Abstract
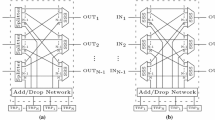
Optical burst switching (OBS) is proposed as suitable switching architectures for directly transporting traffic over a bufferless wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) networks. Parallel optical burst switching (POBS) is a variant of the OBS model that takes this concept further by transmitting data bursts wavelength and time dimensions. However, there is a lack of simulator that simulates POBS networks. This paper presents an update to the conventional OBS model in the NCTUns-6.0 simulator (\(\hbox {NCTU}_{\mathrm{ns}\text {-}\mathrm{POBS}}\)). The \(\hbox {NCTU}_{\mathrm{ns}\text {-}\mathrm{POBS}}\) tool is capable of simulating POBS networks for ultra-dense WDM. It analyzes the features of POBS networks, enables to adjust the parameters of POBS networks and enhances their switching technology. To test and validate the performance of the tool, the proposed random wavelength assignment technique (RWAT) is compared with the existing sequential wavelength assignment technique (SWAT) of the POBS model and the conventional OBS model. The results of the simulation show that, the \(\hbox {NCTU}_{\mathrm{ns}\text {-}\mathrm{POBS}}\) successfully simulates the POBS networks in which the proposed RWAT enables the POBS to yield higher throughput compared to the existing SWAT and the OBS conventional technique.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, F., Fox, G., Hey, A.J.: Grid Computing: Making the Global Infrastructure a Reality, vol. 2. Wiley, London (2003)
Hirosaki, B., Emura, K., Hayano, S.-I., Tsutsumi, H.: Next-generation optical networks as a value creation platform. IEEE Commun. Mag. 41, 65–71 (2003)
Tucker, R.S., Parthiban, R., Baliga, J., Hinton, K., Ayre, R.W., Sorin, W.V.: Evolution of WDM optical IP networks: a cost and energy perspective. J. Lightwave Technol. 27, 243–252 (2009)
Soares, V.N., Veiga, I.D., Rodrigues, J.J.: OBS simulation tools: a comparative study. In: Communications Workshops, 2008. ICC Workshops’ 08. IEEE International Conference on 2008, pp. 256–260 (2008)
Pattavina, A.: Multi-wavelength switching in IP optical nodes adopting different buffering strategies. Opt. Switch. Netw. 1, 65–75 (2005)
Qiao, C., Yoo, M.: Choices, features and issues in optical burst switching. Opt. Netw. Mag. 1, 36–44 (2000)
Vokkarane, V.M.: Design and Analysis of Architectures and Protocols for Optical Burst-Switched Networks. Citeseer (2004)
Lazzez, A.: Optical burst-switched networks: design, modeling and performances analysis. Ph. D. Thesis, University of 7th of November at Carthage, Tunisia (2008)
Abdelouahab, A., Abbou, F., Ewe, H.: Parallel optical burst switching (POBS) for ultra-dense WDM (U-DWDM) systems. In: Information Technology and Multimedia (ICIM), 2011 International Conference on, pp. 1–6 (2011)
Cai, J.-X., Nissov, M., Davidson, C.R., Pilipetskii, A.N., Mohs, G., Li, H., Cai, Y., Golovchenko, E.A., Lucero, A.J., Foursa, D.G.: Long-haul 40 Gb/s DWDM transmission with aggregate capacities exceeding 1 Tb/s. J. Lightwave Technol. 20, 2247–2258 (2002)
Zhu, B., Nelson, L., Stulz, S., Gnauck, A., Doerr, C., Leuthold, J., Gruner-Nielsen, L., Pedersen, M., Kim, J., Lingle Jr, R.: High spectral density long-haul 40-Gb/s transmission using CSRZ-DPSK format. J. Lightwave Technol. 22, 208–214 (2004)
Chbat, M.W., Penninckx, D.: High-spectral-efficiency transmission systems. In: Optical Fiber Conference (OFC2000), pp. 134–136 (2000)
Xu, J., Qiao, C., Li, J., Xu, G.: Efficient channel scheduling algorithms in optical burst switched networks. In: INFOCOM 2003. Twenty-Second Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications. IEEE Societies, pp. 2268–2278 (2003)
Dolzer, K., Gauger, C., Späth, J., Stefan, B.: Evaluation of reservation mechanisms for optical burst switching. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 55, 18–26 (2001)
Baldine, I., Cassada, M., Bragg, A., Karmous-Edwards, G., Stevenson, D.: Just-in-time optical burst switching implementation in the ATDnet all-optical networking testbed. In: Global Telecommunications Conference, 2003. GLOBECOM’03. IEEE, pp. 2777–2781 (2003)
Turner, J.S.: Terabit burst switching. J. High Speed Netw. 8, 3–16 (1999)
Yoo, M., Qiao, C., Dixit, S.: QoS performance of optical burst switching in IP-over-WDM networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 18, 2062–2071 (2000)
Hsu, C.-F., Liu, T.-L., Huang, N.-F.: Performance analysis of deflection routing in optical burst-switched networks. In: INFOCOM 2002 Twenty-First Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies. Proceedings. IEEE, pp. 66–73 (2002)
Vokkarane, V.M., Haridoss, K., Jue, J.P.: Threshold-based burst assembly policies for QoS support in optical burst-switched networks. In: ITCom The Convergence of Information Technologies and Communications, 2002, pp. 125–136 (2002)
DeCusatis, C.: Dense wavelength division multiplexing for parallel sysplex and metropolitan/storage area networks. Opt. Netw. 2, 69–80 (2001)
Sano, A., Masuda, H., Kobayashi, T., Fujiwara, M., Horikoshi, K., Yoshida, E., Miyamoto, Y., Matsui, M., Mizoguchi, M., Yamazaki, H.: 69.1-Tb/s (432 \(\times \) 171-Gb/s) C-and extended L-band transmission over 240 km using PDM-16-QAM modulation and digital coherent detection. In: Optical Fiber Communication Conference, 2010, p. PDPB7
Tarara, H., Yamawaku, J., Ohara, T., Yamazaki, E., Masuda, H., Yamamoto, T., Suzuki, K., Takada, A., Morioka, T.: 3-2 1000 channel WDM transmission and grouped wavelength path routing experiments using JGNII test bed (2005)
Amstutz, S.R.: Burst switching-an update. IEEE Commun. Mag. 27, 50–57 (1989)
Parthiban, R., Leckie, C., Zalesky, A., Tucker, R.S.: Waveband burst switching-a new approach to networking. In: National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference, p. JThB47 (2006)
Huang, Y., Heritage, J.P., Mukherjee, B.: A new node architecture employing waveband-selective switching for optical burst-switched networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 11, 756–758 (2007)
Wang, S.-Y., Chou, C.-L., Lin, C.-C., Huang, C.: The GUI User Manual for the NCTUns 6.0 Network Simulator and Emulator. National Chiao Tung University, Tajwan (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salih, A.I., Abdelouhahab, A., Mostafa, S.A. et al. Updating the NCTUns-6.0 tool to simulate parallel optical burst switching of all-optical ultra-dense WDM systems. Photon Netw Commun 29, 106–117 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-014-0473-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-014-0473-z