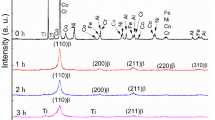
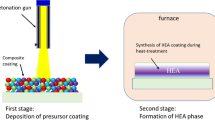
The cold spraying (CS) process was applied to deposit coatings using the AlCoNiFeCrTi high-entropy alloy (HEA) powder. The HEA powder was produced by short-time mechanical alloying (MA) of an equiatomic mixture in a planetary-ball mill followed by annealing at 1200°C and grinding of the resultant agglomerates. X-ray diffraction and microstructural analyses were employed to study the phase and structural transformations at different stages of producing the AlCoNiFeCrTi alloy powder and after it was sprayed onto a steel substrate. When the powder mixture was subjected to the MA process, a metastable nanostructured bcc solid solution formed. Annealing changed the phase composition of the alloy to an ordered bcc solid solution (B2 phase), intermetallic σ-phase (FeCr), and titanium carbide TiC. Grinding in a planetary-ball mill for 1 h turned the ordered B2 phase into a disordered nanostructured bcc solid solution. The titanium carbide and σ phase remained in the alloy, but particles of the σ phase significantly refined and partially dissolved in the bcc solid solution. Following deposition, the phase composition and nanostructured state of the starting alloy powder remained unchanged and the cold-sprayed coating consisted of a bcc solid solution, an intermetallic σ phase, and TiC carbide. The average coating thickness was 405 μm and Vickers microhardness HV was 10.0 ± 0.3 GPa. The high hardness of the coating was due to hardening effects: solid-solution and nanostructured hardening, hardening by inclusions of intermetallic and carbide phases, and strain hardening under severe plastic deformation in deposition at supersonic speeds (~105–107 sec–1) at low temperatures. The HEA coating showed good adhesion to the substrate and low porosity (<1%).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.C. Gao, J.-W. Yeh, P.K. Liaw, and Y. Zhang (eds.), High-Entropy Alloys. Fundamentals and Applications, Elsevier, Amsterdam (2016), p. 516, DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27013-5.
B.S. Murty, J.-W. Yeh, S. Ranganathan, and P.P. Bhattacharjee, High-Entropy Alloys, 2nd ed.: Elsevier, Amsterdam (2019), p. 388, Paperback ISBN: 9780128160671, eBook ISBN: 9780128160688, https://www.elsevier.com/books/high-entropy-alloys/murty/978-0-12-816067-1.
Yong Zhang, High-Entropy Materials. A Brief Introduction (eBook), Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. (2019), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8526-1
Y.F. Ye, Q. Wang, J. Lu, C.T. Liu, and Y. Yang, “High-entropy alloys: challenges and prospects,” Mater. Today, 19, No. 6, 349–362 (2016), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2015.11.026.
D.B. Miracle and O.N. Senkov, “A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts,” Acta Mater., 122, 488–511 (2017), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.08.081.
K.K. Alanemea, M.O. Bodunrin, and S.R. Oke, “Processing, alloy composition and phase transition effect on the mechanical and corrosion properties of high entropy alloys: a review,” J. Mater. Res. Technol., 5, Issue 4, 384–393 (2016), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2016.03.004.
J. Chen, X. Zhou, W. Wang, B. Liu, Y. Lv, D. Xu, W. Yang, and Y. Liu, “A review on fundamental of high entropy alloys with promising high-temperature properties,” J. Alloys Compd., 760, 15–30 (2018), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.067.
Ch. Zhang, M.C. Gao, and Sh.-K. Lin, “Progress in high-entropy alloys,” JOM, 71, No. 10, 3417–3418 (2019), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03728-w.
J. Li, Y. Huang, X. Meng, and Xie Yu, “A review on high entropy alloys coatings: fabrication processes and property assessment,” Adv. Eng. Mater., 21, 15–30 (2019), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201900343.
M. Vaidya, G.M. Muralikrishna, and B.S. Murty, “High-entropy alloys by mechanical alloying: A review,” J. Mater. Res., 34, 664–686 (2019), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.37.
Weijie Yu, Yun Wang, Ruitao Li, and Junhong Mao, “Phase evolution, microstructure and mechanical property of AlCoCrFeNiTi high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by mechanical alloying and laser cladding,” Metals, 9, 1036–1047 (2019), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/met9101036.
F.Y. Shu, S. Liu, H.Y. Zhao, W.X. He, S.H. Sui, J. Zhang, P. He, and B.S. Xu, “Structure and hightemperature property of amorphous composite coating synthesized by laser cladding FeCrCoNiSiB highentropy alloy powder,” J. Alloys Compd., 731, 662–666 (2018), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.248.
Z. Cai, X. Cui, Z. Liu, Y. Li, M. Dong, and G. Jin, “Microstructure and wear resistance of laser cladded Ni–Cr–Co–Ti–V high-entropy alloy coating after laser remelting processing,” Opt. Laser Technol., 99, 276–281 (2018), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.09.012.
B. Jin, N. Zhang, S. Guan, Y. Zhang, and D. Li, “Microstructure and properties of laser re-melting FeCoCrNiAl0.5Six high-entropy alloy coatings,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 349, 867–873 (2018), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.06.032.
Z. Cai, Y. Wang, X. Cui, G. Jin, Y. Li, Z. Liu, and M. Dong, “Design and microstructure characterization of FeCoNiAlCu high-entropy alloy coating by plasma cladding: In comparison with thermodynamic calculation,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 330, 163–169 (2017), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.09.083.
J. Lu, B. Wang, X. Qiu, Z. Peng, and M. Ma, “Microstructure evolution and properties of CrCuFexNiTi high-entropy alloy coating by plasma cladding on Q235,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 328, 313–318 (2017), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.08.019.
W.L. Hsu, H. Murakami, J.W. Yeh, A.C. Yeh, and K. Shimoda, “On the study of thermal-sprayed Ni0.2Co0.6Fe0.2CrSi0.2AlTi0.2 HEA overlay coating,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 316, 71–74 (2017), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.02.073.
W.L. Hsu, Y.C. Yang, C.Y. Chen, and J.-W. Yeh, “Thermal sprayed high-entropy NiCo0.6Fe0.2Cr1.5SiAlTi0.2 coating with improved mechanical properties and oxidation resistance,” Intermetallics, 89, 105–110 (2017), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2017.05.015.
L.M. Wang, C.C. Chen, J.-W. Yeh, and S. T. Ke, “The microstructure and strengthening mechanism of thermal spray coating NixCo0.6Fe0.2CrySizAlTi0.2 high-entropy alloys,” Mater. Chem. Phys., 126, No. 3, 880–885 (2011), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.12.022.
Q. Xing, H. Wang, M. Chen, Z. Chen, R. Li, P. Jin, and Y. Zhang, “Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of NbTiAlSiZrNx high-entropy films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering,” Entropy, 21, 396–409 (2019), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/e21040396.
W. Zhang, R. Tang, Z.B. Yang, C.H. Liu, H. Chang, J.J. Yang, J.L. Liao, Y.Y. Yang, and N. Liu, “Preparation, structure, and properties of an AlCrMoNbZr high-entropy alloy coating for accident-tolerant fuel cladding,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 347, 13–19 (2018), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.04.037.
F. Cao, P. Munroe, Z. Zhou, and Z. Xie, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of a multilayered CoCrNi/Ti coating with varying structure,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 350, 596–602 (2018), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.07.066.
W. Li, H. Assadi, F. Gaertner, and S. Yin, “A review of advanced composite and nanostructured coatings by solid-state cold spraying process,” Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci., 44, 109–156 (2019), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1080/10408436.2017.1410778.
A. Papyrin, V. Kosarev, S. Klinkov, A. Alkhimov, and V. Fomin, Cold Spray Technology, Elsevier Sci. (2007), p. 336, Hardcover ISBN: 9780080451558, eBook ISBN: 9780080465487, DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-045155-8.X5000-5.
A.P. Alkhimov, A.N. Papyrin, V.F. Kosarev, N.I. Nesterovich, and M.M. Shushpanov, Gas-Dynamic Spraying Method for Applying a Coating, U.S. Patent 5302414A, publication date April 12 (1994).
A. Moridi, S.M. Hassani-Gangaraj, M. Guagliano, and M. Dao, “Review cold spray coating: review of material systems and future perspectives,” Surf. Eng., 36, No. 6, 369–395 (2014), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1179/1743294414y.0000000270.
S. Yin, P. Cavaliere, B. Aldwell, R. Jenkins, H. Liao, W. Li, and R. Lupoi, “Cold spray additive manufacturing and repair: Fundamentals and applications,” Addit. Manuf., 21, 628–650 (2018), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.04.017.
R.N. Raoelison, Y. Xie, T. Sapanathan, M.P. Planche, R. Kromer, S. Costil, and C. Langlade, “Cold gas dynamic spray technology: A comprehensive review of processing conditions for various technological developments till to date,” Addit. Manuf., 19, 134–159 (2018), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2017.07.001.
M.R. Rokni, S.R. Nutt, C.A. Widener, V.K. Champagne, and R.H. Hrabe, “Review of relationship between particle deformation, coating microstructure, and properties in high-pressure cold spray,” J. Therm. Spray Technol., 26, No. 6, 1308–1355 (2017), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-017-0575-0.
C. Huang, W. Li, Y. Xie, M.P. Planche, H. Liao, and G. Montavon, “Effect of substrate type on deposition behavior and wear performance of Ni-coated graphite/Al composite coatings deposited by cold spraying,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 33, Issue 4, 338–346 (2017), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2016.11.016.
R. Jenkins, S. Yin, B. Aldwell, M. Meyer, and R. Lupoi, “New insights into the in-process densification mechanism of cold spray Al coatings: Low deposition efficiency induced densification,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 35, 427–431 (2019), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2018.09.045. URL: https://www.jmst.org/EN/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2018.09.045 or https://www.jmst.org/EN/Y2019/V35/I3/427.
Yin Shuo, Emmanuel J. Ekoi, Thomas L. Lupton, Denis P. Dowling, and Rocco Lupoi, “Cold spraying of WC–Co–Ni coatings using porous WC–17Co powders: Formation mechanism, microstructure characterization and tribological performance,” Mater. Des., 126, 305–313 (2017), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.04.040.
A. Anupam, S. Kumar, N.M. Chavan, B.S. Murty, and R.S. Kottada, “First report on cold-sprayed AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy and its isothermal oxidation,” J. Mater. Res., 34, Issue 5 (2019), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.38.
S. Yin, W. Li, B. Song, X. Yan, M. Kuang, Y. Xu, K. Wen, and R. Lupoi, “Deposition of FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy (HEA) coating via cold spraying,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 35, No. 6, 1003–1007 (2019), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2018.12.015.
M.-H. Tsai, R.-C. Tsai, T. Chang, and W.-F. Huang, “Intermetallic phases in high-entropy alloys: statistical analysis of their prevalence and structural inheritance,” Metals, 9, 247–265 (2019), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/met9020247.
S. Guo and C.T. Liu, “Phase stability in HEAs: formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase,” Prog. Mater. Sci: Mater. Int., No. 21, 433–446 (2011), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/s1002-0071(12)60080-x.
B.D. Cullity and S.R. Stock, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 3rd ed., Pearson Education Limited (2014), p. 654, ISBN 10: 1-292-04054-8. ISBN 13: 978-1-292-04054-7.
B.A. Galanov, Yu.V. Milman, S.I. Chugunova, and I.V. Goncharova, “Investigation of mechanical properties of high-hardness materials by indentation,” Superhard Mater., 21, No. 3, 23–35 (1998).
S. Varalakshmi, M. Kamaraj, and B. S. Murty, “Formation and stability of equiatomic and nonequiatomic nanocrystalline CuNiCoZnAlTi high-entropy alloys by mechanical alloying,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 41, No. 10, 2703–2709 (2010), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-010-0344-x.
A.I. Yurkova, V.V.Chernyavskii, and V.F. Gorban, “Structure and mechanical properties of high-entropy AlCuNiFeТі and AlCuNiFeCr alloys produced by mechanical activation followed by pressure sintering,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 55, No. 3–4, 152–163 (2016).
A.I. Yurkova, V.V. Chernyavsky, V. Bolbut, M. Krüger, and I. Bogomol, “Structure formation and mechanical properties of high-entropy AlCuNiFeCr alloy prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering,” J. Alloys Compd., 786, 139–148 (2019), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.341.
J.-W. Yeh, S.-Y. Chang, Y.-D. Hong, S.-K. Chen, and S.-J. Lin, “Anomalous decrease in X-ray diffraction intensities of Cu–Ni–Al–Co–Cr–Fe–Si alloy systems with multi-principal elements,” J. Mater. Chem. Phys., 103, No. 41, 41–46 (2007), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2007.01.003.
C. Suryanarayana, “Mechanical alloying and milling,” Prog. Mater. Sci., 46, No. 1–2, 1–184 (2001), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/s0079-6425(99)00010-9.
Sherif El-Eskandarany, Mechanical Alloying Nanotechnology, Materials Science and Powder Metallurgy, Second ed., Elsevier (2015), p. 340, ISBN: 978-1-4557-7752-5, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4557-7752-5.00001-2.
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, J. Shi, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, and Q.J. Zhang, “Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiCuAl high-entropy solid solution synthesized by mechanical alloying,” J. Alloys Compd., 485, No. 1–2, 31–34 (2009), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.05.144.
H.X. Sui, M. Zhu, M. Qi, G.B. Li, and D.Z. Yang, “The enhancement of solid solubility limits of AlCo intermetallic compound by high-energy ball milling,” J. Appl. Phys., 71, No. 6, 2945–2949 (1992), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/1.351028.
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, J. Shi, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, and Q.J. Zhang, “Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiCuAl high-entropy solid solution synthesized by mechanical alloying,” J. Alloys Compd., 485, L31–L34 (2009), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.05.144.
M.H. Tsai, K.Y. Tsai, C.W. Tsai, C. Lee, C.C. Juan, and J.W. Yeh, “Criterion for sigma phase formation in Cr- and V-containing high-entropy alloys,” Mater. Res. Lett., 1, 207–212 (2013), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2013.831382.
B.S. Murty and S. Ranganathan, “Novel materials synthesis by mechanical alloying/milling,” Int. Mater. Rev., 43, 101–141 (1998), DOI: https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1179/imr.1998.43.3.101.
Y.F. Juan, J. Li, Y.Q. Jiang, W.L. Jia, and Z.J. Lu, “Modified criterions for phase prediction in the multicomponent laser-clad coatings and investigations into microstructural evolution/wear resistance of FeCrCoNiAlMo. laser-clad coatings,” Appl. Surf. Sci., 465, 700–714 (2019), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.264.
H. Zhang, Y. Pan, Y. He, and H. Jiao, “Microstructure and properties of Fe6NiCoSiCrAlTi high-entropy alloy coating prepared by laser cladding,” Appl. Surf. Sci., 257, 2259–2263 (2011).
L. Tian, Z. Feng, and W. Xiong, “Microstructure, microhardness, and wear resistance of AlCoCrFeNiTi/Ni60 coating by plasma spraying,” Coatings, 8, 112 (2018), DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8030112.
A.S.M. Ang, C.C. Berndt, M.L. Sesso, A. Anupam, P.S. Rathod, R.S. Kottada, and B.S. Murty, “Plasmasprayed high entropy alloys: Microstructure and properties of AlCoCrFeNi and MnCoCrFeNi,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 46, 791–800 (2015), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2644-z.
L. Tian, “Microstructure and wear behavior of atmospheric plasma-sprayed AlCoCrFeNiTi high-entropy alloy coating,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 25, 5513–5521 (2016), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2396-6.
M. Löbel, T. Lindner, T. Mehner, and L. Thomas, “Microstructure and wear resistance of AlCoCrFeNiTi highentropy alloy coatings produced by HVOF,” Coatings, 7, 144–152 (2017), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7090144.
L. Chen, K. Bobzin, Z. Zhou, L. Zhao, M. Ote, T. Königstein, Z. Tan, and D. He, “Wear behavior of HVOF-sprayed Al0.6TiCrFeCoNi high entropy alloy coatings at different temperatures,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 358, 215–222 (2019), DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.11.052.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkova Metallurgiya, Vol. 59, Nos. 11–12 (536), pp. 85–102, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yurkova, A.I., Hushchyk, D.V. & Minitsky, A.V. Synthesis of High-Entropy AlNiCoFeCrTi Coating by Cold Spraying. Powder Metall Met Ceram 59, 681–694 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-021-00203-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-021-00203-7