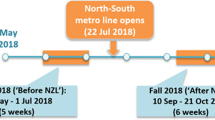
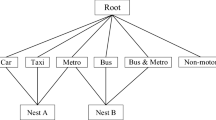
Abstract
The sustained expansion of mega-city regions and the development of multimodal transport networks have catalysed intercity mobility, thereby restructuring regional travel demand patterns. This study aims to interpret the behaviour of intermodal travellers in a short-haul intercity context within mega-city regions. A comparative modelling framework, utilising both simultaneous and sequential estimation methods, is proposed based on stated preference survey data collected in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. The simultaneous estimation framework examines the integrated measurement of the perceived utility of multiple stages of travel using cross-nested logit models. In contrast, the sequential estimation framework systematically investigates the bidirectional interactions associated with the intercity mode decision and decisions related to access and egress modes in a stepwise manner. The latter quantifies the accessibility of transport hubs and destinations to assess the implicit cost of feeder trips in the intercity mode decision. It validates the sequential impact on feeder mode choice preferences. In addition to identifying behavioural determinants, the models’ relative performance is assessed regarding behaviour prediction accuracy for diverse groups of travellers categorised by travel purpose, fellow traveller, baggage size, and travel frequency. Statistically, the weighted prediction errors for access, intercity, and egress mode choices are 1.12%, 1.33%, and 0.89% under the simultaneous estimation framework. In contrast, under the sequential estimation framework, these errors are reduced to 0.81%, 0.63%, and 0.50%, respectively. The results suggest the superior applicability of the latter in interpreting intermodal mobility patterns.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, Y., Hu, Q., Ho, T.K., Guo, H., Mao, B.: Timetable optimization for metro lines connecting to intercity railway stations to minimize passenger waiting time. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22, 79–90 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2019.2954895
Bergantino, A.S., Madio, L.: Intermodal competition and substitution. HSR versus air transport: Understanding the socio-economic determinants of modal choice. Res. Transp. Econ. 79, 100823 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.retrec.2020.100823
Bierlaire, M.: Estimating choice models with latent variables with PythonBiogeme. Report TRANSP-OR 160628. Series on Biogeme. Transport and Mobility Laboratory, ENAC, EPFL. (2016). https://www.transp-or.epfl.ch/documents/technicalReports/Bier16.pdf
Bierlaire, M.: A short introduction to PandasBiogeme. Technical report TRANSP-OR 200605. Transport and Mobility Laboratory, ENAC, EPFL. (2020). https://www.transp-or.epfl.ch/documents/technicalReports/Bier20.pdf
Bushell, J., Merkert, R., Beck, M.J.: Consumer preferences for operator collaboration in intra- and intercity transport ecosystems: Institutionalising platforms to facilitate MaaS 2.0. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 160, 160–178 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2022.04.013
Capurso, M., Hess, S., Dekker, T.: Modelling the role of consideration of alternatives in mode choice: An application on the Rome-Milan corridor. Transp Res Part A Policy Pract. 129, 170–184 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2019.07.011
Chaichannawatik, B., Kanitpong, K., Limanond, T.: Departure Time Choice (DTC) behavior for intercity travel during a long-holiday in Bangkok, Thailand. J. Adv. Transp. 1896261 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1896261
Cheng, Y.H., Tseng, W.C.: Exploring the effects of perceived values, free bus transfer, and penalties on intermodal metro-bus transfer users’ intention. Transp Policy (oxf). 47, 127–138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2016.01.001
Diederich, A.: Sequential decision making. In: International encyclopedia of the social & behavioral sciences. pp. 13917–13922. Elsevier (2001)
Dobruszkes, F., Dehon, C., Givoni, M.: Does European high-speed rail affect the current level of air services? An EU-wide analysis. Transp Res Part A Policy Pract. 69, 461–475 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2014.09.004
Donkers, B., Dellaert, B.G.C., Waisman, R.M., Häubl, G.: Preference dynamics in sequential consumer choice with defaults. J. Mark. Res. 57, 1096–1112 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/0022243720956642
Fang, C., Yu, D.: Urban agglomeration: An evolving concept of an emerging phenomenon. Landsc. Urban Plan. 162, 126–136 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.02.014
Freidin, E., Aw, J., Kacelnik, A.: Sequential and simultaneous choices: Testing the diet selection and sequential choice models. Behav. Proc. 80, 218–223 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2008.12.001
Gokasar, I., Gunay, G.: Mode choice behavior modeling of ground access to airports: A case study in Istanbul, Turkey. J Air Transp Manag. 59, 1–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jairtraman.2016.11.003
Gottmann, J.: Megalopolis: The urbanized Northeastern Seaboard of the United States. MIT Press, Massachusetts (1961)
Hall, P.G., Pain, K.: The Polycentric Metropolis: Learning from Mega-city Regions in Europe. Routledge, London (2006)
Hensher, D.A., Rose, J.M.: Development of commuter and non-commuter mode choice models for the assessment of new public transport infrastructure projects: A case study. Transp Res Part A Policy Pract. 41, 428–443 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2006.09.006
Hess, S., Spitz, G., Bradley, M., Coogan, M.: Analysis of mode choice for intercity travel: Application of a hybrid choice model to two distinct US corridors. Transp Res Part A Policy Pract. 116, 547–567 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2018.05.019
Huan, N., Yao, E., Xiao, Y.: Roles of accessibility and air-rail intermodality in shaping mobility patterns in mega-city regions: Behavioural insights from China. Cities 143, 104591 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2023.104591
Huang, Y., Gan, H., Jing, P., Wang, X.: Analysis of park and ride mode choice behavior under multimodal travel information service. Transp. Lett. 14, 1080–1090 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/19427867.2021.1988438
Llorca, C., Molloy, J., Ji, J., Moeckel, R.: Estimation of a long-distance travel demand model using trip surveys, location-based big data, and trip planning services. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board. 2672, 103–113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/0361198118777064
Lu, M., Zhu, H., Luo, X., Lei, L.: Intercity travel demand analysis model. Adv. Mech. Eng. 6, 108180 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/10818
Luo, Q., Li, S., Hampshire, R.C.: Optimal design of intermodal mobility networks under uncertainty: Connecting micromobility with mobility-on-demand transit. EURO J. Transp. Logist. 10, 100045 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejtl.2021.100045
Menard, S.: Applied logistic regression analysis. SAGE Publications, Inc (2001)
Meyer de Freitas, L., Becker, H., Zimmermann, M., Axhausen, K.W.: Modelling intermodal travel in Switzerland: A recursive logit approach. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 119, 200–213 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2018.11.009
Miskeen, M.A., Alhodairi, A.M., Rahmat, R.A.: Modeling a multinomial logit model of intercity travel mode choice behavior for all trips in Libya. Int. J. Civil Environ. Eng. 7, 636–645 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1087592
Rahman, M., Akther, M.S., Recker, W.: The first-and-last-mile of public transportation: A study of access and egress travel characteristics of Dhaka’s suburban commuters. J Public Trans. 24, 100025 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubtr.2022.100025
Ranjbari, A., Chiu, Y.C., Hickman, M.: Exploring factors affecting demand for possible future intercity transit options. Public Transport. 9, 463–481 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12469-017-0161-3
Raveau, S., Álvarez-Daziano, R., Yáñez, M.F., Bolduc, D., de Dios Ortúzar, J.: Sequential and simultaneous estimation of hybrid discrete choice models. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board. 2156, 131–139 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3141/2156-15
Román, C., Martín, J.C., Espino, R., Cherchi, E., Ortúzar, J. de D., Rizzi, L.I., González, R.M., Amador, F.J.: Valuation of travel time savings for intercity travel: The Madrid-Barcelona corridor. Transp. Policy (Oxf). 36, 105–117 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2014.07.007
Shrestha, N.: Detecting multicollinearity in regression analysis. Am. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 8, 39–42 (2020). https://doi.org/10.12691/ajams-8-2-1
Simonson, I.: The effect of purchase quantity and timing on variety-seeking behavior. J. Mark. Res. 27, 150–162 (1990). https://doi.org/10.2307/3172842
Tam, M.L., Lam, W.H.K., Lo, H.P.: The impact of travel time reliability and perceived service quality on airport ground access mode choice. J. Choice Model. 4, 49–69 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1755-5345(13)70057-5
van der Waerden, P., van der Waerden, J.: The relation between train access mode attributes and travelers’ transport mode-choice decisions in the context of medium- and long-distance trips in the Netherlands. Transp. Res. Rec. 2672, 719–730 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/0361198118801346
Wang, Y., Li, L., Wang, L., Moore, A., Staley, S., Li, Z.: Modeling traveler mode choice behavior of a new high-speed rail corridor in China. Transp. Plan. Technol. 37, 466–483 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/03081060.2014.912420
Wang, K., Bhat, C.R., Ye, X.: A multinomial probit analysis of Shanghai commute mode choice. Transportation (Amst). 50, 1471–1495 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-022-10284-x
Wang, Y., Wu, B., Dong, Z., Ye, X.: A joint modeling analysis of passengers’ intercity travel destination and mode choices in Yangtze River Delta megaregion of China. Math. Probl. Eng. 5293210 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5293210
Wen, C.H., Wang, W.C., Fu, C.: Latent class nested logit model for analyzing high-speed rail access mode choice. Transp. Res. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 48, 545–554 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2011.09.002
Wong, B., Habib, K.M.N.: Effects of accessibility to the transit stations on intercity travel mode choices in contexts of high speed rail in the Windsor-Quebec corridor in Canada. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 42, 930–939 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1139/cjce-2014-0493
Yamamoto, T., Komori, R.: Mode choice analysis with imprecise location information. Transportation (Amst). 37, 491–503 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-009-9254-4
Yang, M., Zhao, J., Wang, W., Liu, Z., Li, Z.: Metro commuters’ satisfaction in multi-type access and egress transferring groups. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 34, 179–194 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2014.11.004
Yang, H., Feng, J., Dijst, M., Ettema, D.: Mode choice in access and egress stages of high-speed railway travelers in china. J. Transp. Land Use. 12, 701–721 (2019). https://doi.org/10.5198/jtlu.2019.1420
Yang, M., Wang, Z., Cheng, L., Chen, E.: Exploring satisfaction with air-HSR intermodal services: A Bayesian network analysis. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 156, 69–89 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2021.12.011
Yao, E., Morikawa, T.: A study of on integrated intercity travel demand model. Transp. Res. Part. A Policy Pract. 39, 367–381 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2004.12.003
Zhang, A., Wan, Y., Yang, H.: Impacts of high-speed rail on airlines, airports and regional economies: A survey of recent research. Transp. Policy (Oxf). 81, A1–A19 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2019.06.010
Zhen, F., Cao, X., Tang, J.: The role of access and egress in passenger overall satisfaction with high speed rail. Transportation (Amst). 46, 2137–2150 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-018-9918-z
Zhou, H., Norman, R., Xia, J., Hughes, B., Kelobonye, K., Nikolova, G., Falkmer, T.: Analysing travel mode and airline choice using latent class modelling: A case study in Western Australia. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 137, 187–205 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2020.04.020
Acknowledgements
Stephane Hess acknowledges the support of the European Research Council through the consolidator grant 615596-DECISIONS. The stated preference survey in this study was designed while Ning Huan stayed with Stephane Hess at the University of Leeds as a visiting PhD student.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52172312).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ning Huan: Conceptualisation, Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing, Visualisation. Stephane Hess: Methodology, Investigation, Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition. Toshiyuki Yamamoto: Methodology, Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision. Enjian Yao: Conceptualisation, Methodology, Investigation, Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huan, N., Hess, S., Yamamoto, T. et al. Modelling intermodal traveller behaviour in mega-city regions: simultaneous versus sequential estimation frameworks. Transportation (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-024-10489-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-024-10489-2