Abstract
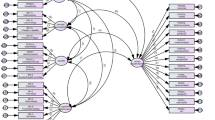
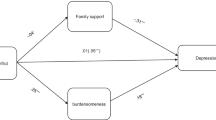
Maternal depression (MD) was one of the most prevalent psychiatric problems worldwide. However, it easily remains untreated and misses the best time to prevent the emergence or worsening of major depressive symptoms due to under-observed stigma and the lack of effective screening tools. Thus, this study aims to develop and validate a machine learning–based MD symptoms prediction model integrating more observable and objective factors to early detect and monitor MD risk. A cross-sectional study was conducted in 10 community vaccination centers in Wenzhou, China, and a total of 1099 mothers were surveyed by using purposive sampling. A questionnaire containing questions regarding socio-demographic variables, psychophysiological variables, wife role–related variables, and mother role-related variables was used to collect data. A framework of data preprocessing, feature selection, and model evaluation was implemented to develop an optimal risk prediction model. Results demonstrated that the XG-Boost algorithm provided robust performance with the highest AUC and well-balanced sensitivity and specificity (AUC = 0.90, sensitivity = 0.74, specificity = 0.90). Furthermore, the causal mediation analysis indicated that wife-mother role conflict positively predicted MD symptoms, and it also exerted influence on mothers suffering through the mediation of anxiety and insomnia. Findings from the present study may help guide the development of MD screening tools to early detect and provide the modifiable risk factor information for timely tailored prevention.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahi, F., Agajani-Delavar, M., Zarghami, M., & Lye, M.-S. (2016). Postpartum mental health in first-time mothers: A cohort study. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.17795/ijpbs-426
Amit, G., Girshovitz, I., Marcus, K., Zhang, Y., Pathak, J., Bar, V., & Akiva, P. (2021). Estimation of postpartum depression risk from electronic health records using machine learning. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, 21(1), 630. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-021-04087-8
Andersson, S., Bathula, D. R., Iliadis, S. I., Walter, M., & Skalkidou, A. (2021). Predicting women with depressive symptoms postpartum with machine learning methods. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86368-y
Bastien, C. H., Vallières, A., & Morin, C. M. (2001). Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Medicine, 2(4), 297–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1389-9457(00)00065-4
Beck, C. T. (2006). Postpartum depression: It isn’t just the blues. AJN the American Journal of Nursing, 106(5), 40–50.
Bishop, C. M., & Nasrabadi, N. M. (2006). Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning (Vol. 4). Springer.
Black, M. M., Walker, S. P., Fernald, L. C., Andersen, C. T., DiGirolamo, A. M., Lu, C., McCoy, D. C., Fink, G., Shawar, Y. R., & Shiffman, J. (2017). Early childhood development coming of age: Science through the life course. The Lancet, 389(10064), 77–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31389-7
Bodnar-Deren, S., Benn, E. K. T., Balbierz, A., & Howell, E. A. (2017). Stigma and postpartum depression treatment acceptability among Black and White women in the first six-months postpartum. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 21(7), 1457–1468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-017-2263-6
Breiman, L. (2001). Random Forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5–32.
Burke, W., & Abidin, R. (1980). Parenting stress index (PSI): A family system assessment approach. Parent Education and Intervention Handbook, 516–527.
Chen, B. B., Qu, Y., Yang, B., & Chen, X. (2022). Chinese mothers’ parental burnout and adolescents’ internalizing and externalizing problems: The mediating role of maternal hostility. Developmental Psychology, 58(4), 768–777. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0001311
Chen, T., & Guestrin, C. (2016). Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining,
Cox, J. L., Holden, J. M., & Sagovsky, R. (1987). Detection of postnatal depression. Development of the 10-item Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. British Journal of Psychiatry, 150, 782–786. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.150.6.782
Dash, S., Shakyawar, S. K., Sharma, M., & Kaushik, S. (2019). Big data in healthcare: Management, analysis and future prospects. Journal of Big Data, 6(1), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-019-0217-0
Eifert, G. H., Forsyth, J. P., Arch, J., Espejo, E., Keller, M., & Langer, D. (2009). Acceptance and commitment therapy for anxiety disorders: Three case studies exemplifying a unified treatment protocol. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice, 16(4), 368–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpra.2009.06.001
Fang, H., Tu, S., Sheng, J., & Shao, A. (2019). Depression in sleep disturbance: A review on a bidirectional relationship, mechanisms and treatment. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 23(4), 2324–2332. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14170
Gdańska, P., Drozdowicz-Jastrzębska, E., Grzechocińska, B., Radziwon-Zaleska, M., Węgrzyn, P., & Wielgoś, M. (2017). Anxiety and depression in women undergoing infertility treatment. Ginekologia Polska, 88(2), 109–112. https://doi.org/10.5603/GP.a2017.0019
Goco, D. E. B., & Diliman, Q. C. (2019). Experiences of mothers from dual-career families on child-rearing of their preschool-aged children. Signature.
Gonzalez, O., & Valente, M. J. (2022). Accommodating a latent XM interaction in statistical mediation analysis. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/00273171.2022.2119928
Goodman, J. H. (2004). Postpartum depression beyond the early postpartum period. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing, 33(4), 410–420. https://doi.org/10.1177/0884217504266915
Hobfoll, S. E. (1989). Conservation of resources. A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. American Psychologist, 44(3), 513–524. https://doi.org/10.1037//0003-066x.44.3.513
Jacques, N., de Mola, C. L., Joseph, G., Mesenburg, M. A., & da Silveira, M. F. (2019). Prenatal and postnatal maternal depression and infant hospitalization and mortality in the first year of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 243, 201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2018.09.055
Jansson-Fröjmark, M., & Lindblom, K. (2008). A bidirectional relationship between anxiety and depression, and insomnia? A prospective study in the general population. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 64(4), 443–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2007.10.016
Jerath, R., Beveridge, C., & Barnes, V. A. (2019). Self-regulation of breathing as an adjunctive treatment of insomnia [perspective]. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00780
Johnson, D. R., White, L. K., Edwards, J. N., & Booth, A. (1986). Dimensions of marital quality: Toward methodological and conceptual refinement. Journal of Family Issues, 7(1), 31–49. https://doi.org/10.1177/019251386007001003
Johnston, C., & Mash, E. J. (1989). A measure of parenting satisfaction and efficacy. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 18(2), 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15374424jccp1802_8
Judd, E. R. (1994). Gender and power in rural North China. Stanford University Press.
Kang, L., Jing, W., Liu, J., Ma, Q., Zhang, S., & Liu, M. (2022). The prevalence of barriers to rearing children aged 0–3 years following China’s new three-child policy: A national cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health, 22(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12880-z
Karatzoglou, A., Smola, A., Hornik, K., & Karatzoglou, M. A. (2016). Package ‘kernlab’. Google Scholar.
Kotsiantis, S., & Pintelas, P. (2004). Combining bagging and boosting. International Journal of Computational Intelligence, 1(4), 324–333.
Kraus, C., Kadriu, B., Lanzenberger, R., Zarate, C. A., Jr., & Kasper, S. (2019). Prognosis and improved outcomes in major depression: A review. Translational Psychiatry, 9(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0460-3
Lapato, D. M., Roberson-Nay, R., Kinser, P. A., & York, T. P. (2020). Predictive validity of a DNA methylation-based screening panel for postpartum depression. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.05.20027847v1
Lavner, J. A., & Bradbury, T. N. (2010). Patterns of change in marital satisfaction over the newlywed years. Journal of Marriage and Family, 72(5), 1171–1187. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-3737.2010.00757.x
Lazarus, R. S. (2000). Evolution of a model of stress, coping, and discrete emotions. Handbook of stress, coping, and health: Implications for nursing research, theory, and practice, 195–222.
Lee, D. T., & Chung, T. K. (2007). Postnatal depression: An update. Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 21(2), 183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2006.10.003
Letourneau, N. L., Dennis, C.-L., Benzies, K., Duffett-Leger, L., Stewart, M., Tryphonopoulos, P. D., Este, D., & Watson, W. (2012). Postpartum depression is a family affair: Addressing the impact on mothers, fathers, and children. Issues in Mental Health Nursing, 33(7), 445–457. https://doi.org/10.3109/01612840.2012.673054
Liu, X., Wang, S., & Wang, G. (2022). Prevalence and risk factors of postpartum depression in women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 31(19–20), 2665–2677. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.16121
MacKinnon, D. P., Valente, M. J., & Gonzalez, O. (2020). The correspondence between causal and traditional mediation analysis: The link is the mediator by treatment interaction. Prevention Science, 21(2), 147–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-019-01076-4
Mickelson, K. D., Biehle, S. N., Chong, A., & Gordon, A. (2017). Perceived stigma of postpartum depression symptoms in low-risk first-time parents: Gender differences in a dual-pathway model. Sex Roles, 76(5), 306–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-016-0603-4
Misra, P., & Yadav, A. S. (2020). Improving the classification accuracy using recursive feature elimination with cross-validation. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 11, 659–665.
Murray, L., Dunne, M. P., Van Vo, T., Anh, P. N., Khawaja, N. G., & Cao, T. N. (2015). Postnatal depressive symptoms amongst women in Central Vietnam: A cross-sectional study investigating prevalence and associations with social, cultural and infant factors. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth, 15, 234. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0662-5
Neckelmann, D., Mykletun, A., & Dahl, A. A. (2007). Chronic insomnia as a risk factor for developing anxiety and depression. Sleep, 30(7), 873–880. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/30.7.873
Ngai, F. W., & Chan, S. W. (2012). Learned resourcefulness, social support, and perinatal depression in Chinese mothers. Nursing Research, 61(2), 78–85. https://doi.org/10.1097/NNR.0b013e318240dd3f
NHFPC. (2017). China health statistics yearbook. Retrieved 27 Dec from http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2015/indexch.htm
Nomaguchi, K., & House, A. N. (2013). Racial-ethnic disparities in maternal parenting stress: The role of structural disadvantages and parenting values. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 54(3), 386–404. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022146513498511
Norhayati, M. N., Hazlina, N. H., Asrenee, A. R., & Emilin, W. M. (2015). Magnitude and risk factors for postpartum symptoms: A literature review. Journal of Affective Disorders, 175, 34–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2014.12.041
Peng, Y. (2018). Migrant mothering in transition: A qualitative study of the maternal narratives and practices of two generations of rural-urban migrant mothers in Southern China. Sex Roles, 79(1), 16–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-017-0855-7
Rotheram-Fuller, E. J., Tomlinson, M., Scheffler, A., Weichle, T. W., Hayati Rezvan, P., Comulada, W. S., & Rotheram-Borus, M. J. (2018). Maternal patterns of antenatal and postnatal depressed mood and the impact on child health at 3-years postpartum. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 86(3), 218–230. https://doi.org/10.1037/ccp0000281
Saqib, K., Khan, A. F., & Butt, Z. A. (2021). Machine learning methods for predicting postpartum depression: Scoping review. JMIR Mental Health, 8(11), e29838. https://doi.org/10.2196/29838
Schmidt, S., Roesler, U., Kusserow, T., & Rau, R. (2014). Uncertainty in the workplace: Examining role ambiguity and role conflict, and their link to depression—A meta-analysis. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 23(1), 91–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/1359432X.2012.711523
Scott, J. T., Prendergast, S., Demeusy, E., McGuire, K., & Crowley, M. (2022). Trends and opportunities for bridging prevention science and US Federal Policy. Prevention Science, 23(8), 1333–1342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-022-01403-2
Shatte, A. B., Hutchinson, D. M., & Teague, S. J. (2019). Machine learning in mental health: A scoping review of methods and applications. Psychological Medicine, 49(9), 1426–1448. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291719000151
Shin, D., Lee, K. J., Adeluwa, T., & Hur, J. (2020). Machine learning-based predictive modeling of postpartum depression. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092899
Soe, N. N., Wen, D. J., Poh, J. S., Li, Y., Broekman, B. F., Chen, H., Chong, Y. S., Kwek, K., Saw, S.-M., & Gluckman, P. D. (2016). Pre-and post-natal maternal depressive symptoms in relation with infant frontal function, connectivity, and behaviors. PLoS ONE, 11(4), e0152991. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0152991
Solomon, M. R., Surprenant, C., Czepiel, J. A., & Gutman, E. G. (1985). A role theory perspective on dyadic interactions: The service encounter. Journal of Marketing, 49(1), 99–111. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224298504900110
Straus, M. A., Hamby, S. L., Boney-McCoy, S., & Sugarman, D. B. (1996). The revised conflict tactics scales (CTS2) development and preliminary psychometric data. Journal of Family Issues, 17(3), 283–316. https://doi.org/10.1177/019251396017003001
Tsao, Y., Creedy, D. K., & Gamble, J. (2015). Prevalence and psychological correlates of postnatal depression in rural Taiwanese women. Health Care for Women International, 36(4), 457–474. https://doi.org/10.1080/07399332.2014.946510
Woolhouse, H., Gartland, D., Mensah, F., & Brown, S. (2015). Maternal depression from early pregnancy to 4 years postpartum in a prospective pregnancy cohort study: Implications for primary health care. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 122(3), 312–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12837
Xiong, J., Fang, Q., Chen, J., Li, Y., Li, H., Li, W., & Zheng, X. (2021). States transitions inference of postpartum depression based on multi-state Markov model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(14), 7449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18147449
Zhang, H.-P., & Tsang, K.-M. (2010). The influence of urban wives’ relative income and education on marital quality. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 18(05), 632–634. https://doi.org/10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2010.05.036
Zheng, A., & Casari, A. (2018). Feature Engineering for Machine Learning: Principles and Techniques for Data Scientists. “ O'Reilly Media, Inc.”.
Zheng, J., Sun, K., Aili, S., Yang, X., & Gao, L. (2022). Predictors of postpartum depression among Chinese mothers and fathers in the early postnatal period: A cross-sectional study. Midwifery, 105, 103233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2021.103233
Zhou, Z.-H. (2012). Ensemble methods: Foundations and algorithms. CRC Press.
Zung, W. W. (1971). A rating instrument for anxiety disorders. Psychosomatics: Journal of Consultation and Liaison Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0033-3182(71)71479-0
Funding
This project was funded by the Zhejiang Provincial Science and Technology Innovation Program (New Young Talent Program) for College Students, 2021R413086, Liuzhi Hong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
This study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards established in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments, and it has been approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Wenzhou Medical University (IRB approval number: 2021-K-23–02).
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, L., Yang, A., Liang, Q. et al. Wife-Mother Role Conflict at the Critical Child-Rearing Stage: A Machine-Learning Approach to Identify What and How Matters in Maternal Depression Symptoms in China. Prev Sci (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-023-01610-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-023-01610-5