Abstract
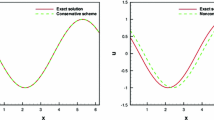
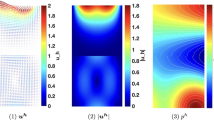
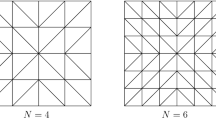
In this paper, we address the finite element method and discontinuous Galerkin method for the stochastic scattering problem of Helmholtz type in ℝd (d = 2, 3). Convergence analysis and error estimates are presented for the numerical solutions. The effects of the noises on the accuracy of the approximations are illustrated. Results of the numerical experiments are provided to examine our theoretical results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, E.J., Novosel, S.J., Zhang, Z.: Difference approximation of some linear stochastic partial differential equations. Stochastics Stochastics Rep. 64, 117–142 (1998)
Alvarez, G.B., Loula, A.F.D., Dutra, E.G., Rochinha, F.A.: A discontinuous finite element formulation for Helmholtz equation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 195(33–36), 4018–4035 (2006)
Babuska, I., Tempone, R., Zouraris, G.: Galerkin fnite element approximations of stochastic elliptic partial differential equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 42, 800–825 (2004)
Brenner, S., Scott, L.R.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1994)
Buckdahn, R., Pardoux, E.: Monotonicity methods for white noise driven quasi-linear PDEs. Progr. Probab. 22, 219–233 (1990)
Cao, Y.Z., Yang, H.T., Yin, L.: Finite element methods for semilinear elliptic stochastic partial differential equations. Numer. Math. 106(2), 181–198 (2007)
Chen, Z.M., Liu, X.Z.: An adaptive perfectly matched layer technique for time-harmonic scattering problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 43(2), 645–671 (2005)
Colton, D., Kress, R.: Integral Equation Methods in Scattering Theory. Wiley, New York (1983)
Du, Q., Zhang, T.Y.: Numerical approximation of some linear stochastic partial differential equations driven by special additive noise. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 4, 1421–1445 (2002)
Gyöngy, I.: Lattice approximations for stochastic quasi-linear parabolic partial differential equations driven by space-time white noise II. Potential Anal. 11, 1–37 (1999)
Hausenblas, E.: Error analysis for approximation of stochastic differential equations driven by Poisson random measures. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40, 87–113 (2002)
Johnson, C.: Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations by the Finite Element Method. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1994)
Keese, A., Matthies, H.: Parallel computation of stochastic groundwater flow. In: Wolf, D., Munster, G., Kremer, M. (eds.) NIC Symposium 2004, Proceedings, NIC series, vol. 20, pp. 399–408. John von Neumann Institute for Computing, Julich (2003)
Kloeden, P., Platen, E.: Numerical Solution of Stochastic Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1992)
Lin, Y.P., Zhang, K., Zou, J.: Studies on some perfectly matched layers for one-dimensional time-dependent systems. Adv. Comput. Math. (2008, in press)
Martínez, T., Sanz-Solé, M.: A lattice scheme for stochastic partial differential equations of elliptic type in dimension d≥4. Appl. Math. Optim. 54(3), 343–368 (2006)
McLean, W.: Strongly Elliptic Systems and Boundary Integral Equations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Melenk, J.M.: On generalized finite element methods. Ph.D. thesis, University of Maryland at College Park (http://www.anum.tuwien.ac.at/~melenk/) (1995)
Milstein, G.N., Platen, E., Schurz, H.: Balanced implicit methods for stochastic systems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 35, 1010–1019 (1998)
Mitchell, A.R., Griffiths, D.F.: The Finite Difference Method in Partial Differential Equations. Wiley, Chichester (1980)
Perugia, I., Schötzau, D.: An hp-analysis of the local discontinuous Galerkin method for diffusion problems. J. Sci. Comput. 17, 561–571 (2002)
Walsh, J.B.: An Introduction to Stochastic Partial Differential Equations. Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 1180, pp. 265–439. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1986)
Zhang, K., Zhang, R., Yin, Y.G., Yu, S.: Domain decomposition methods for linear and semi linear elliptic stochastic partial differential equations. Appl. Math. Comput. (2008 in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first author is supported by NSF under grand number 0609918 and AFOSR under grant numbers FA9550-06-1-0234 and FA9550-07-1-0154, the second author is supported by NSFC(10671082, 10626026, 10471054), and the third author is supported by NNSF (No. 10701039 of China) and 985 program of Jilin University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Y., Zhang, R. & Zhang, K. Finite Element Method and Discontinuous Galerkin Method for Stochastic Scattering Problem of Helmholtz Type in ℝd (d = 2, 3). Potential Anal 28, 301–319 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11118-008-9078-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11118-008-9078-4