Health, for obtaining the datasets that allowed us to identify the necessary population whose information was analyzed in this study. Support for this study was provided by an Economic Development assistantship, to BDH, from the Graduate School of Louisiana State University; the Graduate School had no further role in the design, data collection, analysis, interpretation, or writing of the report, or the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Advokat, C., Hill, B.D. & Comaty, J.E. ‘Real World’ Comparison of First- and Second-Generation Antipsychotics in Regard to Length of Inpatient Hospitalization and Number of Re-hospitalizations. Psychiatr Q 79, 55–64 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11126-007-9061-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11126-007-9061-z