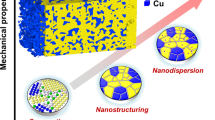
W–Cu composites, as a traditional material, have attracted tremendous research interest in fields such as electric engineering, electronic information, aerospace, weapons, etc., owing to their excellent properties. This critical review presents and discusses the current development of W–Cu composites. After introduction of the synthesis methods for W–Cu composites, including the conventional and modern preparation approaches, we focus on the description of the improvement of mechanical properties and arc-erosion properties by modification techniques. Finally, the advantages of W–Cu composites in applications such as electrical contacts, electronic packaging materials, and heat sinks, as well as military materials, are described.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. V. Sebastian and G. S. Tendolkar, “High density tungsten–copper liquid phase sintering composites from co-reduced oxide powders,” Int. J. Powder Metall., 15, 45–53 (1979).
F. A. Da Costa, A. G. P. da Silvab, U. U. Gomes, “The influence of the dispersion technique on the characteristics of the W–Cu powders and on the sintering behavior,” Powder Technol., 134, 123–132 (2003).
A. Upadhyaya and R. M. German, “Densification and dilation of sintered W–Cu alloys,” Int. J. Powder Metall., 34, 43–55 (1998).
S. Nigarura and L. Desrosiers, “High performance tungsten–copper composites for electrical contacts,” Met. Powder Rep., 53, 37–44 (1998).
Y. F. Meng, J. P. Zhang, et al., “Microstructures and properties of W–Cu functionally graded composite coatings on copper substrate via high-energy mechanical alloying method,” Adv. Powder Technol., 26, 382–400 (2015).
N. F. Shkodich, A. S. Rogachev, et al., “Bulk Cu–Cr nanocomposites by high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering,” J. Alloys Compd., 617, 39–46 (2014).
J. G. Cheng, L. Wan, et al., “Fabrication of W–20 wt.% Cu alloys by powder injection molding,” J. Mater. Process. Techol., 210, 137–142 (2010).
I. H. Moon, M. K. Kang, et al., “MIM of the nanocomposite W–Cu powders,” in: Proc. 1994 Powder Metallurgy World Congress, EPMA, Paris (1994), p. 1807.
A. G. Hamidi, H. Arabi, and S. Rastegari, “Tungsten–copper composite production by activated sintering and infiltration,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 29, 538–541 (2011).
J. L. Fan, T. Liu, et al., “Synthesis of ultrafine/nanocrystalline W–(30–50)Cu composite powders and microstructure characteristics of the sintered alloys,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 30, 33–37 (2012).
V. N. Eremenko, R. V. Minakova, et al., “Solubility of tungsten in copper–nickel melts,” Powder Metall. Metal. Ceram., 16, No. 4, 283–286 (1977).
J. L. Johnson and R. M. German, “Chemically activated liquid phase sintering of tungsten–copper,” Int. J. Powder Metall., 30, No. 1, 91–92 (1944).
J. L. Johnson and R. M. German, “Phase equilibria effects on the enhanced liquid phase sintering of W–Cu,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 24, No. 11, 2369–2377 (1933).
R. M. German, G. L. Messing, and R. G. Cornwall (eds.), Sintering Technology, Marcel Dekker, New York (1996), pp. 237–244.
F. Doré, S. Lay, et al., “Segregation of Fe during the sintering of doped W–Cu alloys,” Sci. Mater., 49, 237–242 (2003).
S. S. Ryu, Y. D. Kim, and I. H. Moon, “Dilatometric analysis on the sintering behavior of nanocrystalline W–Cu prepared by mechanical alloying,” J. Alloys Compd., 335, 233–240 (2002).
Y. V. Bykov, K. I. Rybakov, and V. E. Semenov, “High-temperature microwave processing of materials,” J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 34, R55–R75 (2001).
M. Bhattacharya and T. Basak, “A review on the susceptor assisted microwave processing of materials,” Energy, 97, 306–338 (2016).
L. Xu, C. Srinivasakannan, et al., “Fabrication of tungsten copper alloys by microwave hot pressing sintering,” J. Alloys Compd., 658, 23–28 (2016).
Y. L. Guo, J. H. Yi, et al., “Microwave sintering of W–Cu contact materials,” J. Cent. South Univ., 40, No. 3, 670–675 (2009).
Y. L. Guo, J. H. Yi, et al., “Fabrication of W–Cu composites by microwave infiltration,” J. Alloys Compd., 492, L75–L78 (2010).
K. Wang, X. P. Wang, et al., “The study on the microwave sintering of tungsten at relatively low temperature,” J. Nucl. Mater., 431, 206–211 (2012).
S. D. Luo, J. H. Yi, et al., “Microwave sintering W–Cu composites: analyses of densification and microstructural homogenization,” J. Alloys Compd., 473, L5–L9 (2009).
X. Q. Tang, H. B. Zhang, et al., “Fabrication of W–Cu functionally graded material by spark plasma sintering method,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 42, 193–199 (2014).
A. Elsayed, W. Li, et al., “Experimental investigations on the synthesis of W–Cu nanocomposite through spark plasma sintering,” J. Alloys Compd., 639, 373–380 (2015).
E. Autissier, M. Richou, et al., “Elaboration and thermomechanical characterization of W/Cu functionally graded materials produced by Spark Plasma Sintering for plasma facing components,” Fusion Eng. Des., 98–99, 1929–1932 (2015).
Z. X. Zheng, W. Xia, et al., “Numerical simulation of tungsten alloy in powder injection molding process,” Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc., 18, 1209–1215 (2008).
J. K. Lee, “On the effect of substituting copper powder with cupric salt for the sintering process of W–Cu MIM Parts,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 26, 290–294 (2008).
W. G. Chen and B. J. Ding, “The process and research of W–Cu matrix composites,” Powder Metall. Ind., 11, No. 3, 45–50 (2001).
D. F. Heaney, Handbook of Metal Injection Molding, Woodhead Press, USA (2012), pp. 50–63.
X. M. Guo and Y. J. Wu, “Preparation technology and research developments of metal powders used for metal injection molding,” Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 39 (suppl. 1), 496–500 (2010).
T. Lin, S. Yin, and Y. P. Wei, “In-situ reaction used in producing composites by casting process,” Mater. Rev., 14, 30–31 (2001).
S. C. Gill, M. Zimmermann, and W. Kurz, “Resolidification of the Al–Al2Cu eutectic the coupled zone,” Acta Mater., 40, No. 11, 2895–2906 (1992).
Z. E. Liu, Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering, 2nd ed., Northwestern Polytechnical University Press, China (2003), pp. 232–262.
S. H. Liang, R. Hu, and Z. K. Fan, “Microstructure and properties of CuCr series pseudobinary alloy by arc melting,” Spec. Cast. Nonferrous Alloys, No. 4, 25–26 (2000).
F. Zhao, H. Xu, et al., “Preparation of CuCr25 alloys through vacuum arc-smelting and their properties,” Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc., 10, No. 1, 73–75 (2000).
Y. M. Shi, Y. H. Xu, et al., “Preparation of fiber-structured W/Cu contact materials,” Foundry Technol., 27, No. 1, 1238–1240 (2006).
L. H. Duan, W. S. Lin, et al., “Thermal properties of W–Cu composites manufactured by copper infiltration into tungsten fiber matrix,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 46, 96–100 (2014).
S. H. Liang, L. Chen, et al., “Infiltrated W–Cu composites with combined architecture of hierarchical particulate tungsten and tungsten fibers,” Mater. Charact., 110, 33–38 (2015).
X. H. Yang, P. Xiao, et al., “Alloying effect of Ni and Cr on the wettability of copper on W substrate,” Acta Metall. Sinica, 21, 369–379 (2008).
K. Zangeneh-Madar, M. Amirjan, and N. Parvin, “Improvement of physical properties of Cu-infiltrated W compacts via electroless nickel plating of primary tungsten powder,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 203, 2333–2336 (2009).
G. Song, Y. Wang, and Y. Zhou, “The mechanical and thermophysical properties of ZrC/W composites at elevated temperature,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 334, 223–232 (2002).
M. Roosta and H. Baharvandi, “The comparison of W/Cu and W/ZrC composites fabricated through hotpress,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 28, 587–592 (2010).
X. H. Yang, Z. K. Fan, et al., “Effects of Y2O3 on properties of W–Cu electrical contact materials,” Chin. J. Mater. Res., 21, No. 4, 414–420 (2007).
W. G. Chen, M. Z. Chen, et al., “Effect of doping on electrical arc characteristic of W–Cu electrical contact materials,” Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 19, No. 1, 2029–2037 (2009).
K. Qian, S. H. Liang, P. Xiao, and X. H. Wang, “In situ synthesis and electrical properties of CuW–La2O3 composites,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 31, 147–151 (2012).
L. M. Luo, Z. L. Lu, X. M. Huang, et al., “Fabrication of W–Cu/La2O3 composite powder with a novel pretreatment prepared by electroless plating and its sintering characterization,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 48, 1–4 (2015).
M. Z. Chen, W. G. Chen, et al., “Effects of different Re additives on properties of W–Cu contact materials,” Spec. Cast. Nonferrous Alloys., 28, No. 7, 570–572 (2008).
G. M. Song, Y. Zhou, et al., “Microstructure and elevated temperature strength of ZrCp/W composites,” Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 9, No. 1, 49–54 (1999).
A. Elsayed, “W–Cu–CNT nanocomposite by vacuum sintering and hot isostatic pressing,” Nanosci. Nanotechnol., No. 1A, 6, 35–38 (2016)
B. H. Tian, X. W. Zhang, et al., “Microstructure and properties of vacuum hot-press sintering W/Cu–Al2O3 composite,” Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci., 33, 219–223 (2013).
K. Zhang, W. Q. Shen, and C. C. Ge, “Comparative study on W/Cu FGMs doping TiC and La2O3,” Powder Metall. Techol., 125, No. 15, 352–354 (2007).
X. L. Shi, H. Yang, G. Q. Shao, et al., “Fabrication and properties of W–Cu alloy reinforced by multiwalled carbon nanotubes,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 457, 18–23 (2007).
X. L. Shi, M. Wang, S. Zhang, and Q. X. Zhang, “Fabrication and properties of W20Cu alloy reinforced by titanium nitride coated SiC fibers,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 41, 60–65 (2013).
L. M. Huang, L. M. Luo, et al., “The influence of TiB2 content on microstructure and properties of W30Cu composites prepared by electroless plating and powder metallurgy,” Adv. Powder Technol., 26, 1058–1063 (2015).
X. H. Yang, Z. K. Fan, S. H. Liang, and P. Xiao, “Effects of TiC on microstructures and properties of CuW electrical contact materials,” Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 36, No. 5, 817–821 (2007).
M. F. Yu, B. S. Files, et al., “Tensile loading of ropes of single wall carbon nanotubes and their mechanical properties,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 84, 5552–5555 (2000).
X. H. Yang, J. T. Zou, P. Xiao, and X. H. Wang, “Effects of Zr addition on properties and vacuum arc characteristics of Cu–W alloy,” Vacuum, 106, 16–20 (2014).
J. W. Wang, J. L. Fan, and H. R. Gong, “Effects of Zr alloying on cohesion properties of Cu/W interfaces,” J. Alloys Compd., 661, L553–L556 (2016).
N. Yang, Z. H. Wang, L. Chen, et al., “A new process for fabricating W–15 wt.% Cu sheet by sintering, cold rolling and re-sintering,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 28, 198–200 (2010).
X. L. Xie, Q. Lin, et al., “Research on the densification of W–30 wt.% Cu composite powder by hot extrusion with steel cup,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 578, 187–190 (2013).
W. G. Chen and H. Ye, “Structure and properties of W–Cu25 alloy wire by swaging process,” Powder Metall. Technol., 29, No. 1, 13–20 (2011).
H. P. Guo, W. G. Chen, and H. Zhang, “Characterization of W80–Cu20 alloy sheet prepared by hotrolling,” Rare Met., 32, No. 6, 569–573 (2013).
P. G. Chen, Q. Shen, et al., “Effect of interface modification by Cu-coated W powders on the microstructure evolution and properties improvement for Cu–W composites,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 288, 8–14 (2016).
H. F. Zhou, W. Q. Huang, et al., “Performance of electroless Ni–P coating on W–Cu alloy,” Corros. Sci. Prot. Technol., 21, No. 3, 347–349 (2009).
J. D. Xu, G. Yu, et al., “Preparation of copper coated tungsten powders by intermittent electrodeposition,” Powder Technol., 264, 561–569 (2014).
Z. F. Wang, Z. C. Liu, and G. S. Jiang, “Hermeticity of W–Cu composites for semiconductor package,” Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 9, No. 2, 323–326 (1999).
C. P. Wu, D. Q. Yi, et al., “Arc erosion behavior of Ag/Ni electrical contact materials,” Mater. Des., 85, 511–519 (2015).
M. Antler, “Survey of contact fretting in electrical connectors,” IEEE Trans. Compon. Hybrids Manuf. Technol., 8, 87–104 (1985).
X. Wei, D. M. Yu, et al., “Arc characteristics and microstructure evolution of W–Cu contacts during the vacuum breakdown,” Vacuum, 107, 83–89 (2014).
B. Liu, W. G. Chen, and Z. J. Zhang, “Tungsten–copper alloy surface nanocrystallization and its properties,” Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 44, No. 12, 3188–3191 (2015).
I. H. Sung, J. W. Kim, H. J. Noh, and H. Jang, “Effect of displacement and humidity on contact resistance of copper electrical contacts,” Tribol. Int., 95, 256–261 (2016).
W. G. Chen, L. L. Dong, et al., “Investigation and analysis of arc ablation on W–Cu electrical contact materials,” J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Electron., 27, 5584–5591 (2016).
W. D. Schubert, “Aspects of research and development in tungsten and tungsten alloys,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 11, 151–157 (1992).
F. S. Wang and M. Y. Zhao, “Investigation on high density tungsten alloy and its application in military industry,” Mater. Sci. Eng. Powder Metall., 2, No. 2, 114–120 (1997).
W. G. Chen, Y. G. Kuang, and W. P. Zhou, “Current research status of W–Cu composites for high temperature in China,” Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 33, No. 1, 11–14 (2004).
W. G. Chen and M. Z. Chen, “Design and analysis of gradient sintering between W–Cu alloy and aldary,” High Voltage Apparatus, 46, No. 8, 10–13 (2010).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from Education Department of Shaanxi Provincial Government Projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 56, Nos. 3–4 (514), pp. 67–83, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Chen, W., Hou, L. et al. W–Cu System: Synthesis, Modification, and Applications. Powder Metall Met Ceram 56, 171–184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-017-9884-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-017-9884-6